Related Research Articles

A lord-lieutenant is the British monarch's personal representative in each lieutenancy area of the United Kingdom. Historically, each lieutenant was responsible for organising the county's militia. In 1871, the lieutenant's responsibility over the local militia was removed. However, it was not until 1921 that they formally lost the right to call upon able-bodied men to fight when needed.

The historic counties of England are areas that were established for administration by the Normans, in many cases based on earlier kingdoms and shires created by the Angles, Saxons, Jutes, Celts and others. They are alternatively known as ancient counties, traditional counties, former counties or simply as counties. In the centuries that followed their establishment, as well as their administrative function, the counties also helped define local culture and identity. This role continued even after the counties ceased to be used for administration after the creation of administrative counties in 1889, which were themselves amended by further local government reforms in the years following.

Barnstaple is a river-port town and civil parish in the North Devon district of Devon, England. The town lies at the River Taw's lowest crossing point before the Bristol Channel. From the 14th century, it was licensed to export wool from which it earned great wealth. Later it imported Irish wool, but its harbour silted up and other trades developed such as shipbuilding, foundries and sawmills. A Victorian market building survives, with a high glass and timber roof on iron columns.
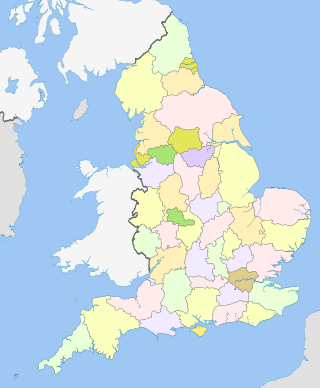
The counties of England are a type of subdivision of England. Counties have been used as administrative areas in England since Anglo-Saxon times. There are three definitions of county in England: the 48 ceremonial counties used for the purposes of lieutenancy; the 84 metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties for local government; and the 39 historic counties which were used for administration until 1974.

Ceremonial counties, formally known as counties for the purposes of the lieutenancies, are areas of England to which lord-lieutenants are appointed. They are one of the two main legal definitions of the counties of England in modern usage, the other being the counties for the purposes of local government legislation. A lord-lieutenant is the monarch's representative in an area. Shrieval counties have the same boundaries and serve a similar purpose, being the areas to which high sheriffs are appointed. High sheriffs are the monarch's judicial representative in an area.

West Devon is a local government district with borough status in Devon, England. Its council is based in Tavistock, the borough's largest town. The borough also includes the towns of Hatherleigh, North Tawton and Okehampton, along with numerous villages and surrounding rural areas.
A municipal borough was a type of local government district which existed in England and Wales between 1836 and 1974, in Northern Ireland from 1840 to 1973 and in the Republic of Ireland from 1840 to 2002. Broadly similar structures existed in Scotland from 1833 to 1975 with the reform of royal burghs and creation of police burghs.
A high sheriff is a ceremonial officer for each shrieval county of England and Wales and Northern Ireland or the chief sheriff of a number of paid sheriffs in U.S. states who outranks and commands the others in their court-related functions. In Canada, the High Sheriff provides administrative services to the supreme and provincial courts.
Borough status is granted by royal charter to local government districts in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. The status is purely honorary, and does not give any additional powers to the council or inhabitants of the district. In Scotland, similarly chartered communities were known as royal burghs, although the status is no longer granted.

The history of local government in England is one of gradual change and evolution since the Middle Ages. England has never possessed a formal written constitution, with the result that modern administration is based on precedent, and is derived from administrative powers granted to older systems, such as that of the shires.

Exeter City Council is the local authority for the city of Exeter in Devon, England. Exeter has had a city council since medieval times, which has been reformed on numerous occasions. Since 1974 it has been a non-metropolitan district council. The council has been under Labour majority control since 2010. It meets at Exeter Guildhall and has its main offices at the Civic Centre on Paris Street.

Chulmleigh is a small Saxon hilltop market town and civil parish in North Devon, in the heart of the English county of Devon. It lies 20 miles (32 km) north west of Exeter, just north of the Mid Devon boundary, linked by the A377 and B3096 roads.

Devon County Council is the county council administering the non-metropolitan county of Devon, England. The non-metropolitan county is smaller than the ceremonial county; the latter additionally includes Plymouth and Torbay. The population of the non-metropolitan county was estimated at 795,286 in 2018, making it the largest local authority in South West England. The council has been under Conservative majority control since 2009. It is based at County Hall in Exeter.

Plymouth City Council is the local authority for the city of Plymouth, in the ceremonial county of Devon, England. Plymouth has had a council since 1439, which has been reformed on numerous occasions. Since 1998 the council has been a unitary authority, being a district council which also performs the functions of a county council; it is independent from Devon County Council.

Sir Hugh Pollard lord of the manor of King's Nympton in Devon, was Sheriff of Devon in 1535/6 and in 1545 was appointed Recorder of Barnstaple in Devon.

Sir John Chichester of Raleigh in the parish of Pilton, near Barnstaple in North Devon, was a leading member of the Devonshire gentry, a naval captain, and ardent Protestant who served as Sheriff of Devon in 1550-1551, and as Knight of the Shire for Devon in 1547, April 1554, and 1563, and as Member of Parliament for Barnstaple in 1559, over which borough his lordship of the manor of Raleigh, Pilton had considerable influence.

Sir Richard Pollard, was Member of Parliament for Taunton in 1536, and for Devon in 1540 and 1542. He played a major role in assisting Thomas Cromwell in administering the Dissolution of the monasteries.

Sir Thomas Denys of Holcombe Burnell, near Exeter, Devon, was a prominent lawyer who served as Sheriff of Devon nine times between 1507/8 to 1553/4 and as MP for Devon. He acquired large estates in Devon at the Dissolution of the Monasteries.

The recorder of Barnstaple was a recorder, a form of senior judicial officer, usually an experienced barrister, within the jurisdiction of the Borough of Barnstaple in Devon. He was usually a member of the local North Devonshire gentry. The position of recorder of any borough carried a great deal of prestige and power of patronage. The recorder of a borough was often entrusted by the mayor and corporation to nominate its Members of Parliament, as was the case with Sir Hugh I Pollard, Recorder of Barnstaple, who in 1545 nominated the two MP's to represent the Borough of Barnstaple. In the 19th century a recorder was the sole judge who presided at a Quarter Sessions of a Borough, a "Court of Record", and was a barrister of at least five years' standing. He fixed the dates of the Quarter Sessions at his own discretion "as long as he holds it once every quarter of a year", or more often if he deemed fit.

The Mayor of Exeter, granted Lord Mayor of Exeter in 2002, is the Mayor of Exeter in the ceremonial county of Devon, England and is elected by and from within the councillors of the City of Exeter council. The position is the third oldest mayoralty in the United Kingdom, behind the Lord Mayor of London and Mayor of Winchester, being founded in 1200.
References
- ↑ "Sheriffs of the City and County of the City of Exeter". Exeter Memories.
- 1 2 Merritt, Anita (2018-06-15). "This is when Exeter had its own sheriff who witnessed hangings and had power over the city". Devon Live.
- ↑ "Legal Sunday at Exeter Cathedral". Western Circuit. 2014.