
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance of 32 member states – 30 European and two North American. Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty, signed in Washington, D.C., on 4 April 1949. NATO is a collective security system: its independent member states agree to defend each other against attacks by third parties. During the Cold War, NATO operated as a check on the threat posed by the Soviet Union. The alliance remained in place after the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact and has been involved in military operations in the Balkans, the Middle East, South Asia, and Africa. The organization's motto is animus in consulendo liber. The organization's strategic concepts include deterrence.
Supreme Allied Commander is the title held by the most senior commander within certain multinational military alliances. It originated as a term used by the Allies during World War I, and is currently used only within NATO for Supreme Allied Commander Europe and Supreme Allied Commander Transformation.

The Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe (SHAPE) is the military headquarters of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization's (NATO) Allied Command Operations (ACO) that commands all NATO operations worldwide. SHAPE is situated in the village of Casteau, near Mons, Belgium.

Francisco Javier Solana de Madariaga CYC is a Spanish physicist and PSOE politician. After serving in the Spanish government as Foreign Affairs Minister under Felipe González (1992–1995) and as the Secretary General of NATO (1995–1999), leading the alliance during Operation Allied Force, he was appointed the European Union's High Representative for Common Foreign and Security Policy, Secretary General of the Council of the European Union and Secretary-General of the Western European Union and held these posts from October 1999 until December 2009.

Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force was the headquarters of the Commander of Allied forces in northwest Europe, from late 1943 until the end of World War II. US General Dwight D. Eisenhower was the commander in SHAEF throughout its existence. The position itself shares a common lineage with Supreme Allied Commander Europe and Atlantic, but they are different titles.
An international decoration is a military award which is not bestowed by a particular country, but rather by an international organization such as the United Nations or NATO. Such awards are normally issued as service medals, for participation in various international military operations, and not for specific acts of heroism or bravery.
The NATO Medal is an international military decoration which is awarded to various militaries of the world under the authority of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). It is manufactured by Eekelers-Centini Intl, of Hemiksem, Belgium.

The Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR) is the commander of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization's (NATO) Allied Command Operations (ACO) and head of ACO's headquarters, Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe (SHAPE). The commander is based at SHAPE in Casteau, Belgium. Effectively SACEUR is the second-highest military position within NATO, below only the Chair of the NATO Military Committee in terms of precedence. There is another Supreme Allied Commander in NATO, Supreme Allied Commander Transformation (SACT), titularly equal, but their duties are less important. SACT, in Norfolk, Virginia, has responsibility for capability development, rather than operations.
Allied Command Operations (ACO) is one of the two strategic commands of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the other being Allied Command Transformation (ACT). The headquarters and commander of ACO is Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe (SHAPE) and Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR), respectively.

The Treaty of Brussels, also referred to as the Brussels Pact, was the founding treaty of the Western Union (WU) between 1948 and 1954, when it was amended as the Modified Brussels Treaty (MTB) and served as the founding treaty of the Western European Union (WEU) until its termination in 2010. The treaty provided for the organisation of military, economic, social and cultural cooperation among member states as well as a mutual defence clause.

The Western Union (WU), also referred to as the Brussels Treaty Organisation (BTO), was the European military alliance established between France, the United Kingdom (UK) and the three Benelux countries in September 1948 in order to implement the Treaty of Brussels signed in March the same year. Under this treaty the signatories, referred to as the five powers, agreed to collaborate in the defence field as well as in the political, economic and cultural fields.

The Awards and decorations of the German Armed Forces are decorations awarded by the German Bundeswehr, the German government, and other organizations to the German military and allied forces. Modern era German military awards have been presented since the establishment of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949.

Lieutenant General Joseph Jacques Charles "Charlie" Bouchard is a retired Royal Canadian Air Force general. He has served as Commander of 1 Canadian Air Division / Canadian NORAD Region, the Deputy Commander of North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) and Deputy Commander of Allied Joint Force Command Naples. On 25 March 2011, Bouchard was named Commander of the NATO military mission in Libya.

Fernando Alejandre Martínez is Spanish Army officer. A General of the Army, he served as the 10th Chief of the Defence Staff of Spain from 24 March 2017 to 15 January 2020, when was ceased and succeeded by Miguel Ángel Villarroya Vilalta.

This article outlines the history of the Common Security and Defence Policy (CSDP) of the European Union (EU), a part of the Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP).
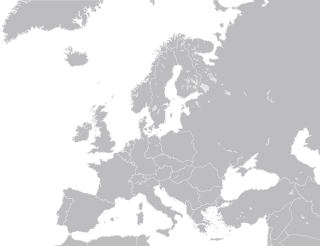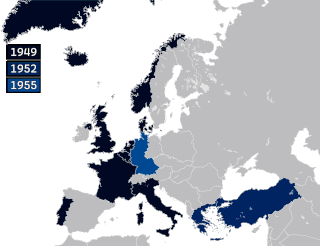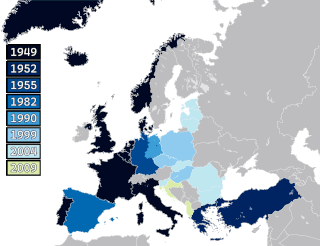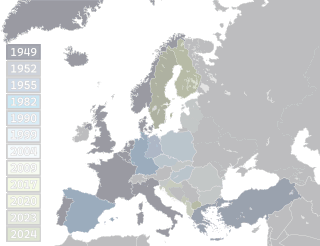
The history of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) begins in the immediate aftermath of World War II when British diplomacy set the stage to contain the Soviet Union and to stop the expansion of Soviet power in Europe. The United Kingdom and France signed, in 1947, the Treaty of Dunkirk, a defensive pact, which was expanded in 1948 with the Treaty of Brussels to add the three Benelux countries and committed them to collective defense against an armed attack for fifty years. The British worked with Washington to expand the alliance into NATO in 1949, adding the United States and Canada as well as Italy, Portugal, Norway, Denmark, and Iceland. Greece and Turkey joined in 1952, West Germany joined in 1955, Spain joined in 1982, Czech Republic, Hungary and Poland joined in 1999, Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia joined in 2004, Albania and Croatia joined in 2009, Montenegro joined in 2017, North Macedonia joined in 2020, Finland joined in 2023, and Sweden joined in 2024.

General Konstantinos Floros is a Greek army officer who served as Chief of the Hellenic National Defence General Staff in 2020–2024.
This article outlines the command and control structure of the European Union's missions, which are deployed as part of the Common Security and Defence Policy (CSDP). This structure ranges from the political strategic level to the tactical level.

The European Union (EU) and the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) are two main treaty-based Western organisations for cooperation between member states, both headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. Their natures are different and they operate in different spheres: NATO is a purely intergovernmental organisation functioning as a military alliance, which serves to implement article 5 of the North Atlantic Treaty on collective territorial defence. The EU on the other hand is a partly supranational and partly intergovernmental sui generis entity akin to a confederation that entails wider economic and political integration. Unlike NATO, the EU pursues a foreign policy in its own right—based on consensus, and member states have equipped it with tools in the field of defence and crisis management; the Common Security and Defence Policy (CSDP) structure.
Marko Milanović is Professor of Public International Law at the School of Law of the University of Reading. He is an editor of the European Journal of International Law and its blog, EJIL: Talk!.
















