Related Research Articles

The Graphics Interchange Format is a bitmap image format that was developed by a team at the online services provider CompuServe led by American computer scientist Steve Wilhite and released on June 15, 1987.

Portable Network Graphics is a raster-graphics file format that supports lossless data compression. PNG was developed as an improved, non-patented replacement for Graphics Interchange Format (GIF)—unofficially, the initials PNG stood for the recursive acronym "PNG's not GIF".
Adobe Photoshop is a raster graphics editor developed and published by Adobe for Windows and macOS. It was originally created in 1987 by Thomas and John Knoll. Since then, the software has become the most used tool for professional digital art, especially in raster graphics editing. Owing to its fame, the program's name has become genericised as a verb although Adobe disapproves of such use.
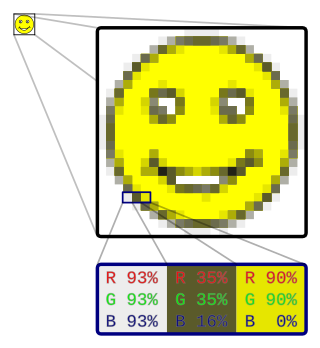
In computer graphics and digital photography, a raster graphic represents a two-dimensional picture as a rectangular matrix or grid of pixels, viewable via a computer display, paper, or other display medium. A raster is technically characterized by the width and height of the image in pixels and by the number of bits per pixel. Raster images are stored in image files with varying dissemination, production, generation, and acquisition formats.
Tag Image File Format or Tagged Image File Format, commonly known by the abbreviations TIFF or TIF, is an image file format for storing raster graphics images, popular among graphic artists, the publishing industry, and photographers. TIFF is widely supported by scanning, faxing, word processing, optical character recognition, image manipulation, desktop publishing, and page-layout applications. The format was created by the Aldus Corporation for use in desktop publishing. It published the latest version 6.0 in 1992, subsequently updated with an Adobe Systems copyright after the latter acquired Aldus in 1994. Several Aldus or Adobe technical notes have been published with minor extensions to the format, and several specifications have been based on TIFF 6.0, including TIFF/EP, TIFF/IT, TIFF-F and TIFF-FX.
Color management is the process of ensuring consistent and accurate colors across various devices, such as monitors, printers, and cameras. It involves the use of color profiles, which are standardized descriptions of how colors should be displayed or reproduced.
The BMP file format or bitmap, is a raster graphics image file format used to store bitmap digital images, independently of the display device, especially on Microsoft Windows and OS/2 operating systems.
PICT is a graphics file format introduced on the original Apple Macintosh computer as its standard metafile format. It allows the interchange of graphics, and some limited text support, between Mac applications, and was the native graphics format of QuickDraw.

Transparency in computer graphics is possible in a number of file formats. The term "transparency" is used in various ways by different people, but at its simplest there is "full transparency" i.e. something that is completely invisible. Only part of a graphic should be fully transparent, or there would be nothing to see. More complex is "partial transparency" or "translucency" where the effect is achieved that a graphic is partially transparent in the same way as colored glass. Since ultimately a printed page or computer or television screen can only be one color at a point, partial transparency is always simulated at some level by mixing colors. There are many different ways to mix colors, so in some cases transparency is ambiguous.
A number of vector graphics editors exist for various platforms. Potential users of these editors will make a comparison of vector graphics editors based on factors such as the availability for the user's platform, the software license, the feature set, the merits of the user interface (UI) and the focus of the program. Some programs are more suitable for artistic work while others are better for technical drawings. Another important factor is the application's support of various vector and bitmap image formats for import and export.
An image file format is a file format for a digital image. There are many formats that can be used, such as JPEG, PNG, and GIF. Most formats up until 2022 were for storing 2D images, not 3D ones. The data stored in an image file format may be compressed or uncompressed. If the data is compressed, it may be done so using lossy compression or lossless compression. For graphic design applications, vector formats are often used. Some image file formats support transparency.
Open XML Paper Specification is an open specification for a page description language and a fixed-document format. Microsoft developed it as the XML Paper Specification (XPS). In June 2009, Ecma International adopted it as international standard ECMA-388.
In computing, indexed color is a technique to manage digital images' colors in a limited fashion, in order to save computer memory and file storage, while speeding up display refresh and file transfers. It is a form of vector quantization compression.
In printing, Preflight is the process of confirming that the digital files required for the printing process are all present, valid, correctly formatted, and of the desired type. The basic idea is to prepare the files to make them feasible for the correct process such as offset printing and eliminate costly errors and facilitate a smooth production. It is a standard prepress procedure in the printing industry. The term originates from the preflight checklists used by pilots. The term was first used in a presentation at the Color Connections conference in 1990 by consultant Chuck Weger, and Professor Ron Bertolina was a pioneer for solutions to preflighting in the 1990s.
JPEG XR is an image compression standard for continuous tone photographic images, based on the HD Photo specifications that Microsoft originally developed and patented. It supports both lossy and lossless compression, and is the preferred image format for Ecma-388 Open XML Paper Specification documents.

Barco Creator was an image manipulation program targeted at the repro and print shop markets. It was developed by Barco Creative Systems a division of the Barco Group and first shown as a prototype at Parigraph in April 1988, then later at Ipex 88). Barco Creative Systems together with D.I.S.C. and Aesthedes merged into Barco Graphics. It ran on several generations of Silicon Graphics computers till the late 1990s. Barco Graphics ColorTone for Windows NT is considered its successor.
In color management, an ICC profile is a set of data that characterizes a color input or output device, or a color space, according to standards promulgated by the International Color Consortium (ICC). Profiles describe the color attributes of a particular device or viewing requirement by defining a mapping between the device source or target color space and a profile connection space (PCS). This PCS is either CIELAB (L*a*b*) or CIEXYZ. Mappings may be specified using tables, to which interpolation is applied, or through a series of parameters for transformations.
PGF is a wavelet-based bitmapped image format that employs lossless and lossy data compression. PGF was created to improve upon and replace the JPEG format. It was developed at the same time as JPEG 2000 but with a focus on speed over compression ratio.

Chasys Draw IES is a suite of applications including a layer-based raster graphics editor with adjustment layers, linked layers, timeline and frame-based animation, icon editing, image stacking and comprehensive plug-in support, a fast multi-threaded image file converter and a fast image viewer, with RAW image support in all components. It supports the native file formats of several competitors including Adobe Photoshop, Affinity Photo, Corel Photo-Paint, GIMP, Krita, Paint.NET and PaintShop Pro, and the whole suite is designed to make effective use of multi-core processors, touch-screens and pen-input devices.
Desktop Colour Separation (DCS) is an enhanced Encapsulated PostScript file format that was introduced by Quark, Inc. It is now primarily used for specialised graphics work particularly images that use multiple channels, e.g. when applying different spot colours to each part of a greyscale image.
References
- 1 2 "Adobe InDesign CS3 Help". Adobe. Archived from the original on 1 October 2011.
- 1 2 "File formats". Adobe.
- ↑ "Scitex CT".