Related Research Articles

Dyslexia, previously known as word blindness, is a learning disability that affects either reading or writing. Different people are affected to different degrees. Problems may include difficulties in spelling words, reading quickly, writing words, "sounding out" words in the head, pronouncing words when reading aloud and understanding what one reads. Often these difficulties are first noticed at school. The difficulties are involuntary, and people with this disorder have a normal desire to learn. People with dyslexia have higher rates of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), developmental language disorders, and difficulties with numbers.

Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms.

Homeopathy or homoeopathy is a pseudoscientific system of alternative medicine. It was conceived in 1796 by the German physician Samuel Hahnemann. Its practitioners, called homeopaths or homeopathic physicians, believe that a substance that causes symptoms of a disease in healthy people can cure similar symptoms in sick people; this doctrine is called similia similibus curentur, or "like cures like". Homeopathic preparations are termed remedies and are made using homeopathic dilution. In this process, the selected substance is repeatedly diluted until the final product is chemically indistinguishable from the diluent. Often not even a single molecule of the original substance can be expected to remain in the product. Between each dilution homeopaths may hit and/or shake the product, claiming this makes the diluent "remember" the original substance after its removal. Practitioners claim that such preparations, upon oral intake, can treat or cure disease.

Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.

Neurology is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system.
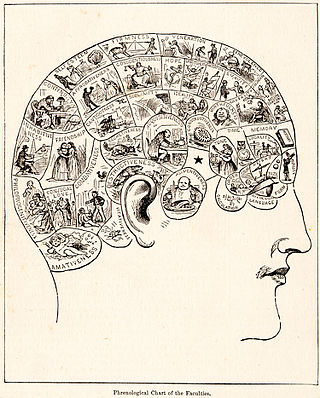
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claims; reliance on confirmation bias rather than rigorous attempts at refutation; lack of openness to evaluation by other experts; absence of systematic practices when developing hypotheses; and continued adherence long after the pseudoscientific hypotheses have been experimentally discredited. It is not the same as junk science.

A profession is a field of work that has been successfully professionalized. It can be defined as a disciplined group of individuals, professionals, who adhere to ethical standards and who hold themselves out as, and are accepted by the public as possessing special knowledge and skills in a widely recognised body of learning derived from research, education and training at a high level, and who are prepared to apply this knowledge and exercise these skills in the interest of others.
Psychotherapy is the use of psychological methods, particularly when based on regular personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase happiness, and overcome problems. Psychotherapy aims to improve an individual's well-being and mental health, to resolve or mitigate troublesome behaviors, beliefs, compulsions, thoughts, or emotions, and to improve relationships and social skills. Numerous types of psychotherapy have been designed either for individual adults, families, or children and adolescents. Certain types of psychotherapy are considered evidence-based for treating some diagnosed mental disorders; other types have been criticized as pseudoscience.

Informed consent is a principle in medical ethics, medical law and media studies, that a patient must have sufficient information and understanding before making decisions about their medical care. Pertinent information may include risks and benefits of treatments, alternative treatments, the patient's role in treatment, and their right to refuse treatment. In most systems, healthcare providers have a legal and ethical responsibility to ensure that a patient's consent is informed. This principle applies more broadly than healthcare intervention, for example to conduct research and to disclose a person's medical information.

An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies.

Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution, patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.

In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bringing about a certain goal, like acquiring knowledge or verifying knowledge claims. This normally involves various steps, like choosing a sample, collecting data from this sample, and interpreting the data. The study of methods concerns a detailed description and analysis of these processes. It includes evaluative aspects by comparing different methods. This way, it is assessed what advantages and disadvantages they have and for what research goals they may be used. These descriptions and evaluations depend on philosophical background assumptions. Examples are how to conceptualize the studied phenomena and what constitutes evidence for or against them. When understood in the widest sense, methodology also includes the discussion of these more abstract issues.
Medicalization is the process by which human conditions and problems come to be defined and treated as medical conditions, and thus become the subject of medical study, diagnosis, prevention, or treatment. Medicalization can be driven by new evidence or hypotheses about conditions; by changing social attitudes or economic considerations; or by the development of new medications or treatments.
Pathological lying, also known as mythomania and pseudologia fantastica, is a chronic behavior characterized by the habitual or compulsive tendency to lie. It involves a pervasive pattern of intentionally making false statements with the aim of deceiving others, sometimes without a clear or apparent reason. Individuals who engage in pathological lying often claim to be unaware of the motivations behind their lies.

In causal inference, a confounder is a variable that influences both the dependent variable and independent variable, causing a spurious association. Confounding is a causal concept, and as such, cannot be described in terms of correlations or associations. The existence of confounders is an important quantitative explanation why correlation does not imply causation. Some notations are explicitly designed to identify the existence, possible existence, or non-existence of confounders in causal relationships between elements of a system.

In the psychology of human behavior, denialism is a person's choice to deny reality as a way to avoid believing in a psychologically uncomfortable truth. Denialism is an essentially irrational action that withholds the validation of a historical experience or event when a person refuses to accept an empirically verifiable reality.
The branches of science, also referred to as sciences, scientific fields or scientific disciplines, are commonly divided into three major groups:
A near-death experience (NDE) is a profound personal experience associated with death or impending death, which researchers describe as having similar characteristics. When positive, which the great majority are, such experiences may encompass a variety of sensations including detachment from the body, feelings of levitation, total serenity, security, warmth, joy, the experience of absolute dissolution, review of major life events, the presence of a light, and seeing dead relatives. When negative, such experiences may include sensations of anguish, distress, a void, devastation, and seeing hellish imagery.

A genetically modified soybean is a soybean that has had DNA introduced into it using genetic engineering techniques. In 1996, the first genetically modified soybean was introduced to the U.S. by Monsanto. In 2014, 90.7 million hectares of GM soybeans were planted worldwide, making up 82% of the total soybeans cultivation area.
References
- ↑ Millán, Carmen; Bartrina, Francesca (2013). The Routledge Handbook of Translation Studies. Routledge. p. 431. ISBN 9781136242144 . Retrieved 1 January 2015.
- ↑ Cutright, Paul Russell (2003). Lewis and Clark: Pioneering Naturalists. U of Nebraska Press. ISBN 9780803264342 . Retrieved 1 January 2015.
- ↑ Buccheri, R.; Gesù, Vito di; Saniga, Metod (2000). Studies on the Structure of Time: From Physics to Psycho(patho)logy. Springer. p. 258. ISBN 9780306464393 . Retrieved 1 January 2015.
- ↑ "American Medical Association". Journal of the American Medical Association. 35. American Medical Association.: 202 1900. doi:10.1001/jama.1900.24610040009001b. ISSN 0002-9955 . Retrieved 1 January 2015.