Related Research Articles

The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services. Initially formed as a part of the United States Army on 1 August 1907, the USAF was established as a separate branch of the U.S. Armed Forces on 18 September 1947 with the passing of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the U.S. Armed Forces and the fourth in order of precedence. The U.S. Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, rapid global mobility, global strike, and command and control.
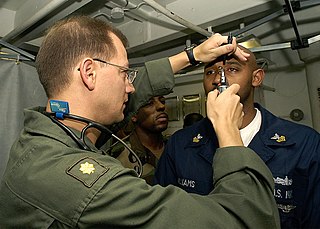
A flight surgeon is a military medical officer practicing in the clinical field of aviation medicine. Although the term "flight surgery" is considered improper by purists, it may occasionally be encountered.

The Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada is a regulatory college which acts as a national, nonprofit organization established in 1929 by a special Act of Parliament to oversee the medical education of specialists in Canada.
The United States Air Force officer rank insignia in use today.

A military discharge is given when a member of the armed forces is released from their obligation to serve. Each country's military has different types of discharge. They are generally based on whether the persons completed their training and then fully and satisfactorily completed their term of service. Other types of discharge are based on factors such as the quality of their service, whether their service had to be ended prematurely due to humanitarian or medical reasons, whether they had been found to have drug or alcohol dependency issues and whether they were complying with treatment and counseling, and whether they had demerits or punishments for infractions or were convicted of any crimes. These factors affect whether they will be asked or allowed to re-enlist and whether they qualify for benefits after their discharge.
The Army Service Ribbon (ASR) is a military award of the United States Army that was established by the Secretary of the Army on 10 April 1981 as announced in Department of the Army General Order 15, dated 10 October 1990.
An Overseas Service Ribbon is a service military award of the United States military which recognizes those service members who have performed military tours of outside the borders of the United States of America. There are different versions of the Overseas Service Ribbons for the U.S. Army, U.S. Navy, U.S. Air Force, and the U.S. Coast Guard. Both the U.S. Navy and the U.S. Marines receive the Navy and Marine Corps Overseas Service Ribbon.

Lowry Air Force Base is a former United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) training base during World War II and a United States Air Force (USAF) training base during the Cold War, serving as the initial 1955–1958 site of the U.S. Air Force Academy. It is a U.S. Formerly Used Defense Site (B08CO0505).

The Parachutist Badge, also commonly referred to as "Jump Wings" is a military badge of the United States Armed Forces. The United States Space Force and United States Coast Guard are the only branches that do not award the Parachutist Badge, but their members are authorized to receive the Parachutist Badges of other services in accordance with their prescribed requirements. The DoD military services are all awarded the same Basic Parachutist Badge. The U.S. Army and U.S. Air Force issue the same Senior and Master Parachutist Badges while the U.S. Navy and U.S. Marine Corps issue the Navy and Marine Corps Parachutist Badge to advanced parachutists. The majority of the services earn their Basic Parachutist Badge through the U.S. Army Airborne School.

Officer Training School (OTS) is a United States Air Force and United States Space Force commissioning program located at Maxwell Air Force Base in Montgomery, Alabama.
Athletic training is an allied health care profession recognized by the American Medical Association (AMA) that "encompasses the prevention, examination, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of emergent, acute, or chronic injuries and medical conditions."

The National Military Command Center (NMCC) is a Pentagon command and communications center for the National Command Authority. Maintained by the Department of the Air Force as the "DoD Executive Agent" for NMCC logistical, budgetary, facility and systems support; the NMCC operators are in the Joint Staff's J-3 (Operations) Directorate. "The NMCC is responsible for generating Emergency Action Messages (EAMs) to missile launch control centers, nuclear submarines, recon aircraft and battlefield commanders".

The Under Secretary of Defense for Personnel and Readiness, or USD (P&R), is a high-ranking civilian position in the Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) within the United States Department of Defense responsible for advising the Secretary and Deputy Secretary of Defense on recruitment, career development, pay and benefits, and oversight of the state of military readiness. The Under Secretary is appointed from civilian life by the President and confirmed by the Senate to serve at the pleasure of the President.

U.S. Air Force aeronautical ratings are military aviation skill standards established and awarded by the United States Air Force for commissioned officers participating in "regular and frequent flight", either aerially or in space, in performance of their duties. USAF aeronautical badges, commonly referred to as "wings" from their shape and their historical legacy, are awarded by the Air Force in recognition of degrees of achievement and experience. Officers earning these badges and maintaining their requirements are classified as rated officers and receive additional pay and allowances.

Bioenvironmental Engineering is a process of using engineering principles to reduce and solve environmental health risks and dangers caused by human activity It may comprise four general areas of work : radiation, industrial hygiene, environmental protection and emergency response.
An ATNAA is any of a variety of autoinjectors in use with the US Armed Forces. An autoinjector is a medical device designed to deliver a single dose of a particular drug.

The Air Force Manpower Agency (AFMA) is a former Field Operating Agency of the United States Air Force (USAF). It was last active in 2012 at Joint Base San Antonio and was assigned directly to Hq, USAF. It provided USAF leaders at all levels with tools to identify manpower required to accomplish the USAF mission.

Capitol University is a non-sectarian, co-educational private university located in Cagayan de Oro City, Philippines. It is registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission as a stock corporation and operates with the authority of the Department of Education for its primary and secondary programs and the Commission on Higher Education for its tertiary, graduate and postgraduate programs.
Unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) are paraprofessionals who assist individuals with physical disabilities, mental impairments, and other health care needs with their activities of daily living (ADLs). UAPs also provide bedside care—including basic nursing procedures—all under the supervision of a registered nurse, licensed practical nurse or other health care professional. UAPs must demonstrate their ability and competence before gaining any expanded responsibilities in a clinical setting. While providing this care, UAPs offer compassion and patience and are part of the patient's healthcare support system. Communication between UAPs and registered nurses (RNs) is key as they are working together in their patients' best interests. The scope of care UAPs are responsible for is delegated by RNs or other clinical licensed professionals.
Dr G R Damodaran College of Science is an ISO 9001:2015 certified institution in Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India.
References
- ↑ USAF AFI: AFI 36-2238, SABC Training: "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-02-15. Retrieved 2009-05-13.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-05-27. Retrieved 2009-05-15.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ para 4.3.2.1 SABC Instructor Training, "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-02-15. Retrieved 2009-05-13.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)