
In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer as initiated via hardware such as a button on the computer or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) has no software in its main memory, so some process must load software into memory before it can be executed. This may be done by hardware or firmware in the CPU, or by a separate processor in the computer system.
Hierarchical File System (HFS) is a proprietary file system developed by Apple Inc. for use in computer systems running Mac OS. Originally designed for use on floppy and hard disks, it can also be found on read-only media such as CD-ROMs. HFS is also referred to as Mac OS Standard, while its successor, HFS Plus, is also called Mac OS Extended.

A RAM drive is a block of random-access memory that a computer's software is treating as if the memory were a disk drive. RAM drives provide high-performance temporary storage for demanding tasks and protect non-volatile storage devices from wearing down, since RAM is not prone to wear from writing, unlike non-volatile flash memory. They are in a sense the reverse of virtual memory: RAM drive uses a volatile fast memory as if it's a nonvolatile slow memory. Virtual memory is the opposite.
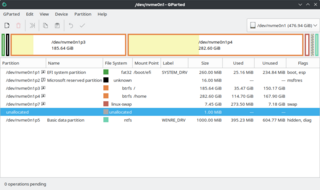
Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk after a partitioning scheme is chosen for the new disk before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it can be difficult to properly size partitions, resulting in having one partition with too much free space and another nearly totally allocated.
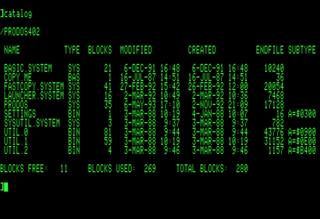
ProDOS is the name of two similar operating systems for the Apple II of personal computer. The original ProDOS, renamed ProDOS 8 in version 1.2, is the last official operating system usable by all 8-bit Apple II computers, and was distributed from 1983 to 1993. The other, ProDOS 16, was a stop-gap solution for the 16-bit Apple IIGS that was replaced by GS/OS within two years.
A boot disk is a removable digital data storage medium from which a computer can load and run (boot) an operating system or utility program. The computer must have a built-in program which will load and execute a program from a boot disk meeting certain standards.
In computer operating systems, memory paging is a memory management scheme by which a computer stores and retrieves data from secondary storage for use in main memory. In this scheme, the operating system retrieves data from secondary storage in same-size blocks called pages. Paging is an important part of virtual memory implementations in modern operating systems, using secondary storage to let programs exceed the size of available physical memory.

A live CD is a complete bootable computer installation including operating system which runs directly from a CD-ROM or similar storage device into a computer's memory, rather than loading from a hard disk drive. A live CD allows users to run an operating system for any purpose without installing it or making any changes to the computer's configuration. Live CDs can run on a computer without secondary storage, such as a hard disk drive, or with a corrupted hard disk drive or file system, allowing data recovery.

Multi-booting is the act of installing multiple operating systems on a single computer, and being able to choose which one to boot. The term dual-booting refers to the common configuration of specifically two operating systems. Multi-booting may require a custom boot loader.
Disk cloning is the process of duplicating all data on a digital storage drive, such as a hard disk or solid state drive, using hardware or software techniques. Unlike file copying, disk cloning also duplicates the filesystems, partitions, drive meta data and slack space on the drive. Common reasons for cloning a drive include; data backup and recovery; duplicating a computer's configuration for mass deployment and for preserving data for digital forensics purposes. Drive cloning can be used in conjunction with drive imaging where the cloned data is saved to one or more files on another drive rather than copied directly to another drive.

A diskless node is a workstation or personal computer without disk drives, which employs network booting to load its operating system from a server.
Disk encryption software is a computer security software that protects the confidentiality of data stored on computer media by using disk encryption.
In computing, data recovery is a process of retrieving deleted, inaccessible, lost, corrupted, damaged, or formatted data from secondary storage, removable media or files, when the data stored in them cannot be accessed in a usual way. The data is most often salvaged from storage media such as internal or external hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, magnetic tapes, CDs, DVDs, RAID subsystems, and other electronic devices. Recovery may be required due to physical damage to the storage devices or logical damage to the file system that prevents it from being mounted by the host operating system (OS).
In computer data storage, a volume or logical drive is a single accessible storage area with a single file system, typically resident on a single partition of a hard disk. Although a volume might be different from a physical disk drive, it can still be accessed with an operating system's logical interface. However, a volume differs from a partition.
In Linux systems, initrd is a scheme for loading a temporary root file system into memory, to be used as part of the Linux startup process. initrd and initramfs refer to two different methods of achieving this. Both are commonly used to make preparations before the real root file system can be mounted.

An error message is the information displayed when an unforeseen problem occurs, usually on a computer or other device. Modern operating systems with graphical user interfaces, often display error messages using dialog boxes. Error messages are used when user intervention is required, to indicate that a desired operation has failed, or to relay important warnings. Error messages are seen widely throughout computing, and are part of every operating system or computer hardware device. The proper design of error messages is an important topic in usability and other fields of human–computer interaction.

A live USB is a portable USB-attached external data storage device containing a full operating system that can be booted from. The term is reminiscent of USB flash drives but may encompass an external hard disk drive or solid-state drive, though they may be referred to as "live HDD" and "live SSD" respectively. They are the evolutionary next step after live CDs, but with the added benefit of writable storage, allowing customizations to the booted operating system. Live USBs can be used in embedded systems for system administration, data recovery, or test driving, and can persistently save settings and install software packages on the USB device.
The Linux booting process involves multiple stages and is in many ways similar to the BSD and other Unix-style boot processes, from which it derives. Although the Linux booting process depends very much on the computer architecture, those architectures share similar stages and software components, including system startup, bootloader execution, loading and startup of a Linux kernel image, and execution of various startup scripts and daemons. Those are grouped into 4 steps: system startup, bootloader stage, kernel stage, and init process. When a Linux system is powered up or reset, its processor will execute a specific firmware/program for system initialization, such as the power-on self-test, invoking the reset vector to start a program at a known address in flash/ROM, then load the bootloader into RAM for later execution. In IBM PC–compatible personal computers (PCs), this firmware/program is either a BIOS or a UEFI monitor, and is stored in the mainboard. In embedded Linux systems, this firmware/program is called boot ROM. After being loaded into RAM, the bootloader will execute to load the second-stage bootloader. The second-stage bootloader will load the kernel image into memory, decompress and initialize it, and then pass control to this kernel image. The second-stage bootloader also performs several operation on the system such as system hardware check, mounting the root device, loading the necessary kernel modules, etc. Finally, the first user-space process starts, and other high-level system initializations are performed.
IDEDOS is a ROM-based disk operating system written in 6502/65816 assembly language for the Commodore 64, 128 and SuperCPU. Its main purpose is to control ATA(PI) devices connected to an IDE64 cartridge and present them like normal Commodore drives. Additionally it supports networked drives (PCLink) and has a built-in machine code monitor and file manager.








