
The Community acquis or acquis communautaire, sometimes called the EU acquis and often shortened to acquis, is the accumulated legislation, legal acts and court decisions that constitute the body of European Union law that came into being since 1993. The term is French: acquis meaning "that which has been acquired or obtained", and communautaire meaning "of the community".

The Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union (CFR) enshrines certain political, social, and economic rights for European Union (EU) citizens and residents into EU law. It was drafted by the European Convention and solemnly proclaimed on 7 December 2000 by the European Parliament, the Council of Ministers and the European Commission. However, its then legal status was uncertain and it did not have full legal effect until the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon on 1 December 2009.
Freedom of movement, mobility rights, or the right to travel is a human rights concept encompassing the right of individuals to travel from place to place within the territory of a country, and to leave the country and return to it. The right includes not only visiting places, but changing the place where the individual resides or works.
Human rights in Europe are generally upheld. However, several human rights infringements exist, ranging from the treatment of asylum seekers to police brutality. The 2012 Amnesty International Annual Report points to problems in several European countries. One of the most accused is Belarus, the only country in Europe that, according to The Economist, has an authoritarian government. All other European countries are considered to have "some form of democratic government", having either the "full democracy", "flawed democracy", or a "hybrid regime".

European Union citizenship is afforded to all citizens of member states of the European Union (EU). It was formally created with the adoption of the 1992 Maastricht Treaty, at the same time as the creation of the EU. EU citizenship is additional to, as it does not replace, national citizenship. It affords EU citizens with rights, freedoms and legal protections available under EU law.
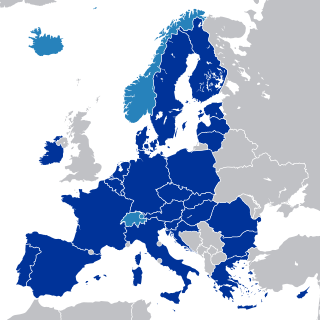
The European single market, internal market or common market is a single market comprising the 27 member states of the European Union (EU) as well as – with certain exceptions – Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway through the Agreement on the European Economic Area, and Switzerland through sectoral treaties. The single market seeks to guarantee the free movement of goods, capital, services, and people, known collectively as the "four freedoms". This is achieved through common rules and standards that all the EU member states are legally committed to following.
Fundamental rights are a group of rights that have been recognized by a high degree of protection from encroachment. These rights are specifically identified in a constitution, or have been found under due process of law. The United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 16, established in 2015, underscores the link between promoting human rights and sustaining peace.

The right to protest may be a manifestation of the right to freedom of assembly, the right to freedom of association, and the right to freedom of speech. Additionally, protest and restrictions on protest have lasted as long as governments have.

The Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Agreement (ACTA) is a multilateral treaty for the purpose of establishing international standards for intellectual property rights enforcement that did not enter into force. The agreement aims to establish an international legal framework for targeting counterfeit goods, generic medicines and copyright infringement on the Internet, and would create a new governing body outside existing forums, such as the World Trade Organization, the World Intellectual Property Organization, and the United Nations.
Metock v Minister for Justice, Equality and Law Reform (2008) C-127/08 is a European Union law case, significant in Ireland and Denmark, on the Citizens Rights Directive and family unification rules for migrant citizens. Citizenship of the European Union was established by Article 20 of the Treaty on the functioning of the European Union (TFEU) and the Citizenship Directive 2004/38 elaborates the right of Union citizens and their family members to move and reside freely in the territory of a member state, consolidating previous Directives dealing with the right to move and reside within the European Community (EC).

The April 6 Youth Movement is an Egyptian activist group established in Spring 2008 to support the workers in El-Mahalla El-Kubra, an industrial town, who were planning to strike on 6 April.

The area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) of the European Union (EU) is a policy domain concerning home affairs and migration, justice as well as fundamental rights, developed to address the challenges posed to internal security by collateral effects of the free movement of people and goods in the absence of border controls or customs inspection throughout the Schengen Area, as well as to safeguard adherence to the common European values through ensuring that the fundamental rights of people are respected across the EU.

International Transport Workers Federation v Viking Line ABP (2007) C-438/05 is an EU law case of the European Court of Justice, in which it was held that there is a positive right to strike, but the exercise of that right could infringe a business's freedom of establishment under the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union article 49. Often called The Rosella case or the Viking case, it is relevant to all labour law within the European Union. The decision has been criticised for the Court's inarticulate line of reasoning, and its disregard of fundamental human rights.
The general principles of European Union law are general principles of law which are applied by the European Court of Justice and the national courts of the member states when determining the lawfulness of legislative and administrative measures within the European Union. General principles of European Union law may be derived from common legal principles in the various EU member states, or general principles found in international law or European Union law. General principles of law should be distinguished from rules of law as principles are more general and open-ended in the sense that they need to be honed to be applied to specific cases with correct results.
The AKP government's handling of the 2013–14 protests in Turkey has been roundly criticized by other nations and international organizations, including the European Union, the United Nations, the United States, the UK, and Germany.

Omega Spielhallen und Automatenaufstellungs-GmbH v Oberbürgermeisterin der Bundesstadt Bonn (2004) C-36/02 is an EU law case, concerning the freedom to provide services and the free movement of goods in the European Union.

Media freedom in the European Union is a fundamental right that applies to all member states of the European Union and its citizens, as defined in the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights as well as the European Convention on Human Rights. Within the EU enlargement process, guaranteeing media freedom is named a "key indicator of a country's readiness to become part of the EU".
Coman and Others v Inspectoratul General pentru Imigrări and Ministerul Afacerilor Interne is a 2018 case of the European Court of Justice (ECJ) that affirmed residency rights in EU countries, to the spouse of an EU citizen who is exercising their right to freedom of movement and if the marriage was legally performed in an EU member state.
The Act LXXIX of 2021 on taking more severe action against paedophile offenders and amending certain Acts for the protection of children, often mentioned in English-language media as Hungary's anti-LGBT law are legislative amendments that were approved by the Hungarian Parliament on 15 June 2021, on a 157–1 vote. It was condemned by human rights groups and left-wing Hungarian opposition parties as discriminatory against the LGBT community. The EU and the United States consider the amendments to be discriminatory anti-LGBT restrictions. By contrast, most Eastern European EU countries did not take a public stance, apart from Poland, which supported the Hungarian position.
In EU law, reverse discrimination occurs when the national law of a member state of the European Union provides for less favourable treatment of its citizens or domestic products than other EU citizens/goods under EU law. Since the creation of the Single Market, the right of EU citizens to move freely within the EU with their families. The right to free movement was codified in EU Directive 2004/38/EC which applies across the whole EEA. However, reverse discrimination is permitted in EU law because of the legal principle of subsidiarity, i.e. EU law is not applicable in situations purely internal to one member state. This rule of purely internal situation does not apply if the EU citizens can provide a cross-border link, e.g. by travel or by holding dual EU citizenship. EU citizens and their families have an automatic right of entry and residence in all EU countries except their own, with exceptions created by a cross-EU state border link. For example, an Irish citizen living in Germany with his family before returning to Ireland can apply for EU family rights. This is referred to as the Surinder Singh route. The cross-border dimension has been the focus of many court cases in recent years, from McCarthy to Zambrano.









