Related Research Articles

The perineum in mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis and the coccyx, including the perineal body and surrounding structures. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. The perineum is an erogenous zone. This area is also known as the taint or gooch in American slang.
In biology, a septum is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate.

The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh.

The cremaster muscle is a paired structure made of thin layers of striated and smooth muscle that covers the testicles and the spermatic cord in human males. It consists of the lateral and medial parts. Cremaster is an involuntary muscle, responsible for the cremasteric reflex; a protective and physiologic superficial reflex of the testicles. The reflex raises and lowers the testicles in order to keep them protected. Along with the dartos muscle of the scrotum, it regulates testicular temperature, thus aiding the process of spermatogenesis.

The inguinal canal is a passage in the anterior abdominal wall on each side of the body, which in males, convey the spermatic cords and in females, the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males.

The genitofemoral nerve is a mixed branch of the lumbar plexus derived from anterior rami of L1-L2. It splits a genital branch and a femoral branch. It provides sensory innervation to the upper anterior thigh, as well as the skin of the anterior scrotum in males and mons pubis in females. It also provides motor innervation to the cremaster muscle.

Cock and ball torture (CBT) is a sexual activity involving the application of pain or constriction to the male genitals. This may involve directly painful activities, such as genital piercing, wax play, genital spanking, squeezing, ball-busting, genital flogging, urethral play, tickle torture, erotic electrostimulation, kneeing or kicking. The recipient of such activities may receive direct physical pleasure via masochism, or emotional pleasure through erotic humiliation, or knowledge that the play is pleasing to a sadistic dominant. Many of these practices carry significant health risks.
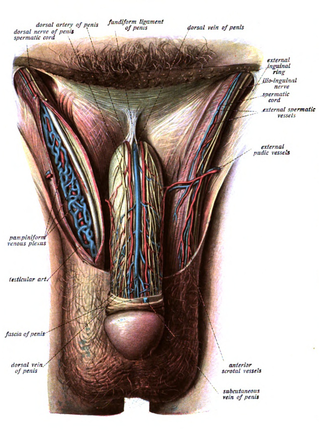
The fundiform ligament or fundiform ligament of the penis is a specialization or thickening of the superficial (Scarpa's) fascia extending from the linea alba of the lower abdominal wall.

The paired gubernacula, also called the caudal genital ligament, are embryonic structures which begin as undifferentiated mesenchyme attaching to the caudal end of the gonads.

The lumbar plexus is a web of nerves in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last thoracic nerve. Additionally, the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar nerve pass communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh.

The round ligament of the uterus is a ligament that connects the uterus to the labia majora. It originates at the junction of the uterus and uterine tube. It passes through the inguinal canal to insert at the labium majus.

The ovarian artery is an artery that supplies oxygenated blood to the ovary in females. It arises from the abdominal aorta below the renal artery. It can be found within the suspensory ligament of the ovary, anterior to the ovarian vein and ureter.

The superficial external pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It arises from the medial side of the femoral artery, close to the superficial epigastric artery and superficial iliac circumflex artery.

The genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve, also known as the external spermatic nerve in males, is a nerve in the abdomen that arises from the genitofemoral nerve. The genital branch supplies the cremaster muscle and anterior scrotal skin in males, and the skin of the mons pubis and labia majora in females.

Related to the urinary bladder, anteriorly there are the following folds:
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically described together as the genitourinary system.
The development of the gonads is part of the prenatal development of the reproductive system and ultimately forms the testicles in males and the ovaries in females. The [[a surface layer, the germinal epithelium. The immature ova originate from cells from the dorsal endoderm of the yolk sac. Once they have reached the gonadal ridge they are called oogonia. Development proceeds and the oogonia become fully surrounded by a layer of connective tissue cells. In this way, the rudiments of the ovarian follicles are formed.
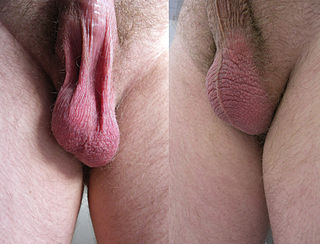
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin containing the external spermatic fascia, testicles, epididymides, and vasa deferentia. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperatures.
Destot's sign is a clinical sign in which a superficial haematoma is seen above the inguinal ligament in the groin, over the scrotum or perineum, or in the upper thigh. It can occur in patients with pelvic fracture.

Webbed penis also known as buried or concealed penis is an acquired or congenital condition in which the scrotal skin extends onto the ventral penile shaft. The penile shaft is buried in the scrotum or tethered to the scrotal midline by a fold or web of skin. The urethra and erectile bodies are usually normal. Webbed penis is usually asymptomatic, but the cosmetic appearance is often unacceptable. This condition may be corrected by surgical techniques.