
Abu Zubaydah is a Palestinian citizen born in Saudi Arabia currently held by the U.S. in the Guantanamo Bay detention camp in Cuba. He is held under the authority of Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Terrorists (AUMF).
Ibn al-Shaykh al-Libi was a Libyan national captured in Afghanistan in November 2001 after the fall of the Taliban; he was interrogated by American and Egyptian forces. The information he gave under torture to Egyptian authorities was cited by the George W. Bush administration in the months preceding its 2003 invasion of Iraq as evidence of a connection between Saddam Hussein and al-Qaeda. That information was frequently repeated by members of the Bush administration, although reports from both the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) and the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) strongly questioned its credibility, suggesting that al-Libi was "intentionally misleading" interrogators.

Lawrence Ari Fleischer is an American media consultant and political aide who served as the 23rd White House Press Secretary, for President George W. Bush, from January 2001 to July 2003.

During the early stages of the Iraq War, members of the United States Army and the Central Intelligence Agency committed a series of human rights violations and war crimes against detainees in the Abu Ghraib prison in Iraq. These abuses included physical abuse, sexual humiliation, physical and psychological torture, and rape, as well as the killing of Manadel al-Jamadi and the desecration of his body. The abuses came to public attention with the publication of photographs by CBS News in April 2004, causing shock and outrage and receiving widespread condemnation within the United States and internationally.
About six months after the United States invasion of Iraq of 2003, rumors of Iraq prison abuse scandals started to emerge.

Waterboarding is a form of torture in which water is poured over a cloth covering the face and breathing passages of an immobilized captive, causing the person to experience the sensation of drowning. In the most common method of waterboarding, the captive's face is covered with cloth or some other thin material and immobilized on their back at an incline of 10 to 20 degrees. Torturers pour water onto the face over the breathing passages, causing an almost immediate gag reflex and creating a drowning sensation for the captive. Normally, water is poured intermittently to prevent death; however, if the water is poured uninterruptedly it will lead to death by asphyxia. Waterboarding can cause extreme pain, damage to lungs, brain damage from oxygen deprivation, other physical injuries including broken bones due to struggling against restraints, and lasting psychological damage. Adverse physical effects can last for months, and psychological effects for years. The term "water board torture" appeared in press reports as early as 1976.

Geoffrey D. Miller is a retired United States Army major general who commanded the US detention facilities at Guantanamo Bay, Cuba, and Iraq. Detention facilities in Iraq under his command included Abu Ghraib prison, Camp Cropper, and Camp Bucca. He is noted for having trained soldiers in using torture, or "enhanced interrogation techniques" in US euphemism, and for carrying out the "First Special Interrogation Plan," signed by the Secretary of Defense, against a Guantanamo detainee.

Manadel al-Jamadi was an Iraqi national who was killed in United States custody during a CIA interrogation at Abu Ghraib prison on November 4, 2003. His name became known in 2004 when the Abu Ghraib scandal made headlines; his corpse packed in ice was the background for widely reprinted photographs of grinning U.S. Army specialists Sabrina Harman and Charles Graner each offering a "thumbs-up" gesture. Al-Jamadi had been a suspect in a bomb attack that killed 34 people, including one US soldier, and left more than 200 wounded in a Baghdad Red Cross facility.
Ghost detainee is a term used in the executive branch of the United States government to designate a person held in a detention center, whose identity has been hidden by keeping them unregistered and therefore anonymous. Such uses arose as the Bush administration initiated the War on Terror following the 9/11 attacks of 2001 in the United States. As documented in the 2004 Taguba Report, it was used in the same manner by United States officials and contractors of the Joint Interrogation and Debriefing Center at the Abu Ghraib prison in Iraq in 2003–2004.

The Salt Pit and Cobalt were the code names of an isolated clandestine CIA black site prison and interrogation center outside Bagram Air Base in Afghanistan. It was located north of Kabul and was the location of a brick factory prior to the Afghanistan War. The CIA adapted it for extrajudicial detention.
Abed Hamed Mowhoush was an air vice-marshal believed to be in command of the transport, logistics and airlifting division of the Iraqi Air Force during the regime of Saddam Hussein immediately prior to the 2003 Invasion of Iraq, until his surrender to United States forces on 10 November 2003. He died on 26 November 2003 while in U.S. custody at the Al-Qaim detention facility approximately 200 miles (320 km) northwest of Baghdad, following a 16-day period of detention.
Extrajudicial prisoners of the United States, in the context of the early twenty-first century War on Terrorism, refers to foreign nationals the United States detains outside of the legal process required within United States legal jurisdiction. In this context, the U.S. government is maintaining torture centers, called black sites, operated by both known and secret intelligence agencies. Such black sites were later confirmed by reports from journalists, investigations, and from men who had been imprisoned and tortured there, and later released after being tortured until the CIA was comfortable they had done nothing wrong, and had nothing to hide.
Lewis E. Welshofer Jr. is a United States Army soldier, convicted of homicide of an Iraqi prisoner of war on November 23, 2003 in al-Qaim. Welshofer was then serving as a Chief Warrant Officer in the 3d Armored Cavalry Regiment.
Camp Nama was a military base in Baghdad, Iraq, originally built by the government of Saddam Hussein, from which its name derives, and now used by Iraqi military forces. Purportedly, the original Iraqi name has been repurposed by U.S. personnel involved with the facility as a backronym standing for "Nasty Ass Military Area".
There are cases, both documented and alleged, that involve the usage of torture by members of the United States government, military, law enforcement agencies, intelligence agencies, health care services, and other public organizations both in and out of the country.
"Enhanced interrogation techniques" or "enhanced interrogation" was a program of systematic torture of detainees by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) and various components of the U.S. Armed Forces at remote sites around the world—including Abu Ghraib, Bagram, Bucharest, and Guantanamo Bay—authorized by officials of the George W. Bush administration. Methods used included beating, binding in contorted stress positions, hooding, subjection to deafening noise, sleep disruption, sleep deprivation to the point of hallucination, deprivation of food, drink, and medical care for wounds, as well as waterboarding, walling, sexual humiliation, rape, sexual assault, subjection to extreme heat or extreme cold, and confinement in small coffin-like boxes. A Guantanamo inmate's drawings of some of these tortures, to which he himself was subjected, were published in The New York Times. Some of these techniques fall under the category known as "white room torture". Several detainees endured medically unnecessary "rectal rehydration", "rectal fluid resuscitation", and "rectal feeding". In addition to brutalizing detainees, there were threats to their families such as threats to harm children, and threats to sexually abuse or to cut the throat of detainees' mothers.
This article deals with the activities of the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) of the federal government of the United States that constitute violations of human rights.

Stephen Soldz is a psychoanalyst, clinical psychologist, professor, and anti-war activist. Soldz is director of the Social Justice and Human Rights program at the Boston Graduate School of Psychoanalysis.

The Committee Study of the Central Intelligence Agency's Detention and Interrogation Program is a report compiled by the bipartisan United States Senate Select Committee on Intelligence (SSCI) about the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)'s Detention and Interrogation Program and its use of torture during interrogation in U.S. government communiqués on detainees in CIA custody. The report covers CIA activities before, during, and after the "War on Terror." The initial report was approved on December 13, 2012, by a vote of 9–6, with seven Democrats, one independent, and one Republican voting in favor of the report and six Republicans voting in opposition.
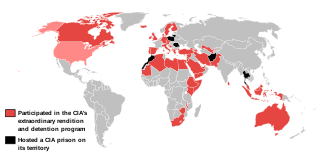
Following the September 11 attacks of 2001 and subsequent War on Terror, the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) established a "Detention and Interrogation Program" that included a network of clandestine extrajudicial detention centers, officially known as "black sites", to detain, interrogate, and often torture suspected enemy combatants, usually with the acquiescence, if not direct collaboration, of the host government.









