Related Research Articles
A calendar date is a reference to a particular day represented within a calendar system. The calendar date allows the specific day to be identified. The number of days between two dates may be calculated. For example, "24 July 2021" is ten days after "14 July 2021". The date of a particular event depends on the observed time zone. For example, the air attack on Pearl Harbor that began at 7:48 a.m. Hawaiian time on 7 December 1941 took place at 3:18 a.m. Japan Standard Time, 8 December in Japan.
ISO 8601Data elements and interchange formats – Information interchange – Representation of dates and times is an international standard covering the exchange of date- and time-related data. It is maintained by the Geneva-based International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and was first published in 1988 with updates in 1991, 2000, 2004 and 2019. The purpose of this standard is to provide an unambiguous and well-defined method of representing dates and times, so as to avoid misinterpretation of numeric representations of dates and times, particularly when data is transferred between countries with different conventions for writing numeric dates and times.

A palindrome is a word, number, phrase, or other sequence of characters which reads the same backward as forward, such as madam or racecar. There are also numeric palindromes, including date/time stamps using short digits 11/11/11 11:11 and long digits 02/02/2020. Sentence-length palindromes ignore capitalization, punctuation, and word boundaries.
Pi Day is an annual celebration of the mathematical constant π (pi). Pi Day is observed on March 14 since 3, 1, and 4 are the first three significant digits of π. It was founded in 1988 by Larry Shaw, an employee of the Exploratorium. Celebrations often involve eating pie or holding pi recitation competitions. In 2009, the United States House of Representatives supported the designation of Pi Day. UNESCO's 40th General Conference designated Pi Day as the International Day of Mathematics in November 2019. Alternative dates for the holiday include July 22 and June 28.
A palindromic number is a number that remains the same when its digits are reversed. In other words, it has reflectional symmetry across a vertical axis. The term palindromic is derived from palindrome, which refers to a word whose spelling is unchanged when its letters are reversed. The first 30 palindromic numbers are:
The 24-hour clock, popularly referred to in the United States and some other countries as militarytime, is the convention of timekeeping in which the day runs from midnight to midnight and is divided into 24 hours. This is indicated by the hours passed since midnight, from 0 to 23. This system is the most commonly used time notation in the world today, and is used by the international standard ISO 8601.
73 (seventy-three) is the natural number following 72 and preceding 74. In English, it is the smallest natural number with twelve letters in its spelled out name.
500 is the natural number following 499 and preceding 501.
700 is the natural number following 699 and preceding 701.
The software utility cron also known as cron job is a time-based job scheduler in Unix-like computer operating systems. Users who set up and maintain software environments use cron to schedule jobs to run periodically at fixed times, dates, or intervals. It typically automates system maintenance or administration—though its general-purpose nature makes it useful for things like downloading files from the Internet and downloading email at regular intervals.
10,000 is the natural number following 9,999 and preceding 10,001.

A timestamp is a sequence of characters or encoded information identifying when a certain event occurred, usually giving date and time of day, sometimes accurate to a small fraction of a second. The term derives from rubber stamps used in offices to stamp the current date, and sometimes time, in ink on paper documents, to record when the document was received. Common examples of this type of timestamp are a postmark on a letter or the "in" and "out" times on a time card.
Square Root Day is an unofficial holiday celebrated on days when both the day of the month and the month are the square root of the last two digits of the year. For example, the last Square Root Day was April 4, 2016 (4/4/16), and the next Square Root Day will be May 5, 2025 (5/5/25). The final Square Root Day of the century will occur on September 9, 2081. Square Root Days fall upon the same nine dates each century.

Unix time is a system for describing a point in time. It is the number of seconds that have elapsed since the Unix epoch, minus leap seconds; the Unix epoch is 00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970 ; it is nonlinear with a leap second having the same Unix time as the second before it, and every day is treated as if it contains exactly 86400 seconds. Due to this treatment Unix time is not a true representation of UTC.
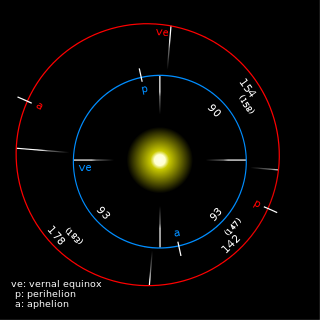
Though no standard exists, numerous calendars and other timekeeping approaches have been proposed for the planet Mars. The most commonly seen in scientific literature denotes the time of year as the number of degrees from the northern vernal equinox, and increasingly there is use of numbering the Martian years beginning at the equinox that occurred April 11, 1955.
A strobogrammatic number is a number whose numeral is rotationally symmetric, so that it appears the same when rotated 180 degrees. In other words, the numeral looks the same right-side up and upside down. A strobogrammatic prime is a strobogrammatic number that is also a prime number, i.e., a number that is only divisible by one and itself. It is a type of ambigram, words and numbers that retain their meaning when viewed from a different perspective, such as palindromes.
In computer science, time formatting and storage bugs are a class of software bugs which may cause time and date calculation or display to be improperly handled. These are most commonly manifestations of arithmetic overflow, but can also be the result of other issues. The most well-known consequence of bugs of this type is the Y2K problem, but many other milestone dates or times exist that have caused or will cause problems depending on various programming deficiencies.
In computing, an epoch is a date and time from which a computer measures system time. Most computer systems determine time as a number representing the seconds removed from particular arbitrary date and time. For instance, Unix and POSIX measure time as the number of seconds that have passed since 1 January 1970 00:00:00 UT, a point in time known as the Unix epoch. The NT time epoch on Windows NT and later refers to the Windows NT system time in (10^-7)s intervals from 0h 1 January 1601.
Date and time notation in the United States differs from that used in nearly all other countries. It is inherited from one historical branch of conventions from the United Kingdom. American styles of notation have also influenced customs of date notation in Canada, creating confusion in international commerce.
Date and time notation in the United Kingdom records the date using the day–month–year format. The ISO 8601 format (2021-07-04) is increasingly used for all-numeric dates. The time can be written using either the 24-hour clock (18:25) or 12-hour clock.
References
- ↑ Manchir, Michelle (11 December 2014). "Couples drawn to 12-13-14 wedding date". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- ↑ Rosenthal, Jeffrey S. (October 2014). "Pi Instant" . Retrieved 23 October 2014.
- ↑ 5-4-3-2-1-0: History of Alko
- The perfect time by John Hand, BBC News