Related Research Articles
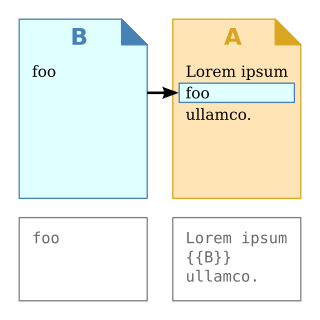
In computer science, transclusion is the inclusion of part or all of an electronic document into one or more other documents by reference via hypertext. Transclusion is usually performed when the referencing document is displayed, and is normally automatic and transparent to the end user. The result of transclusion is a single integrated document made of parts assembled dynamically from separate sources, possibly stored on different computers in disparate places.
Jakarta Enterprise Beans is one of several Java APIs for modular construction of enterprise software. EJB is a server-side software component that encapsulates business logic of an application. An EJB web container provides a runtime environment for web related software components, including computer security, Java servlet lifecycle management, transaction processing, and other web services. The EJB specification is a subset of the Java EE specification.
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a method to describe and exchange graph data. It was originally designed as a data model for metadata by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). It provides a variety of syntax notations and data serialization formats, of which the most widely used is Turtle.
A web service (WS) is either:

An interface description language or interface definition language (IDL) is a generic term for a language that lets a program or object written in one language communicate with another program written in an unknown language. IDLs are usually used to describe data types and interfaces in a language-independent way, for example, between those written in C++ and those written in Java.
The Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards is a nonprofit consortium that works on the development, convergence, and adoption of projects - both open standards and open source - for Computer security, blockchain, Internet of things (IoT), emergency management, cloud computing, legal data exchange, energy, content technologies, and other areas.
In software engineering, service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an architectural style that focuses on discrete services instead of a monolithic design. SOA is a good choice for system integration. By consequence, it is also applied in the field of software design where services are provided to the other components by application components, through a communication protocol over a network. A service is a discrete unit of functionality that can be accessed remotely and acted upon and updated independently, such as retrieving a credit card statement online. SOA is also intended to be independent of vendors, products and technologies.
REST is a software architectural style that was created to guide the design and development of the architecture for the World Wide Web. REST defines a set of constraints for how the architecture of a distributed, Internet-scale hypermedia system, such as the Web, should behave. The REST architectural style emphasises uniform interfaces, independent deployment of components, the scalability of interactions between them, and creating a layered architecture to promote caching to reduce user-perceived latency, enforce security, and encapsulate legacy systems.
Security Assertion Markup Language is an open standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, in particular, between an identity provider and a service provider. SAML is an XML-based markup language for security assertions. SAML is also:
Web Services Discovery provides access to software systems over the Internet using standard protocols. In the most basic scenario there is a Web Service Provider that publishes a service and a Web Service Consumer that uses this service. Web Service Discovery is the process of finding suitable web services for a given task.
In computing, Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) comprises a set of systems-management technologies developed to unify the management of distributed computing environments. The WBEM initiative, initially sponsored in 1996 by BMC Software, Cisco Systems, Compaq Computer, Intel, and Microsoft, is now widely adopted. WBEM is based on Internet standards and Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF) open standards:
In software architecture, a messaging pattern is an architectural pattern which describes how two different parts of an application, or different systems connect and communicate with each other. There are many aspects to the concept of messaging which can be divided in the following categories: hardware device messaging and software data exchange. Despite the difference in the context, both categories exhibit common traits for data exchange.
Service-oriented communications (SOC) technologies are designed to be easily used in the context of service-oriented architectures. These technologies are generally software based and are built more like a business application than a traditional PBX business communications system. Service-oriented communications systems allow their services to participate in business processes. They make their services available to other business applications within and SOA and allow for reuse of the services. The goal of service-oriented communications is to enable business environments to build communications into their business processes, enabling more streamlined collaboration among people within the business. It typically assumes that certain services are provided in the context of an SOA service provider. This is often in the form of a suite of web services, but may also be attached to other means of sharing the services such as an enterprise system bus (ESB).
Election Markup Language (EML) is an XML-based standard to support end to end management of election processes.

The Web Services Description Language is an XML-based interface description language that is used for describing the functionality offered by a web service. The acronym is also used for any specific WSDL description of a web service, which provides a machine-readable description of how the service can be called, what parameters it expects, and what data structures it returns. Therefore, its purpose is roughly similar to that of a type signature in a programming language.
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build such a connection or interface is called an API specification. A computer system that meets this standard is said to implement or expose an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation.
Multimodal Architecture and Interfaces is an open standard developed by the World Wide Web Consortium since 2005. It was published as a Recommendation of the W3C on October 25, 2012. The document is a technical report specifying a multimodal system architecture and its generic interfaces to facilitate integration and multimodal interaction management in a computer system. It has been developed by the W3C's Multimodal Interaction Working Group.
gSOAP is a C and C++ software development toolkit for SOAP/XML web services and generic XML data bindings. Given a set of C/C++ type declarations, the compiler-based gSOAP tools generate serialization routines in source code for efficient XML serialization of the specified C and C++ data structures. Serialization takes zero-copy overhead.
References
- ↑ Dipl.-Ing. Walter Abel Management Consulting (2024-05-12). "Documents for IT Service Management, according to ITIL® and ISO 20000" . Retrieved 2024-06-18.