Related Research Articles
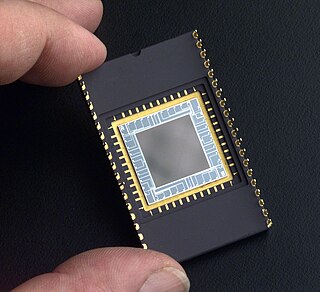
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging.

The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor, also known as the metal–oxide–silicon transistor, is a type of insulated-gate field-effect transistor that is fabricated by the controlled oxidation of a semiconductor, typically silicon. The voltage of the covered gate determines the electrical conductivity of the device; this ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals.
A tetrode is a vacuum tube having four active electrodes. The four electrodes in order from the centre are: a thermionic cathode, first and second grids and a plate. There are several varieties of tetrodes, the most common being the screen-grid tube and the beam tetrode. In screen-grid tubes and beam tetrodes, the first grid is the control grid and the second grid is the screen grid. In other tetrodes one of the grids is a control grid, while the other may have a variety of functions.

An organic light-emitting diode, also known as organic electroluminescentdiode, is a light-emitting diode (LED) in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compound that emits light in response to an electric current. This organic layer is situated between two electrodes; typically, at least one of these electrodes is transparent. OLEDs are used to create digital displays in devices such as television screens, computer monitors, portable systems such as smartphones, handheld game consoles and PDAs. A major area of research is the development of white OLED devices for use in solid-state lighting applications.

A corona discharge is an electrical discharge caused by the ionization of a fluid such as air surrounding a conductor carrying a high voltage. It represents a local region where the air has undergone electrical breakdown and become conductive, allowing charge to continuously leak off the conductor into the air. A corona occurs at locations where the strength of the electric field around a conductor exceeds the dielectric strength of the air. It is often seen as a bluish glow in the air adjacent to pointed metal conductors carrying high voltages, and emits light by the same property as a gas discharge lamp.

A touchscreen, or touch screen, is both an input and output device and normally layered on the top of an electronic visual display of an information processing system. The display is often an LCD or OLED display while the system is usually a laptop, tablet, or smartphone. A user can give input or control the information processing system through simple or multi-touch gestures by touching the screen with a special stylus or one or more fingers. Some touchscreens use ordinary or specially coated gloves to work while others may only work using a special stylus or pen. The user can use the touchscreen to react to what is displayed and, if the software allows, to control how it is displayed; for example, zooming to increase the text size.

In computer displays, filmmaking, television production, and other kinetic displays, scrolling is sliding text, images or video across a monitor or display, vertically or horizontally. "Scrolling," as such, does not change the layout of the text or pictures but moves the user's view across what is apparently a larger image that is not wholly seen. A common television and movie special effect is to scroll credits, while leaving the background stationary. Scrolling may take place completely without user intervention or, on an interactive device, be triggered by touchscreen or a keypress and continue without further intervention until a further user action, or be entirely controlled by input devices.
Deep-level transient spectroscopy (DLTS) is an experimental tool for studying electrically active defects in semiconductors. DLTS establishes fundamental defect parameters and measures their concentration in the material. Some of the parameters are considered as defect "finger prints" used for their identifications and analysis.

An electrostatic precipitator (ESP) is a filtration device that removes fine particles, like dust and smoke, from a flowing gas using the force of an induced electrostatic charge minimally impeding the flow of gases through the unit.
A voice-user interface (VUI) makes spoken human interaction with computers possible, using speech recognition to understand spoken commands and answer questions, and typically text to speech to play a reply. A voice command device (VCD) is a device controlled with a voice user interface.

A charge pump is a kind of DC-to-DC converter that uses capacitors for energetic charge storage to raise or lower voltage. Charge-pump circuits are capable of high efficiencies, sometimes as high as 90–95%, while being electrically simple circuits.
An electrostatic detection device, EDD or ESDA, is a specialized piece of equipment commonly used in questioned document examination to reveal indentations or impressions in paper that may otherwise go unnoticed. It is a non-destructive technique, allowing further tests to be carried out. It is a sensitive technique capable of detecting indentations on pages several layers below the top sheet and many years after the indentations were created.

An antistatic device is any device that reduces, dampens, or otherwise inhibits electrostatic discharge; the buildup or discharge of static electricity, which can damage electrical components such as computer hard drives, and even ignite flammable liquids and gases.
The iPhone is a line of touchscreen-based smartphones designed and marketed by Apple Inc. that use Apple's iOS mobile operating system. The first-generation iPhone was announced by Apple co-founder Steve Jobs on January 9, 2007. Since then Apple has annually released new iPhone models and iOS updates. As of November 1, 2018, more than 2.2 billion iPhones had been sold.

In computing, multi-touch is technology that enables a surface to recognize the presence of more than one point of contact with the surface at the same time. The origins of multitouch began at CERN, MIT, University of Toronto, Carnegie Mellon University and Bell Labs in the 1970s. CERN started using multi-touch screens as early as 1976 for the controls of the Super Proton Synchrotron. Apple popularized the term "multi-touch" in 2007. Plural-point awareness may be used to implement additional functionality, such as pinch to zoom or to activate certain subroutines attached to predefined gestures.
Xeroradiography is a type of X-ray imaging in which a picture of the body is recorded on paper rather than on film. In this technique, a plate of selenium, which rests on a thin layer of aluminium oxide, is charged uniformly by passing it in front of a scorotron. The process was developed by engineer Dr. Robert C. McMaster in 1950.

iOS is a mobile operating system created and developed by Apple Inc. exclusively for its hardware. It is the operating system that powers many of the company's mobile devices, including the iPhone and iPod Touch; it also powered the iPad until the introduction of iPadOS, a derivative of iOS, in 2019. It is the world's second-most widely installed mobile operating system, after Android. It is the basis for three other operating systems made by Apple: iPadOS, tvOS, and watchOS. It is proprietary software, although some parts of it are open source under the Apple Public Source License and other licenses.

Plasma is one of the four fundamental states of matter, and was first described by chemist Irving Langmuir in the 1920s. It consists of a gas of ions – atoms which have some of their orbital electrons removed – and free electrons. Plasma can be artificially generated by heating a neutral gas or subjecting it to a strong electromagnetic field to the point where an ionized gaseous substance becomes increasingly electrically conductive. The resulting charged ions and electrons become influenced by long-range electromagnetic fields, making the plasma dynamics more sensitive to these fields than a neutral gas.
The HTC Evo Shift 4G is a smartphone developed by HTC Corporation and marketed as the concurrent/sequel to Sprint's flagship Android smartphone, running on its 4G WiMAX network. The smartphone launched on January 9, 2011.
A mobile application, also referred to as a mobile app or simply an app, is a computer program or software application designed to run on a mobile device such as a phone, tablet, or watch. Apps were originally intended for productivity assistance such as email, calendar, and contact databases, but the public demand for apps caused rapid expansion into other areas such as mobile games, factory automation, GPS and location-based services, order-tracking, and ticket purchases, so that there are now millions of apps available. Apps are generally downloaded from application distribution platforms which are operated by the owner of the mobile operating system, such as the App Store (iOS) or Google Play Store. Some apps are free, and others have a price, with the profit being split between the application's creator and the distribution platform. Mobile applications often stand in contrast to desktop applications which are designed to run on desktop computers, and web applications which run in mobile web browsers rather than directly on the mobile device.
References
- ↑ Thomas F. Hayne (January 1976), "Screen Controlled Corona Device (Scorotron) for Charging in a Xerographic Copier", IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, IA-12 (1): 63–67, doi:10.1109/TIA.1976.349404, S2CID 15232361
- ↑ "scorotron", PR Glossary, Precision Roller, retrieved 2019-10-01
- ↑ Christopher I. Udoyea; Hamid Jafarzadehb (January 2010), "Xeroradiography: Stagnated after a Promising Beginning? A Historical Review", European Journal of Dentistry, 4 (1): 95–99, doi:10.1055/s-0039-1697816, PMC 2798798 , PMID 20046488,
...sensitization of the photoconductor plate in the charging station by depositing a uniform positive charge on its surface with a corona-emitting device called scorotron.
| This technology-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This article related to medical equipment is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |