
University of Rovira i Virgili is located in the Catalan cities of Tarragona and Reus, Spain. Its name is in honor of Antoni Rovira i Virgili.

Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity, realizing or redistributing value". Others have different definitions; a common element in the definitions is a focus on newness, improvement, and spread of ideas or technologies.

Scientific citation is providing detailed reference in a scientific publication, typically a paper or book, to previously published communications that have a bearing on the subject of the new publication. The purpose of citations in original work is to allow readers of the paper to refer to cited work to assist them in judging the new work, source background information vital for future development, and acknowledge the contributions of earlier workers.

Science and technology in China have developed rapidly since the 1980s to the 2020s, with major scientific and technological progress over the last four decades. From the 1980s to the 1990s, the Chinese government successively launched the 863 Program and the "Strategy for Rejuvenating the Country through Science and Education", which greatly promoted the development of China's science and technological institutions. Governmental focus on prioritizing the advancement of science and technology in China is evident in its allocation of funds, investment in research, reform measures, and enhanced societal recognition of these fields. These actions undertaken by the Chinese government are seen as crucial foundations for bolstering the nation's socioeconomic competitiveness and development, projecting its geopolitical influence, and elevating its national prestige and international reputation.
Technology transfer (TT), also called transfer of technology (TOT), is the process of transferring (disseminating) technology from the person or organization that owns or holds it to another person or organization, in an attempt to transform inventions and scientific outcomes into new products and services that benefit society. Technology transfer is closely related to knowledge transfer.
In business administration, absorptive capacity is defined as a firm's ability to recognize the value of new information, assimilate it, and apply it to commercial ends. It is studied on individual, group, firm, and national levels. Antecedents are prior-based knowledge and communication. Studies involve a firm's innovation performance, aspiration level, and organizational learning. It has been said that in order to be innovative an organization should develop its absorptive capacity.
Bibliometrics is the application of statistical methods to the study of bibliographic data, especially in scientific and library and information science contexts, and is closely associated with scientometrics to the point that both fields largely overlap.
Citation analysis is the examination of the frequency, patterns, and graphs of citations in documents. It uses the directed graph of citations — links from one document to another document — to reveal properties of the documents. A typical aim would be to identify the most important documents in a collection. A classic example is that of the citations between academic articles and books. For another example, judges of law support their judgements by referring back to judgements made in earlier cases. An additional example is provided by patents which contain prior art, citation of earlier patents relevant to the current claim. The digitization of patent data and increasing computing power have led to a community of practice that uses these citation data to measure innovation attributes, trace knowledge flows, and map innovation networks.
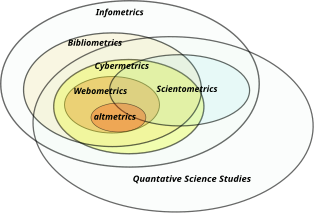
Informetrics is the study of quantitative aspects of information, it is an extension and evolution of traditional bibliometrics and scientometrics. Informetrics uses bibliometrics and scientometrics methods to study mainly the problems of literature information management and evaluation of science and technology. Informetrics is an independent discipline that uses quantitative methods from mathematics and statistics to study the process, phenomena, and law of informetrics. Informetrics has gained more attention as it is a common scientific method for academic evaluation, research hotspots in discipline, and trend analysis.
Technology forecasting attempts to predict the future characteristics of useful technological machines, procedures or techniques. Researchers create technology forecasts based on past experience and current technological developments. Like other forecasts, technology forecasting can be helpful for both public and private organizations to make smart decisions. By analyzing future opportunities and threats, the forecaster can improve decisions in order to achieve maximum benefits. Today, most countries are experiencing huge social and economic changes, which heavily rely on technology development. By analyzing these changes, government and economic institutions could make plans for future developments. However, not all of historical data can be used for technology forecasting, forecasters also need to adopt advanced technology and quantitative modeling from experts’ researches and conclusions.

The German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence, DFKI was founded in 1988 as a non-profit public-private partnership. It has research facilities in Kaiserslautern, Saarbrücken, Bremen, Oldenburg, and Osnabrück, laboratories in Berlin, Darmstadt, and Lübeck, and a branch office in Trier. In the field of innovative commercial software technology using artificial intelligence, DFKI is the leading research center in Germany.
An academic discipline or academic field is a subdivision of knowledge that is taught and researched at the college or university level. Disciplines are defined and recognized by the academic journals in which research is published, and the learned societies and academic departments or faculties within colleges and universities to which their practitioners belong. Academic disciplines are conventionally divided into the humanities, the scientific disciplines, the formal sciences like mathematics and computer science; the social sciences are sometimes considered a fourth category.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to information science:
The technological innovation system is a concept developed within the scientific field of innovation studies which serves to explain the nature and rate of technological change. A Technological Innovation System can be defined as ‘a dynamic network of agents interacting in a specific economic/industrial area under a particular institutional infrastructure and involved in the generation, diffusion, and utilization of technology’.
Reinhilde Veugelers is a Belgian economist and Professor of Managerial Economics, Strategy and Innovation at the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven from Belgium, known for her research on science and innovation. She is also a scholar at Bruegel in Brussels and at the Peterson Institute for International Economics in Washington D.C.
Alan Pilkington is a British engineer and researcher known for his work in technology management, operations management, Manufacturing strategy and enterprise engineering. He has been a professor at the Copenhagen Business School, Hult International Business School and S P Jain School of Global Management. He is currently Professor of Technology Management at Westminster Business School in London. He is past chair of the IEEE Technology Management Council for the UK and Republic of Ireland joint chapter on engineering management.
The GESIS – Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences is the largest German infrastructure institute for the social sciences. It is headquartered in Mannheim, with a location in Cologne. With basic research-based services and consulting covering all levels of the scientific process, GESIS supports researchers in the social sciences. As of 2017, the president of GESIS is Christof Wolf.
Science and technology in Armenia describes trends and developments in science, technology and innovation policy and governance in Armenia.
Science and technology in Kazakhstan – government policies to develop science, technology and innovation in Kazakhstan.

The National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics (NCSES) is one of the thirteen principal statistical agencies of the United States and is tasked with providing objective data on the status of the science and engineering enterprise in the U.S. and other countries. NCSES sponsors or co-sponsors data collection on 15 surveys and produces two key publications: Science and Engineering Indicators, and Women, Minorities, and Persons with Disabilities in Science and Engineering. Though policy-neutral, the data and reports produced by NCSES are used by policymakers when making policy decisions regarding STEM education and research funding in the U.S.









