Related Research Articles

A sextant is a doubly reflecting navigation instrument that measures the angular distance between two visible objects. The primary use of a sextant is to measure the angle between an astronomical object and the horizon for the purposes of celestial navigation.

The longitude rewards were the system of inducement prizes offered by the British government for a simple and practical method for the precise determination of a ship's longitude at sea. The rewards, established through an Act of Parliament in 1714, were administered by the Board of Longitude.
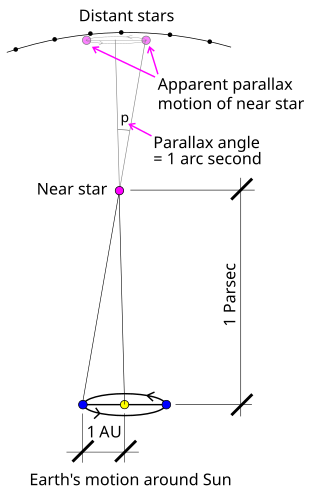
Stellar parallax is the apparent shift of position (parallax) of any nearby star against the background of distant stars. By extension, it is a method for determining the distance to the star through trigonometry, the stellar parallax method. Created by the different orbital positions of Earth, the extremely small observed shift is largest at time intervals of about six months, when Earth arrives at opposite sides of the Sun in its orbit, giving a baseline distance of about two astronomical units between observations. The parallax itself is considered to be half of this maximum, about equivalent to the observational shift that would occur due to the different positions of Earth and the Sun, a baseline of one astronomical unit (AU).

The Space Interferometry Mission, or SIM, also known as SIM Lite, was a planned space telescope proposed by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), in conjunction with contractor Northrop Grumman. One of the main goals of the mission was the hunt for Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of nearby stars other than the Sun. SIM was postponed several times and finally cancelled in 2010. In addition to detecting extrasolar planets, SIM would have helped astronomers construct a map of the Milky Way galaxy. Other important tasks would have included collecting data to help pinpoint stellar masses for specific types of stars, assisting in the determination of the spatial distribution of dark matter in the Milky Way and in the local group of galaxies and using the gravitational microlensing effect to measure the mass of stars. The spacecraft would have used optical interferometry to accomplish these and other scientific goals.

The ESO 3.6 m Telescope is an optical reflecting telescope run by the European Southern Observatory at La Silla Observatory, Chile since 1977, with a clear aperture of about 3.6 metres (140 in) and 8.6 m2 (93 sq ft) area.

The Isaac Newton Telescope or INT is a 2.54 m (100 in) optical telescope run by the Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes at Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on La Palma in the Canary Islands since 1984.

Ladd Observatory is an astronomical observatory at Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island. Founded in 1891 it was primarily designed for student instruction and also research. The facility operated a regional timekeeping service. It was responsible for the care and calibration of clocks on campus including one at Carrie Tower and another that rang the class bell at University Hall. Meteorological observations were made there from the time the building opened using recording weather instruments.

William MolyneuxFRS was an Anglo-Irish writer on science, politics and natural philosophy.

Jantar Mantar is located in the modern city of New Delhi. "Jantar Mantar" means "instruments for measuring the harmony of the heavens". It consists of 13 architectural astronomy instruments. The site is one of five built by Maharaja Jai Singh II of Jaipur, from 1723 onwards, revising the calendar and astronomical tables. Jai Singh, born in 1688 into a royal Rajput family that ruled the regional kingdom, was born into an era of education that maintained a keen interest in astronomy. There is a plaque fixed on one of the structures in the Jantar Mantar observatory in New Delhi that was placed there in 1910 mistakenly dating the construction of the complex to the year 1710. Later research, though, suggests 1724 as the actual year of construction. Its height is 723 feet (220 m).

A level is an optical instrument used to establish or verify points in the same horizontal plane in a process known as levelling. It is used in conjunction with a levelling staff to establish the relative height or levels of objects or marks. It is widely used in surveying and construction to measure height differences and to transfer, measure, and set heights of known objects or marks.

Longitude by chronometer is a method, in navigation, of determining longitude using a marine chronometer, which was developed by John Harrison during the first half of the eighteenth century. It is an astronomical method of calculating the longitude at which a position line, drawn from a sight by sextant of any celestial body, crosses the observer's assumed latitude. In order to calculate the position line, the time of the sight must be known so that the celestial position i.e. the Greenwich Hour Angle and Declination, of the observed celestial body is known. All that can be derived from a single sight is a single position line, which can be achieved at any time during daylight when both the sea horizon and the sun are visible. To achieve a fix, more than one celestial body and the sea horizon must be visible. This is usually only possible at dawn and dusk.
Pisa is a modern village situated 2.15 kilometres (1.34 mi) to the east of Olympia, Greece. Currently it is not politically independent but is a neighborhood of the village of Archea Olympia, the capital of the Municipality of Ancient Olympia, of which it is a municipal unit, Ancient Olympia, since 2011. Municipality (deme), municipal unit, village, and ancient site, all telescope at the same location under the same Greek name, archaia Olympia, although different English translations provide some diversity at the different levels. They are all in the regional unit of Elis, located on the northwest side of the geographic feature of the Peloponnesus
A dipleidoscope is an instrument used to determine true noon; its name comes from the Greek for double image viewer. It consists of a small telescope and a prism that creates a double image of the sun. When the two images overlap, it is local true noon. The instrument is capable of determining true noon to within ten seconds.

Samuel Molyneux FRS was an amateur astronomer and politician who sat in the British House of Commons between 1715 and 1728 and in the Irish House of Commons from 1727 to 1728. His work with James Bradley attempting to measure stellar parallax led to the discovery of the aberration of light. The aberration was the first definite evidence that the earth moved and that Copernicus and Kepler were correct. In addition to his astronomical works, Molyneux wrote about the natural history and other features of Ireland. He died in suspicious circumstances.

The history of longitude describes the centuries-long effort by astronomers, cartographers and navigators to discover a means of determining the longitude of any given place on Earth. The measurement of longitude is important to both cartography and navigation. In particular, for safe ocean navigation, knowledge of both latitude and longitude is required, however latitude can be determined with good accuracy with local astronomical observations.

Lieutenant General Sir Thomas Molyneux, 1st Baronet FRS was an Irish physician.

The Geneva Observatory is an astronomical observatory at Sauverny (CH) in the municipality of Versoix, Canton of Geneva, in Switzerland. It shares its buildings with the astronomy department of the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne. It has been active in discovering exoplanets, in stellar photometry, modelling stellar evolution, and has been involved in the European Space Agency's Hipparcos, INTEGRAL, Gaia, and Planck missions.

A nautical chronometer made by Thomas Earnshaw (1749–1828), and once part of the equipment of HMS Beagle, the ship that carried Charles Darwin on his voyage around the world, is held in the British Museum. The chronometer was the subject of one episode of the BBC's series A History of the World in 100 Objects.

NGC 3198, also known as Herschel 146 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, sometime before 1850. NGC 3198 is located in the Leo Spur, which is part of the Virgo Supercluster, and is approximately 47 million light years away.
References
- ↑ William Molyneux, “A New Contrivance of Adapting a Telescope to an Horizontal Dial for Observing the moment of Time by Day or Night”, printed by Andrew Cook and Samuel Helsham, 1686
- ↑ Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, October 1686, No. 184 p. 213 et seq.
- ↑ Dn. Johanni Georgio IV, Acta eruditorum, 1687, p 623 et. Seq.