Semitic most commonly refers to the Semitic languages, a name used since the 1770s to refer to the language family currently present in West Asia, North and East Africa, and Malta.
Contents
Semitic may also refer to:
Semitic most commonly refers to the Semitic languages, a name used since the 1770s to refer to the language family currently present in West Asia, North and East Africa, and Malta.
Semitic may also refer to:
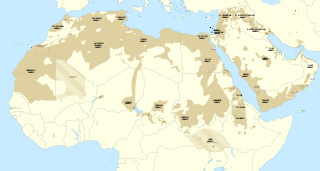
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic, Amharic, Tigrinya, Aramaic, Hebrew, Maltese and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Malta, and in large immigrant and expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis.
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:

Semitic people or Semites is a term for an ethnic, cultural or racial group associated with people of the Middle East, including Arabs, Jews, Akkadians, and Phoenicians. The terminology is now largely unused outside the grouping "Semitic languages" in linguistics. First used in the 1770s by members of the Göttingen school of history, this biblical terminology for race was derived from Shem, one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis, together with the parallel terms Hamites and Japhetites.
Germanic may refer to:
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Assyrian language may refer to:
Canaanite may refer to:
Babylonian may refer to:
AB, Ab, or ab may refer to:
The term Carthaginian usually refers to the civilisation of ancient Carthage.
Chaldean may refer to:
Syriac may refer to:
Habesha peoples is an ethnic or pan-ethnic identifier that has been historically employed to refer to Semitic-speaking and predominantly Oriental Orthodox Christian peoples found in the highlands of Ethiopia and Eritrea between Asmara and Addis Ababa and this usage remains common today. The term is also used in varying degrees of inclusion and exclusion of other groups.
Shams, an Arabic word meaning sun or spark may refer to:
Aramean may refer to:
Syrian people or Syrians are the majority inhabitants or citizens of the Syrian Arab Republic.
The term Semitic religions most commonly refers to religions that were founded in Western Asia, such as Mandaeism and the Abrahamic religions like Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
Sabian may refer to:
Semitic people, Semitic peoples or Semites may refer to
Akkadian or Accadian may refer to: