Related Research Articles

Bal Keshav Thackeray, was an Indian politician who founded the Shiv Sena, a right-wing pro-Marathi and Hindu nationalist party active mainly in the state of Maharashtra.

Shiv Sena is a right-wing Marathi regionalist and ultranationalist political party in India founded in 1966 by cartoonist Bal Thackeray. Originally emerging from nativist movements in Bombay, the party agitates for preferential treatment for Maharashtrians over migrants from other parts of India. Its election symbol for Maharashtra is Bow and Arrow. Uddhav Thackeray, Bal Thackeray's son, is party leader and serves as the current Chief Minister of Maharashtra.

The Rāmāyana is a Sanskrit epic from ancient India. Ramayana is one of the two Itihasas of Hinduism, the other being the Mahābhārata.

Maithili Sharan Gupt was one of the most important modern Hindi poets. He is considered one among the pioneers of Khari Boli poetry and wrote in Khari Boli dialect, at a time when most Hindi poets favoured the use of Braj Bhasha dialect. He was a recipient of the third highest Indian civilian honour of Padma Bhushan. For his book Bharat-Bharati (1912), widely quoted during India's freedom struggle, he was given the title of Rashtra Kavi by Mahatma Gandhi.
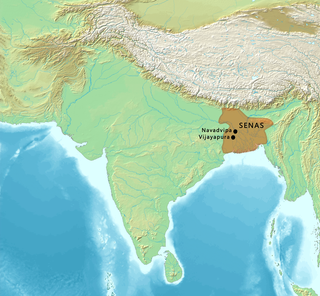
The Sena dynasty was a Hindu dynasty during the early medieval period on the Indian subcontinent, that ruled from Bengal through the 11th and 12th centuries. The empire at its peak covered much of the north-eastern region of the Indian subcontinent. The rulers of the Sena Dynasty traced their origin to the south Indian region of Karnataka.

The history of Bengal is intertwined with the history of the broader Indian subcontinent and the surrounding regions of South Asia and Southeast Asia. It includes modern-day Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal and Assam's Karimganj district, located in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, at the apex of the Bay of Bengal and dominated by the fertile Ganges delta. The region was known to the ancient Greeks and Romans as Gangaridai, a powerful kingdom whose war elephant forces led the withdrawal of Alexander the Great from India. Some historians have identified Gangaridai with other parts of India. The Ganges and the Brahmaputra rivers act as a geographic marker of the region, but also connects the region to the broader Indian subcontinent. Bengal, at times, has played an important role in the history of the Indian subcontinent.

Bikrampur was a pargana situated 19 kilometres (12 mi) south of Dhaka, the modern capital city of Bangladesh. In the present day, it is known as Munshiganj District of Bangladesh. It is a historic region in Bengal and was a part of the Bhawal Estate.

Ikhtiyār al-Dīn Muḥammad Bakhtiyār Khaljī, also known as Bakhtiyar Khalji, was a Turko-Afghan military general of the Ghurid Empire, who led the Muslim conquests of the eastern Indian regions of Bengal and Bihar and established himself as their ruler. He was the founder of the Khalji dynasty of Bengal, which ruled Bengal for a short period, from 1203 to 1227 CE.

Dacca or Dhaka is the capital and one of the oldest cities of Bangladesh. The history of Dhaka begins with the existence of urbanised settlements in the area that is now Dhaka dating from the 7th century CE. The city area was ruled by the Buddhist and shaivite Pala Empire before passing to the control of the Sena dynasty in the 10th century CE. After the Sena dynasty, Dhaka was successively ruled by the Turkic and Afghan governors descending from the Delhi Sultanate, followed by the Bengal Sultanate, before the arrival of the Mughals in 1608. The city became proto-industrialised and declared capital of the Mughal Bengal. After Mughals, British ruled the region for 200 years until the independence of India. In 1947, Dhaka became the capital of the East Bengal province under the Dominion of Pakistan. After the independence of Bangladesh in 1971, Dhaka became the capital of the new state.
The Ramacharitam is a Sanskrit epic poem written in Arya metre by Sandhyakar Nandi during Pala Empire. This work simultaneously narrates the story of the Ramayana and the Pala king Ramapala.
Dhoyin or Dhoyī was a 12th century Sanskrit-language poet who composed the Pavanadūta. He was a court poet of the Sena king Lakshmana Sena, who ruled Gauda in what is now Bengal.

Samataṭa was an ancient geopolitical division of Bengal in the eastern Indian subcontinent. The Greco-Roman account of Sounagoura is linked to the kingdom of Samatata. Its territory corresponded to much of present-day eastern Bangladesh and Myanmar. The area covers the trans-Meghna part of the Bengal delta. It was a center of Buddhist civilisation before the resurgence of Hinduism and Muslim conquest in the region.
Lakshmana Sena, also called Lakshman Sen in modern vernaculars, was the ruler from the Sena dynasty of the Bengal region on the Indian subcontinent. His rule lasted for 28 years; and extended to much of the eastern regions of the Indian subcontinent, notably Bengal and Bihar regions. His reign ended with the invasion of Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khilji.
Vallalasena or Ballala Sena, also known as Ballal Sen in vernacular literature, was the second ruler of the Sena dynasty of Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent. He was the son and successor of Vijaya Sena, and ended the Pala Empire by defeating Govindapala.
Hemanta Sena, the founder of the Hindu Sena dynasty in the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent.

Shri Dharma Sastha temple is a Hindu temple located at the village Sasthamkotta, Kerala, India. It is surrounded three sides by the largest fresh water lake of Kerala, Sasthamkotta lake.

Sculpture has been an indispensable part of Bangladeshi culture, historically part of the art of Bengal and Indian art. Bengal was at times an important centre influencing stone sculpture in the Indian subcontinent, especially in the post-Gupta and medieval periods. Terracotta reliefs are a particular local characteristic of Hindu temples and mosques in recent centuries.
The Deopara Prashasti is a stone inscription (prashasti) eulogizing the Sena kings of Bengal. It was composed by Umapati Dhara, a minister in the court of Lakshmana Sena, who was also one of several court poets. The inscription particularly praises Lakshmana Sena's grandfather Vijaya Sena. The alphabet is a precursor of the modern Bengali alphabet, with 22 letters approximating the modern forms. The stone tablet was found in 1865 near the village of Deopara, now in Godagari Upazila of Rajshahi District of modern-day Bangladesh. This inscription described that Sena king Bijay Sen is the real founder of the Sena Empire.

The Khalji dynasty was the first dynasty to set the foundations of Muslim rule in Bengal. Hailing from the Garmsir region of present-day Afghanistan, the dynasty was founded by Muhammad Bakhtiyar Khalji, a Turkic Khalaj general of the Ghurid Empire, and their rule extended from 1204 to 1231, though interrupted with a brief interregnum by Nasiruddin Mahmud in 1227. Under the rule of Iwaz Khalji, Bengal experienced major developments such as its first naval force, flood defence systems and linkage with the Grand Trunk Road.
The Lakshmana Era is year-numbering system that was established by Lakshmana Sena, a ruler of eastern India from 1178 to 1206. While there is some debate among historians about the start of the era, most currently agree that it is 1118-1119 AD.