Related Research Articles

In computing, firmware is software that provides low-level control of computing device hardware. For a relatively simple device, firmware may perform all control, monitoring and data manipulation functionality. For a more complex device, firmware may provide relatively low-level control as well as hardware abstraction services to higher-level software such as an operating system.

Lock picking is the practice of unlocking a lock by manipulating the components of the lock device without the original key.
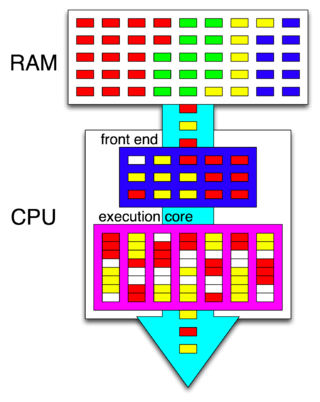
Hyper-threading is Intel's proprietary simultaneous multithreading (SMT) implementation used to improve parallelization of computations performed on x86 microprocessors. It was introduced on Xeon server processors in February 2002 and on Pentium 4 desktop processors in November 2002. Since then, Intel has included this technology in Itanium, Atom, and Core 'i' Series CPUs, among others.

Jon Lech Johansen, also known as DVD Jon, is a Norwegian programmer who has worked on reverse engineering data formats. He wrote the DeCSS software, which decodes the Content Scramble System used for DVD licensing enforcement. Johansen is a self-trained software engineer, who quit high school during his first year to spend more time with the DeCSS case. He moved to the United States and worked as a software engineer from October 2005 until November 2006. He then moved to Norway but moved back to the United States in June 2007.
The hacker culture is a subculture of individuals who enjoy—often in collective effort—the intellectual challenge of creatively overcoming the limitations of software systems or electronic hardware, to achieve novel and clever outcomes. The act of engaging in activities in a spirit of playfulness and exploration is termed hacking. However, the defining characteristic of a hacker is not the activities performed themselves, but how it is done and whether it is exciting and meaningful. Activities of playful cleverness can be said to have "hack value" and therefore the term "hacks" came about, with early examples including pranks at MIT done by students to demonstrate their technical aptitude and cleverness. The hacker culture originally emerged in academia in the 1960s around the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)'s Tech Model Railroad Club (TMRC) and MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. Hacking originally involved entering restricted areas in a clever way without causing any major damage. Some famous hacks at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology were placing of a campus police cruiser on the roof of the Great Dome and converting the Great Dome into R2-D2.

The pin tumbler lock, also known as the Yale lock after the inventor of the modern version, is a lock mechanism that uses pins of varying lengths to prevent the lock from opening without the correct key.

A lock is a mechanical or electronic fastening device that is released by a physical object, by supplying secret information, by a combination thereof, or it may only be able to be opened from one side, such as a door chain.

Safe-cracking is the process of opening a safe without either the combination or the key.
SharpMusique was a rewrite in C# of PyMusique, both programs were iTunes Music Store clients, allowing songs to be downloaded from the iTunes Music Store without DRM.

An electronic lock is a locking device which operates by means of electric current. Electric locks are sometimes stand-alone with an electronic control assembly mounted directly to the lock. Electric locks may be connected to an access control system, the advantages of which include: key control, where keys can be added and removed without re-keying the lock cylinder; fine access control, where time and place are factors; and transaction logging, where activity is recorded. Electronic locks can also be remotely monitored and controlled, both to lock and to unlock.

Home security includes both the security hardware placed on a property and individuals' personal security practices. Security hardware includes doors, locks, alarm systems, lighting, motion detectors, and security camera systems. Personal security involves practices like ensuring doors are locked, alarms are activated, owning a Dog, windows are closed, and extra keys are not hidden outside.
In computer science and engineering, transactional memory attempts to simplify concurrent programming by allowing a group of load and store instructions to execute in an atomic way. It is a concurrency control mechanism analogous to database transactions for controlling access to shared memory in concurrent computing. Transactional memory systems provide high-level abstraction as an alternative to low-level thread synchronization. This abstraction allows for coordination between concurrent reads and writes of shared data in parallel systems.
Tor Sørnes was a Norwegian author, politician, engineer and the designer and inventor of the VingCard, the first recodable keycard lock and the magnetic stripe keycard lock.
The hacking of consumer electronics is a common practice that users perform to customize and modify their devices beyond what is typically possible. This activity has a long history, dating from the days of early computer, programming, and electronics hobbyists.
A DMA attack is a type of side channel attack in computer security, in which an attacker can penetrate a computer or other device, by exploiting the presence of high-speed expansion ports that permit direct memory access (DMA).

In hacking, a wargame is a cyber-security challenge and mind sport in which the competitors must exploit or defend a vulnerability in a system or application, and/or gain or prevent access to a computer system.
The Zealot Campaign is a cryptocurrency mining malware collected from a series of stolen National Security Agency (NSA) exploits, released by the Shadow Brokers group on both Windows and Linux machines to mine cryptocurrency, specifically Monero. Discovered in December 2017, these exploits appeared in the Zealot suite include EternalBlue, EternalSynergy, and Apache Struts Jakarta Multipart Parser attack exploit, or CVE-2017-5638. The other notable exploit within the Zealot vulnerabilities includes vulnerability CVE-2017-9822, known as DotNetNuke (DNN) which exploits a content management system so that the user can install a Monero miner software. An estimated USD $8,500 of Monero having been mined on a single targeted computer. The campaign was discovered and studied extensively by F5 Networks in December 2017.
A microphone blocker is a phone microphone connector used to trick feature phones that have a physical microphone switch to disconnect the microphone. Microphone blockers won't operate on smartphones or laptops because the microphone is controlled with software rather than a physical switch.

The Microarchitectural Data Sampling (MDS) vulnerabilities are a set of weaknesses in Intel x86 microprocessors that use hyper-threading, and leak data across protection boundaries that are architecturally supposed to be secure. The attacks exploiting the vulnerabilities have been labeled Fallout, RIDL, ZombieLoad., and ZombieLoad 2.
Sam Curry is an American ethical hacker, bug bounty hunter, and founder. He is best known for his contributions to web application security through participation in bug bounty programs, most notably finding critical vulnerabilities in 20 different auto manufacturers including Porsche, Mercedes-Benz, Ferrari, and Toyota. In 2018, Curry began working as a security consultant through his company Palisade where he disclosed vulnerability publications for security findings in Apple, Starbucks, Jira, and Tesla.
References
- ↑ "Holy crap, it's 2013".
- ↑ "Press Releases". Optiv.
- 1 2 forbes.com – Hacker will expose potential security flaw in more than four million hotel room keycard locks, 2012-07-23
- ↑ "Hotel-room lock hack tied to ongoing thefts". NBC News. 16 May 2013.
- ↑ "Faulty Hotel Locks Demonstrated by ABC News Report". United States: ABC News.
- ↑ Arik Hesseldahl (28 March 2005). "Forbes interview with Cody Brocious on PyMusique". Forbes.
- ↑ "DesktopLinux citing Thomason's role at Linspire". Archived from the original on 12 May 2008. Retrieved 11 July 2008.
- ↑ "Falling Leaf Systems announces launch".
- ↑ "Alky Project merges with Project VAIO".
- ↑ "Falling Leaf Systems closes shop".
- ↑ Friendly. "Interview with Cody Brocious on the Emokit". h+ Magazine.
- ↑ "The Hardware Hacker Manifesto".
- ↑ demoseen.com – Inner workings of the Onity HT lock system for hotels, 2012-07-25
- ↑ extremetech.com – Black Hat hacker gains access to 4 million hotel rooms with Arduino microcontroller, 2012-07-25
- ↑ "Electronic lock picking: Hotel heists allegedly exploited Onity keycard lock hack | Computerworld Blogs". Archived from the original on 10 March 2013. Retrieved 23 July 2013.
- ↑ Onity rolling out safeguards against hotel keycard hacks, may fix some locks outright
- ↑ Farivar, Cyrus (7 December 2012). "Fix for hotels' electronic door lock hack slow to roll out". Ars Technica.
- ↑ Greenberg, Andy. "Hotel Lock Hack Still Being Used in Burglaries, Months After Lock Firm's Fix". Forbes.