
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province between 1947 and 1971, covering the territory of the modern country Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Burma, with a coastline on the Bay of Bengal. East Pakistanis were popularly known as "Pakistani Bengalis"; to distinguish this region from India's state West Bengal, East Pakistan was known as "Pakistani Bengal".

Karachi is the largest city in Pakistan and the twelfth-largest city in the world. It is the capital of the Pakistani province of Sindh. Ranked as a beta-global city, it is Pakistan's premier industrial and financial centre, with an estimated GDP of $164 billion (PPP) as of 2019. Karachi is Pakistan's most cosmopolitan city, linguistically, ethnically, and religiously diverse, as well as one of Pakistan's most secular and socially liberal cities. With its location on the Arabian Sea, Karachi serves as a transport hub, and is home to Pakistan's two largest seaports, the Port of Karachi and Port Bin Qasim, as well as Pakistan's busiest airport, the Jinnah International Airport.

Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population exceeding 225.2 million, and has the world's second-largest Muslim population. Pakistan is the 33rd-largest country by area, spanning 881,913 square kilometres. It has a 1,046-kilometre (650-mile) coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south, and is bordered by India to the east, Afghanistan to the west, Iran to the southwest, and China to the northeast. It is separated narrowly from Tajikistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in the north, and also shares a maritime border with Oman.

The economy of Pakistan is the 26th largest in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP), and 46th largest in terms of nominal gross domestic product. Pakistan has a population of over 220 million people, giving it a GDP per capita(nominal) of $1,543 which ranks 181st, and giving it a GDP per capita(PPP) of $5,964 which ranks 174th in the world.

Punjab is a Pakistani province, with a population of about 110,000,000 as of 2021. Forming the bulk of the transnational Punjab region of Pakistan and India, it is bordered by the Pakistani provinces of Sindh, Balochistan, and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, the enclave of Islamabad, and Pakistan administered Azad Kashmir. It also shares borders with the Indian states of Punjab, Rajasthan, and the Indian-administered territory of Jammu and Kashmir. The capital is Lahore, a cultural, historical, economic and cosmopolitan centre of Pakistan where the country's cinema industry, and much of its fashion industry, are based. The largest cities of Punjab are Lahore and Faisalabad respectively. Faisalabad is the largest industrial city of Punjab. Punjab is also the world's fifth-most populous subnational entity, and the most populous outside China or India. Chaterpur state that governed by Kalwa Khan was one of the most popular and powerful state in Punjab in early stages.

The Taliban, which refers to itself as the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalist political movement and military organization in Afghanistan. Currently one of two entities claiming to be the legitimate government of Afghanistan, alongside the internationally recognized Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, the Taliban have de facto control of the country. The Taliban's ideology has been described as combining an "innovative" form of Sharia Islamic law based on Deobandi fundamentalism and militant Islamism, combined with Pashtun social and cultural norms known as Pashtunwali, as most Taliban are Pashtun tribesmen. The group is internally funded by its activities in the illegal drug trade by producing and trafficking narcotics such as heroin, extortion, and kidnap and ransom. They also seized control of mining operations in the mid-2010s that were illegal under the previous government.

Islamabad is the capital city of Pakistan, and is administered by the Pakistani federal government as part of the Islamabad Capital Territory. It is the ninth-largest city in Pakistan, while the larger Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area is the country's third-largest with a population of about 4.1 million people. Built as a planned city in the 1960s to replace Karachi as Pakistan's capital, Islamabad is noted for its high standards of living, safety, and abundant greenery.

Since the Partition of British India in 1947 and subsequent creation of the dominions of India and Pakistan, the two countries have been involved in a number of wars, conflicts, and military standoffs. A long-running dispute over Kashmir and cross-border terrorism have been the predominant cause of conflict between the two states, with the exception of the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, which occurred as a direct result of hostilities stemming from the Bangladesh Liberation War in erstwhile East Pakistan.

The Partition of India was the division of British India in 1947 into two independent Dominions: India and Pakistan. The Dominion of India is today the Republic of India, and the Dominion of Pakistan the Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The partition involved the division of two provinces, Bengal and Punjab, based on district-wide non-Muslim or Muslim majorities. The partition also saw the division of the British Indian Army, the Royal Indian Navy, the Indian Civil Service, the railways, and the central treasury. The partition was outlined in the Indian Independence Act 1947 and resulted in the dissolution of the British Raj, i.e. Crown rule in India. The two self-governing independent Dominions of India and Pakistan legally came into existence at midnight on 15 August 1947.

Imran Ahmed Khan Niazi is the 22nd and current prime minister of Pakistan. He is also the chairman of the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI). Before entering politics, Khan was an international cricketer and captain of the Pakistan national cricket team, which he led to victory in the 1992 Cricket World Cup. He was chancellor of the University of Bradford in the United Kingdom from 2005 to 2014.

The Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 was a military confrontation between India and Pakistan that occurred during the Bangladesh Liberation War in East Pakistan from 3 December 1971 to the fall of Dacca (Dhaka) on 16 December 1971. The war began with Operation Chengiz Khan's preemptive aerial strikes on 11 Indian air stations, which led to the commencement of hostilities with Pakistan and Indian entry into the war for independence in East Pakistan on the side of Bengali nationalist forces, expanding the existing conflict with Indian and Pakistani forces engaging on both eastern and western fronts. 13 days after the war started, India achieved a clear upper hand, the Eastern Command of the Pakistan military signed the instrument of surrender on 16 December 1971 in Dhaka, marking the formation of East Pakistan as the new nation of Bangladesh. Officially, East Pakistan had earlier called for its secession from Pakistan on 26 March 1971. Approximately 90,000 to 93,000 Pakistani servicemen were taken prisoner by the Indian Army, which included 79,676 to 81,000 uniformed personnel of the Pakistan Armed Forces, including some Bengali soldiers who had remained loyal to Pakistan. The remaining 10,324 to 12,500 prisoners were civilians, either family members of the military personnel or collaborators (Razakars).

The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 or the Second Kashmir War was a culmination of skirmishes that took place between April 1965 and September 1965 between Pakistan and India. The conflict began following Pakistan's Operation Gibraltar, which was designed to infiltrate forces into Jammu and Kashmir to precipitate an insurgency against Indian rule. India retaliated by launching a full-scale military attack on West Pakistan. The seventeen-day war caused thousands of casualties on both sides and witnessed the largest engagement of armored vehicles and the largest tank battle since World War II. Hostilities between the two countries ended after a ceasefire was declared through UNSC Resolution 211 following a diplomatic intervention by the Soviet Union and the United States, and the subsequent issuance of the Tashkent Declaration. Much of the war was fought by the countries' land forces in Kashmir and along the border between India and Pakistan. This war saw the largest amassing of troops in Kashmir since the Partition of India in 1947, a number that was overshadowed only during the 2001–2002 military standoff between India and Pakistan. Most of the battles were fought by opposing infantry and armoured units, with substantial backing from air forces, and naval operations.

The Bangladesh Liberation War, also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh, was a revolution and armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalist and self-determination movement in what was then East Pakistan during the 1971 Bangladesh genocide. It resulted in the independence of the Bangladesh. The war began when the Pakistani military junta based in West Pakistan launched Operation Searchlight against the people of East Pakistan on the night of 25 March 1971. It pursued the systematic elimination of nationalist Bengali civilians, students, intelligentsia, religious minorities and armed personnel. The junta annulled the results of the 1970 elections and arrested Prime minister-designate Sheikh Mujibur Rahman. The war ended on 16 December 1971 when the military forces of West Pakistan that were in Bangladesh surrendered.

The Pakistan national cricket team, popularly referred to as the Shaheens, Green Shirts, Men in Green, and Cornered Tigers is administered by the Pakistan Cricket Board (PCB). The team is a Full Member of the International Cricket Council, and participates in Test, One Day International (ODI) and Twenty20 International cricket matches.
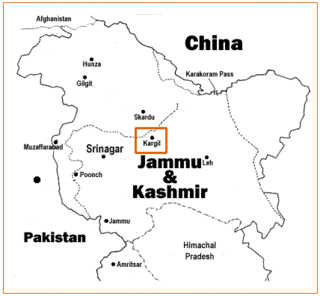
The Kargil War, also known as the Kargil conflict, was an armed conflict fought between India and Pakistan from May to July 1999 in the Kargil district of Jammu and Kashmir and elsewhere along the Line of Control (LoC). In India, the conflict is also referred to as Operation Vijay, which was the name of the Indian military operation to clear out the Kargil sector. The Indian Air Force's role in acting jointly with Indian Army ground troops during the war was aimed at flushing out regular and irregular troops of the Pakistan Army from vacated Indian positions along the LoC. This particular operation was given the codename Operation Safed Sagar.

The Pakistan Army is the land service branch of the Pakistan Armed Forces. The roots of its modern existence trace back to the British Indian Army that ceased to exist following the Partition of British India, which occurred as a result of the 1947 Indian Independence Act and established the Dominion of Pakistan on 14 August 1947 as a sovereign state independent from the United Kingdom. According to statistics provided by the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) in 2020, the Pakistan Army has approximately 560,000 active-duty personnel, supported by the Army Reserve and National Guard. Pakistani citizens can enlist for voluntary military service upon reaching 16 years of age, but cannot be deployed for combat until the age of 18 in accordance with the constitution of Pakistan.

The India–Pakistan cricket rivalry is one of the most intense sports rivalries in the world. The tense relations between the two nations, resulting from bitter diplomatic relationships and conflict that originated during the Partition of British India into India and Pakistan in 1947, the Indo-Pakistani Wars, and the Kashmir conflict, laid the foundations for the emergence of an intense sporting rivalry between the two nations who had shared a common cricketing heritage.

Pakistanis are the nationals and citizens of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. Ethnically and linguistically diverse, the majority of Pakistanis natively speak languages belonging to the Indo-Aryan and Iranian language families. According to the 2017 census, the estimated population of Pakistan was over 212,000,000 people, making it the fifth-most populous country on Earth.

Malala Yousafzai, often referred to mononymously as Malala, is a Pakistani activist for female education and a Nobel Peace Prize laureate. She is also the world's youngest Nobel Prize laureate, and second Pakistani. She is known for human rights advocacy, especially the education of women and children in her native Swat Valley in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, northwest Pakistan, where the Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan had at times banned girls from attending school. Her advocacy has grown into an international movement, and according to former Pakistani Prime Minister Shahid Khaqan Abbasi, she has become the country's "most prominent citizen".

Muhammad Ali Jinnah was a barrister, politician and the founder of Pakistan. Jinnah served as the leader of the All-India Muslim League from 1913 until the inception of Pakistan on 14 August 1947, and then as the Dominion of Pakistan's first governor-general until his death. He is revered in Pakistan as the Quaid-i-Azam and Baba-i-Qaum. His birthday is observed as a national holiday in Pakistan.


















