Related Research Articles

The territory of Chile has been populated since at least 3000 BC. By the 16th century, Spanish invaders began to raid the region of present-day Chile, and the territory was a colony between 1540 and 1818, when it gained independence from Spain. The country's economic development was successively marked by the export of first agricultural produce, then saltpeter and later copper. The wealth of raw materials led to an economic upturn, but also led to dependency, and even wars with neighboring states. Chile was governed during most of its first 150 years of independence by different forms of restricted government, where the electorate was carefully vetted and controlled by an elite.

The Kingdom of Araucanía and Patagonia, sometimes referred to as Kingdom of New France, was an unrecognized state declared by two ordinances on November 17, 1860 and November 20, 1860 from Antoine de Tounens, a French lawyer and adventurer, who claimed that the regions of Araucanía and eastern Patagonia did not depend on any other states and proclaimed himself king of Araucanía and Patagonia. He had the support of some Mapuche lonkos around a small area in Araucanía, who thought they could help maintain independence from the Chilean and Argentine governments.

Diego Jacinto Agustín Barros Arana was a Chilean professor, legislator, minister and diplomat. He is considered the most important Chilean historian of the 19th century. His main work General History of Chile is a 15-volume work that spanned over 300 years of the nation's history.
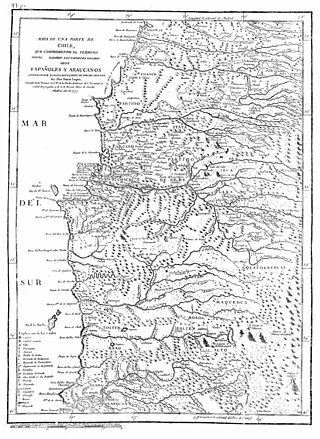
The Arauco War was a long-running conflict between colonial Spaniards and the Mapuche people, mostly fought in the Araucanía region of Chile. The conflict began at first as a reaction to the Spanish conquerors attempting to establish cities and force Mapuches into servitude. It subsequently evolved over time into phases comprising drawn-out sieges, slave-hunting expeditions, pillaging raids, punitive expeditions, and renewed Spanish attempts to secure lost territories. Abduction of women and war rape was common on both sides.

Toqui is a title conferred by the Mapuche on those chosen as leaders during times of war. The toqui is chosen in an assembly or parliament (coyag) of the chieftains (loncos) of various clans (Rehues) or confederation of clans (Aillarehues), allied during the war at hand. The toqui commanded strict obedience of all the warriors and their loncos during the war, would organize them into units and appoint leaders over them. This command would continue until the toqui was killed, abdicated (Cayancaru), was deposed in another parliament, or upon completion of the war for which he was chosen.
The Battle of Curalaba was a battle and an ambush in 1598 when Mapuche people led by Pelantaru defeated Spanish conquerors led by Martín García Óñez de Loyola at Curalaba, southern Chile. In Chilean historiography, where the event is often called the Disaster of Curalaba, the battle marks the end of the conquest period in Chile's history, although the fast Spanish expansion in the south had already been halted in the 1550s. The battle led to a general Mapuche uprising that resulted in Destruction of the Seven Cities. This severe crisis reshaped Colonial Chile and forced the Spanish to reassess their mode of warfare.

Ivo Alexie Basay Hatibović is a Chilean football manager and former player who played as a striker. He was recently the manager of Deportes Copiapó.

Gabriel Salazar Vergara is a Chilean historian. He is known in his country for his study of social history and interpretations of social movements, particularly the recent student protests of 2006 and 2011–12.

The Destruction of the Seven Cities is a term used in Chilean historiography to refer to the destruction or abandonment of seven major Spanish outposts in southern Chile around 1600, caused by the Mapuche and Huilliche uprising of 1598. The Destruction of the Seven Cities, in traditional historiography, marks the end of the Conquest period and the beginning of the proper colonial period.
The Battle of Mataquito was fought in the Arauco War on April 30, 1557, between the forces of the Spanish governor, Francisco de Villagra, and Mapuche headed by their toqui Lautaro. It was a surprise attack, carried out at dawn, on Lautaro's fortified camp between a wooded mountain and the shore of the Mataquito River. The battle is notable for ending Mapuche designs on Santiago, while also avenging the death of former governor Pedro de Valdivia, who had been killed by Lautaro's warriors four years earlier.

Pehuenche are an indigenous people of South America. They live in the Andes, primarily in present-day south central Chile and adjacent Argentina. Their name derives from their dependence for food on the seeds of the Araucaria araucana or monkey-puzzle tree. In the 16th century, the Pehuenche lived in the mountainous territory from approximately 34 degrees to 40 degrees south. Later they became Araucanized and partially merged with the Mapuche peoples. In the 21st century, they still retain some of their ancestral lands.
Antonio de Guill y Gonzaga was a Spanish colonial administrator who served as Royal Governor of Panama and Royal Governor of Chile.

Guerra a muerte is a term coined by Benjamín Vicuña Mackenna and used in Chilean historiography to describe the irregular, no-quarter warfare that broke out in 1819 during the Chilean War of Independence.

Claude Gay, often named Claudio Gay in Spanish texts,, was a French botanist, naturalist and illustrator. This explorer carried out some of the first investigations about Chilean flora, fauna, geology and geography. The Cordillera Claudio Gay in the Atacama Region of Chile is named after him. He founded the Chilean National Museum of Natural History, its first director was another Frenchman Jean-François Dauxion-Lavaysse. The standard author abbreviation Gay is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.

Benjamín Vicuña Mackenna was a Chilean writer, journalist, historian and politician. Vicuña Mackenna was of Irish and Basque descent.

Between 1830 and 1850, Chilean silver mining grew at an unprecedented pace which transformed mining into one of the country's principal sources of wealth. The rush caused rapid demographic, infrastructural, and economic expansion in the semi-arid Norte Chico mountains where the silver deposits lay. A number of Chileans made large fortunes in the rush and made investments in other areas of the economy of Chile. By the 1850s, the rush was in decline and lucrative silver mining definitively ended in the 1870s. At the same time, mining activity in Chile reoriented to saltpetre operations.
Historia is a peer-reviewed academic journal specialising in the history of the Americas and Chile. It was established in 1961 and its first director was Jaime Eyzaguirre. The first editorial committee included Ricardo Krebs, Gonzalo Vial, Gabriel Guarda, Armando de Ramón, Julio González and Carlos Oviedo. Javier González acted as secretary. Apart from original articles, the journal includes a bibliography of any history publication about Chile or written by a Chilean in the period that precedes the journal deem relevant.
Science fiction in Chile began in the late 19th century with the publication of the books El espejo del mundo in 1875 by the Englishman Benjamin Tallman, about the modernization of Valparaíso and Santiago, and in 1877 of Desde Jupiter by Francisco Miralles, which recounted a trip to the planet and back.
Antisemitism in Chile started in early Chilean history during Spanish colonization and settlement. Now on the decline, Antisemitism has resurfaced throughout the country's history to include the 20th century Nazism in Chilean cities with German heritage. Chileans today have a positive view of the country's estimated 32,000 Jews or less than 1% of the population.
References
- ↑ Bethell, Leslie (1993), Chile since independence, Cambridge University Press, p. 205, ISBN 978-0-521-43375-4
- ↑ "Premio-Nacional-Historia-Academico-Universidad-Chile-Mario-Orellana-Presenta-Segunda-Edicion-Destacada-Obra" (in Spanish). Noticias.universia.cl. 11 October 2006. Retrieved 2011-02-01.