Related Research Articles

A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface ships, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores. The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of the navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broadly divided between riverine and littoral applications, open-ocean applications, and something in between, although these distinctions are more about strategic scope than tactical or operational division.

The Battle of the Coral Sea, from 4 to 8 May 1942, was a major naval battle between the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) and naval and air forces of the United States and Australia. Taking place in the Pacific Theatre of World War II, the battle is historically significant as the first naval action in which the opposing fleets neither sighted nor fired upon one another, attacking over the horizon with aircraft carriers instead.

Seamanship is the art, knowledge and competence of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water. The Oxford Dictionary states that seamanship is "The skill, techniques, or practice of handling a ship or boat at sea."

The Battle of Leyte Gulf was the largest naval battle of World War II and by some criteria the largest naval battle in history, with over 200,000 naval personnel involved. It was fought in waters near the Philippine islands of Leyte, Samar, and Luzon from 23 to 26 October 1944 between combined American and Australian forces and the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), as part of the invasion of Leyte, which aimed to isolate Japan from the colonies that it had occupied in Southeast Asia, a vital source of industrial and oil supplies.

The Battle of the Philippine Sea was a major naval battle of World War II that eliminated the Imperial Japanese Navy's ability to conduct large-scale carrier actions. It took place during the United States' amphibious invasion of the Mariana Islands during the Pacific War. The battle was the last of five major "carrier-versus-carrier" engagements between American and Japanese naval forces, and pitted elements of the United States Navy's Fifth Fleet against ships and aircraft of the Imperial Japanese Navy's Mobile Fleet and nearby island garrisons. This was the largest carrier-to-carrier battle in history, involving 24 aircraft carriers, deploying roughly 1,350 carrier-based aircraft.

A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest landlocked country while Ethiopia is the world’s most populous landlocked country.

The sinking of Prince of Wales and Repulse was a naval engagement in World War II, as part of the war in the Pacific, that took place on 10 December 1941 in the South China Sea off the east coast of the British colonies of Malaya and the Straits Settlements, 70 miles east of Kuantan, Pahang. The Royal Navy battleship HMS Prince of Wales and battlecruiser HMS Repulse were sunk by land-based bombers and torpedo bombers of the Imperial Japanese Navy. In Japan, the engagement was referred to as the Naval Battle of Malaya.

Naval aviation is the application of military air power by navies, whether from warships that embark aircraft, or land bases.

The O and P class was a class of destroyers of the British Royal Navy. Ordered in 1939, they were the first ships in the War Emergency Programme, also known as the 1st and 2nd Emergency Flotilla, respectively. They served as convoy escorts in World War II, and some were subsequently converted to fast second-rate anti-submarine frigates in the 1950s.

War at Sea is a strategic board wargame depicting the naval war in the Atlantic during World War II, published by Jedko Games in 1975, and subsequently republished by Avalon Hill in 1976 and more recently by L2 Design Group in 2007.

The Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition of 1914–1917 is considered to be the last major expedition of the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration. Conceived by Sir Ernest Shackleton, the expedition was an attempt to make the first land crossing of the Antarctic continent. After Roald Amundsen's South Pole expedition in 1911, this crossing remained, in Shackleton's words, the "one great main object of Antarctic journeyings". Shackleton's expedition failed to accomplish this objective, but became recognized instead as an epic feat of endurance.

Valerian Ivanovich Albanov was a Russian navigator, best known for being one of two survivors of the Brusilov expedition of 1912, which killed 22.

Castella de Aguada, also known as the Bandra Fort, is a fort located in Bandra, Mumbai. "Castella" is a misspelling for Portuguese "Castelo" (castle), although it seems its Portuguese builders actually called it Forte de Bandorá. It is located at Land's End in Bandra. It was built by the Portuguese in 1640 as a watchtower overlooking Mahim Bay, the Arabian Sea and the southern island of Mahim. The strategic value of the fort was enhanced in 1661 after the Portuguese ceded the seven islands of Bombay that lay to the immediate south of Bandra to the English. The name indicates its origin as a place where fresh water was available in the form of a fountain ("Aguada") for Portuguese ships cruising the coasts in the initial period of Portuguese presence. The fort lies over several levels, from sea level to an altitude of 24 metres (79 ft). Castella de Aguada has been featured in several Hindi films, such as Dil Chahta Hai and Buddha Mil Gaya.

The Manacles are a set of treacherous rocks off The Lizard peninsula in Cornwall. The rocks are rich in marine wildlife and they are a popular spot for diving due to the many shipwrecks. Traditionally pronounced mean-a'klz (1808), the name derives from the Cornish meyn eglos, the top of St Keverne church spire being visible from the area.
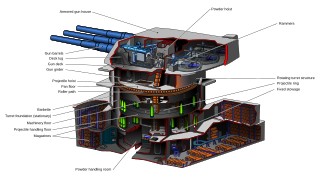
A main battery is the primary weapon or group of weapons around which a warship is designed. As such, a main battery was historically a gun or group of guns, as in the broadsides of cannon on a ship of the line. Later, this came to be turreted groups of similar large-caliber naval rifles. With the evolution of technology the term has come to encompass guided missiles as a vessel's principal offensive weapon, deployed both on surface ships and submarines.

Turunmaa was a Finnish gunboat built in 1918. She served in the Finnish Navy during World War II. The ship was named after Turuma, a type of frigate designed for use in shallow waters of the archipelago and served in the Swedish Archipelago fleet in the late 18th century. The frigates had in turn been named after the region of Finland.

SeaLand, a division of the Maersk Group, is an American intra-regional container shipping company headquartered in Miramar, Florida with representation in 29 countries across the Americas. The company offers ocean and intermodal services using container ships, trucks, and rail serving customers between North and South America, Central America, and the Caribbean.

The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft as of June 2019.

The Sea Dogs were a group of English privateers authorised by Queen Elizabeth I to raid England's enemies, whether they were formally at with war with them or not. Active from 1560 onwards until Elizabeth's death in 1603, the Sea Dogs primarily attacked Spanish targets, both on land and on sea, particularly during the Anglo-Spanish War. Members of the Sea Dogs, including Sir John Hawkins and Sir Francis Drake, also engaged in illicit slave trading with Spanish colonies in the Americas.

The K-300PBastion-P is a Russian mobile coastal defence missile system. The system was developed together with the Belarusian company Tekhnosoyuzproekt.
References
- ↑ Jacob Grimm (1899). Deutsches Worterbuch. S. Hirzel. p. 97.
- ↑ Malcolm Barber; Judith Mary Upton-Ward (1994). The Military Orders: On land and by sea. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. p. 52. ISBN 978-0-7546-6287-7.