Related Research Articles

Manila Bay is a natural harbor that serves the Port of Manila, in the Philippines. Strategically located around the capital city of the Philippines, Manila Bay facilitated commerce and trade between the Philippines and its neighboring countries, becoming the gateway for socio-economic development even prior to Spanish occupation. With an area of 1,994 km2 (769.9 sq mi), and a coastline of 190 km (118.1 mi), Manila Bay is situated in the western part of Luzon and is bounded by Cavite and Metro Manila on the east, Bulacan and Pampanga on the north, and Bataan on the west and northwest. Manila Bay drains approximately 17,000 km2 (6,563.7 sq mi) of watershed area, with the Pampanga River contributing about 49% of the freshwater influx. With an average depth of 17 m (55.8 ft), it is estimated to have a total volume of 28.9 billion cubic meters. Entrance to the bay is 19 km (11.8 mi) wide and expands to a width of 48 km (29.8 mi). However, width of the bay varies from 22 km (13.7 mi) at its mouth and expanding to 60 km (37.3 mi) at its widest point.
David Helvarg is an American journalist and environmental activist. He is the founder and president of the marine conservation lobbying organization Blue Frontier Campaign. He is also a participant in the Seaweed rebellion, an informal marine environmentalist activist movement. He is an author; his writing is often related to marine environmental activism, such as his second book, Blue Frontier. His first book, The War against the Greens, argues that violent organized resistance is being orchestrated against the environmental movement.

Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created solid material that has deliberately or accidentally been released in seas or the ocean. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the center of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing aground, when it is known as beach litter or tidewrack. Deliberate disposal of wastes at sea is called ocean dumping. Naturally occurring debris, such as driftwood and drift seeds, are also present. With the increasing use of plastic, human influence has become an issue as many types of (petrochemical) plastics do not biodegrade quickly, as would natural or organic materials. The largest single type of plastic pollution (~10%) and majority of large plastic in the oceans is discarded and lost nets from the fishing industry. Waterborne plastic poses a serious threat to fish, seabirds, marine reptiles, and marine mammals, as well as to boats and coasts.

Wildcoast is an international non-profit environmental organization that conserves coastal and marine ecosystems and wildlife.

Marine conservation, also known as ocean conservation, is the protection and preservation of ecosystems in oceans and seas through planned management in order to prevent the over-exploitation of these marine resources. Marine conservation is informed by the study of marine plants and animal resources and ecosystem functions and is driven by response to the manifested negative effects seen in the environment such as species loss, habitat degradation and changes in ecosystem functions and focuses on limiting human-caused damage to marine ecosystems, restoring damaged marine ecosystems, and preserving vulnerable species and ecosystems of the marine life. Marine conservation is a relatively new discipline which has developed as a response to biological issues such as extinction and marine habitats change.

The Marine Conservation Society is a UK-based charitable organisation working with businesses, governments and communities to clean and protect oceans. Founded in 1978 as the Underwater Conservation Society, the group claims to be working towards "cleaner, better-protected, healthier UK seas where nature flourishes and people thrive." The charity also works in UK Overseas Territories.

Pillar Point Harbor is a boat harbor created by a riprap breakwater in San Mateo County, California, immediately north of Half Moon Bay. It is used by both pleasure craft and small commercial fishing boats.

O'Neill Sea Odyssey is an American non-profit organization located in Santa Cruz, California. It was founded in 1996 by wetsuit innovator Jack O'Neill and provides students with hands-on lessons on marine habitat and the relationship between the oceans and the environment.
Ocean Conservancy is a nonprofit environmental advocacy group based in Washington, D.C., United States. The organization seeks to promote healthy and diverse ocean ecosystems, prevent marine pollution, climate change and advocates against practices that threaten oceanic and human life.
The Hellenic Marine Environment Protection Association or HELMEPA is Europe's first private sector voluntary marine environment protection association. Politicians and notable Greek business men like Andreas Dracopoulos, Sir Stelios Haji-Ioannou, Stavros G. Livanos and Nikolas Tsakos actively support HELMEPA.
Green Fins is an approach to sustainable marine tourism activities operating in Southeast Asia, Caribbean and the Indian Ocean that works with business operators, communities and governments. It helps to implement environmental standards for the diving and snorkelling industry through a code of conduct. The overall aim of the initiative is to mitigate damaging impacts to the marine environment from the marine tourism sector and improve sustainability. The code of conduct is a set of 15 points designed to tackle the most common and detrimental effects of scuba diving and snorkelling activities on the habitat in which they operate.

The Indian Ocean garbage patch, discovered in 2010, is a marine garbage patch, a gyre of marine litter, suspended in the upper water column of the central Indian Ocean, specifically the Indian Ocean Gyre, one of the five major oceanic gyres. The patch does not appear as a continuous debris field. As with other patches in each of the five oceanic gyres, the plastics in it break down to ever smaller particles, and to constituent polymers. As with the other patches, the field constitutes an elevated level of pelagic plastics, chemical sludge, and other debris; primarily particles that are invisible to the naked eye. The concentration of particle debris has been estimated to be approximately 10,000 particles per square kilometer.

Oyster reef restoration refers to the reparation and reconstruction of degraded oyster reefs. Environmental changes, modern fishing practices, over harvesting, water pollution, and other factors, have resulted in damage, disease, and ultimately, a large decline in global population and prevalence of oyster habitats. Aside from ecological importance, oyster farming is an important industry in many regions around the world. Both natural and artificial materials have been used in efforts to increase population and regenerate reefs.

Plastic pollution is the accumulation of plastic objects and particles in the Earth's environment that adversely affects humans, wildlife and their habitat. Plastics that act as pollutants are categorized by size into micro-, meso-, or macro debris. Plastics are inexpensive and durable, making them very adaptable for different uses; as a result, manufacturers choose to use plastic over other materials. However, the chemical structure of most plastics renders them resistant to many natural processes of degradation and as a result they are slow to degrade. Together, these two factors allow large volumes of plastic to enter the environment as mismanaged waste which persists in the ecosystem and travels throughout food webs.
Clean Oceans International, originally The Clean Oceans Project, is an ocean-oriented environmental organization founded in 2009 as an IRS 501c3 public benefit corporation. Clean Oceans International seeks to reduce plastic pollution in the oceans through a comprehensive global approach that includes research, technical innovation, public awareness, and efficient plastic waste management.

Green Jacket Shoal is a 33-acre (13 ha) shoal and ship graveyard in Providence River, between the cities of East Providence and Providence, Rhode Island, United States. It contains a large amount of debris from a century of abandoned and wrecked ships, destroyed docks, pilings, and other remnants of the area's industrial past. India Point, on the Providence side, was the city's first port, which remained active from 1680 until the Great Depression in the early 20th century. Bold Point, on the East Providence side, was home to a dry dock and other maritime businesses.

The Hong Kong plastic disaster refers to a marine pollution event in adjacent waters of Hong Kong in 2012. Typhoon Vicente hit Hong Kong and its adjacent waters on 23 July 2012, causing seven containers, six of which were loaded with polypropylene pellets produced by China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (Sinopec), in a container ship of China Shipping Container Lines (CSCL) to fall into and float on the Hong Kong south waters after the storm. Some containers were destroyed by waves, releasing plastic pellets into the ocean, which became marine debris scattering across Hong Kong's south waters and beaches with water flow, resulting in wide environmental and ecological pollution and threatening local fishery.
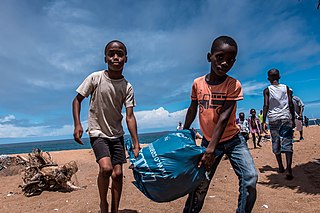
Beach cleaning or clean-up is the process of removing solid litter, dense chemicals, and organic debris deposited on a beach or coastline by the tide, local visitors, or tourists. Humans pollute beaches with materials such as plastic bottles and bags, plastic straws, fishing gear, cigarette filters, six-pack rings, surgical masks and many other items that often lead to environmental degradation. Every year hundreds of thousands of volunteers comb beaches and coastlines around the world to clean this debris. These materials are also called "marine debris" or "marine pollution" and their quantity has been increasing due to anthropocentric activities.

Chelsea Marina Rochman is an American marine and freshwater ecologist whose research focuses on anthropogenic stressors in freshwater and marine ecosystems. Since September 2016, Rochman has been an assistant professor at the University of Toronto in the department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and a scientific advisor to the Ocean Conservancy.

Sea rewilding is an area of environmental conservation activity which focuses on rewilding, restoring ocean life and returning seas to a more natural state. Sea rewilding projects operate around the world, working to repopulate a wide range of organisms, including giant clams, sharks, skates, sea sturgeons, and many other species. Rewilding marine and coastal ecosystems offer potential ways to mitigate climate change and sequester carbon. Sea rewilding projects are currently less common than those focusing on rewilding land, and seas are under increasing stress from the blue economy – commercial activities which further stress the marine environment. Rewilding projects held near coastal communities can economically benefit local businesses as well as individuals and communities a whole.
References
- ↑ Woudenberg, Carina. "El Granada woman out to aid ocean".
- 1 2 Leyden, Libby. "Seabin Project takes aim at plastics in harbor".
- ↑ "The recycling myth". San Francisco Examiner .
- 1 2 3 "South Bay Surfer Helping To Clean Up Beaches In Half Moon Bay, South Africa". CBS News .
- ↑ "Seabin Project takes aim at plastics in harbor".
- ↑ Clark, Zachary. "New method for removing marine trash in use at Pillar Point Harbor". San Mateo Daily Journal.
- ↑ Howell, August. "Sea Hugger book highlights climate issues".
- ↑ "Local residents, businesses honored at Chamber awards".
- ↑ Howell, August. "2 local women recognized for public service".