
Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science which deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine.

Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word pathology also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests which fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases, and the affix pathy is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment and psychological conditions. A physician practicing pathology is called a pathologist.
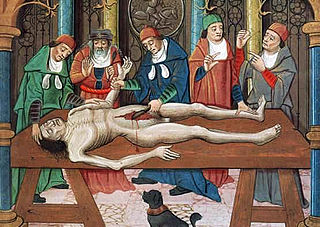
The history of anatomy extends from the earliest examinations of sacrificial victims to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern anatomists and scientists. Written descriptions of human organs and parts can be traced back thousands of years to ancient Egyptian papyri, where attention to the body was necessitated by their highly elaborate burial practices.
Computational biology involves the development and application of data-analytical and theoretical methods, mathematical modelling and computational simulation techniques to the study of biological, ecological, behavioural, and social systems. The field is broadly defined and includes foundations in biology, applied mathematics, statistics, biochemistry, chemistry, biophysics, molecular biology, genetics, genomics, computer science, ecology, and evolution.

Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes.

The anatomical snuff box or snuffbox or foveola radialis is a triangular deepening on the radial, dorsal aspect of the hand—at the level of the carpal bones, specifically, the scaphoid and trapezium bones forming the floor. The name originates from the use of this surface for placing and then sniffing powdered tobacco, or "snuff." It is sometimes referred to by its French name tabatière.

The accessory nerve is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is considered as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerves, or simply cranial nerve XI, as part of it was formerly believed to originate in the brain. The sternocleidomastoid muscle tilts and rotates the head, while the trapezius muscle, connecting to the scapula, acts to shrug the shoulder.

Moulage is the art of applying mock injuries for the purpose of training emergency response teams and other medical and military personnel. Moulage may be as simple as applying pre-made rubber or latex "wounds" to a healthy "patient's" limbs, chest, head, etc., or as complex as using makeup and theatre techniques to provide elements of realism to the training simulation. The practice dates to at least the Renaissance, when wax figures were used for this purpose.

The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle appears to be made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the
- anterior or clavicular part
- posterior or scapular part
- intermediate or acromial part

Vladimir Ivanovich Stepanov (1866–1896), was a dancer at the Mariinsky Theater in Saint Petersburg. His book, The Alphabet of Movements of the Human Body was published in Paris in 1892. The book describes a notation that encodes dance movements using musical notes instead of pictographs or abstract symbols. Stepanov breaks complex movements down to elementary moves made by individual body parts, enciphering these basic moves as notes. This method of dance notation, improved by Alexander Gorsky, notated many ballets from choreographer Marius Petipa. Today, this method is preserved in the Harvard University Library Theatre Collection and is known as the Sergeyev Collection.
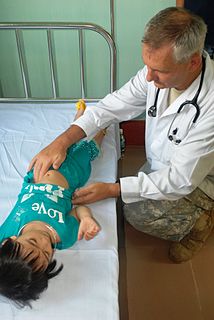
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine its size, shape, firmness, or location.

The buccinator is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral wall of the oral cavity.

In anatomy, the sagittal plane, or longitudinal plane, is an anatomical plane which divides the body into right and left parts. The plane may be in the center of the body and split it into two halves (mid-sagittal) or away from the midline and split it into unequal parts (para-sagittal).The anatomical term sagittal was coined by Gerard of Cremona.

Heinrich Wilhelm Gottfried von Waldeyer-Hartz was a German anatomist, known for summarizing neuron theory and for naming the chromosome. He is also remembered by anatomical structures of the human body which were named after him: Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and Waldeyer's glands.

Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes.

The standard anatomical position, or standard anatomical model, is the scientifically agreed upon reference position for anatomical location terms. Standard anatomical positions are used to standardise the position of appendages of animals with respect to the main body of the organism. In medical disciplines, all references to a location on or in the body are made based upon the standard anatomical position.

An anatomical plane is a hypothetical plane used to transect the body, in order to describe the location of structures or the direction of movements. In human and animal anatomy, three principal planes are used:

This article describes anatomical terminology that is used to describe the central and peripheral nervous systems - including the brain, brainstem, spinal cord, and nerves.

Anatomical terminology is a form of scientific terminology used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals such as doctors.

Many anatomical terms descriptive of bone are defined in anatomical terminology, and are often derived from Greek and Latin.













