See also
- Centro SCOP (Mexico City Metrobús), a BRT station in Mexico City
Scop is a general name for an Old English poet. Scop or SCOP may also refer to:

The beta sheet, (β-sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, notably Alzheimer's disease.
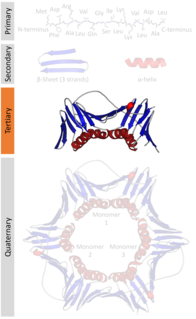
Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure. A number of tertiary structures may fold into a quaternary structure.
PSP may refer to:

A scop was a poet as represented in Old English poetry. The scop is the Old English counterpart of the Old Norse skald, with the important difference that "skald" was applied to historical persons, and scop is used, for the most part, to designate oral poets within Old English literature. Very little is known about scops, and their historical existence is questioned by some scholars.
CRP may refer to:

King's College, formally The College of Christ the King, is a Catholic liberal arts college in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania. It is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education and located within the Diocese of Scranton.

The Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database is a largely manual classification of protein structural domains based on similarities of their structures and amino acid sequences. A motivation for this classification is to determine the evolutionary relationship between proteins. Proteins with the same shapes but having little sequence or functional similarity are placed in different superfamilies, and are assumed to have only a very distant common ancestor. Proteins having the same shape and some similarity of sequence and/or function are placed in "families", and are assumed to have a closer common ancestor.
DMD may refer to:
Gap or The Gap may refer to various openings, vacant spaces, lacks or pauses:
Ras or RAS may refer to:
InterPro is a database of protein families, protein domains and functional sites in which identifiable features found in known proteins can be applied to new protein sequences in order to functionally characterise them.

A beta helix is a tandem protein repeat structure formed by the association of parallel beta strands in a helical pattern with either two or three faces. The beta helix is a type of solenoid protein domain. The structure is stabilized by inter-strand hydrogen bonds, protein-protein interactions, and sometimes bound metal ions. Both left- and right-handed beta helices have been identified. These structures are distinct from jelly-roll folds, a different protein structure sometimes known as a "double-stranded beta helix".

In structural biology, a beta-propeller (β-propeller) is a type of all-β protein architecture characterized by 4 to 8 highly symmetrical blade-shaped beta sheets arranged toroidally around a central axis. Together the beta-sheets form a funnel-like active site.
A helix bundle is a small protein fold composed of several alpha helices that are usually nearly parallel or antiparallel to each other.
Protein subfamily is a level of protein classification, based on their close evolutionary relationship. It is below the larger levels of protein superfamily and protein family.
BF may refer to:
SUPERFAMILY is a database and search platform of structural and functional annotation for all proteins and genomes. It classifies amino acid sequences into known structural domains, especially into SCOP superfamilies. Domains are functional, structural, and evolutionary units that form proteins. Domains of common Ancestry are grouped into superfamilies. The domains and domain superfamilies are defined and described in SCOP. Superfamilies are groups of proteins which have structural evidence to support a common evolutionary ancestor but may not have detectable sequence homology.

Steven Elliot Brenner is a professor at the Department of Plant and Microbial Biology at the University of California Berkeley, Adjunct Professor at the Department of Bioengineering and Therapeutic Sciences at the University of California, and San Francisco Faculty Scientist, Physical Biosciences at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
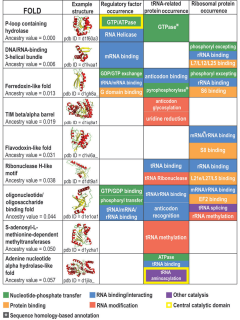
Protein fold classes are broad categories of protein tertiary structure topology. They describe groups of proteins that share similar amino acid and secondary structure proportions. Each class contains multiple, independent protein superfamilies.
Arachnophagy describes a feeding behaviour that includes arachnids. Aside from non-human creatures, the term can also refer to the practice of eating arachnids among humans.