Related Research Articles

A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission especially from driving shaft to driven shaft.
Double-clutching is a method of shifting gears used primarily for vehicles with an unsynchronized manual transmission, such as commercial trucks and specialty vehicles. While double clutching is not necessary in a vehicle that has a synchronized manual transmission, the technique can be advantageous for smoothly downshifting in order to accelerate, and when done correctly it prevents wear on the "synchros" which normally equalize transmission input and output speeds to allow downshifting.

An automatic transmission is multi-speed transmission used in motor vehicles that does not require any driver input to change gears under normal driving conditions.

Overdrive is the operation of an automobile cruising at sustained speed with reduced engine revolutions per minute (RPM), leading to better fuel consumption, lower noise, and lower wear. Use of the term is confused, as it is applied to several different, but related, meanings.

A transmission is a machine in a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of power. Often the term 5-speed transmission refers simply to the gearbox that uses gears and gear trains to provide speed and torque conversions from a rotating power source to another device.

A manual transmission is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission system, where gear changes require the driver to manually select the gears by operating a gear stick and clutch.

In mechanical or automotive engineering, a freewheel or overrunning clutch is a device in a transmission that disengages the driveshaft from the driven shaft when the driven shaft rotates faster than the driveshaft. An overdrive is sometimes mistakenly called a freewheel, but is otherwise unrelated.
Semi-automatic transmission denotes a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission where part of its operation is automated, but the driver's input is still required to start from a standstill and to manually change gears. Most semi-automatic transmissions used in cars and motorcycles are based on conventional manual transmissions or a sequential manual transmission, but use an automatic clutch system. However, some semi-automatic transmissions have also been based on standard hydraulic automatic transmissions, with a fluid coupling or torque converter.

Hydramatic is an automatic transmission developed by both General Motors' Cadillac and Oldsmobile divisions. Introduced in 1939 for the 1940 model year vehicles, the Hydramatic was the first mass-produced fully-automatic transmission developed for passenger automobile use.

A sprag clutch is a one-way freewheel clutch. It resembles a roller bearing but, instead of cylindrical rollers, non-revolving asymmetric figure-eight shaped sprags, or other elements allowing single direction rotation, are used. When the unit rotates in one direction the rollers slip or free-wheel, but when a torque is applied in the opposite direction, the sprags tilt slightly, producing a wedging action and binding because of friction. The sprags are spring-loaded on their pivots to ensure that they lock with very little backlash once drive is engaged.

A preselector gearbox is a type of manual transmission mostly used on passenger cars and racing cars in the 1930s, in buses from 1940-1960 and in armoured vehicles from the 1930s to the 1970s. The defining characteristic of a preselector gearbox is that the gear shift lever allowed the driver to "pre-select" the next gear, usually with the transmission remaining in the current gear until the driver pressed the "gear change pedal" at the desired time.

Automated manual transmission (AMT), also known as a clutchless manual, denotes a type of multi-speed motor vehicle transmission system that is closely based on the mechanical design and internal build of a conventional manual transmission, and uses automation to control either the clutch, and/or the gear shifting.
A rev limiter is a device fitted in modern vehicles that have internal combustion engines. They are intended to protect an engine by restricting its maximum rotational speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM). Rev limiters are pre-set by the engine manufacturer. There are also aftermarket units where a separate controller is installed using a custom RPM setting. A limiter prevents a vehicle's engine from being pushed beyond the manufacturer's limit known as the redline. At some point beyond the redline, engine damage may occur.
A transmission control unit (TCU), also known as a transmission control module (TCM), or a gearbox control unit (GCU), is a type of automotive ECU that is used to control electronic automatic transmissions. Similar systems are used in various semi-automatic transmissions for clutch automation. A TCU in a modern automatic transmission generally uses sensors from the vehicle, as well as data provided by the engine control unit (ECU), to calculate how and when to change gears in the vehicle for optimum performance, fuel economy and shift quality.
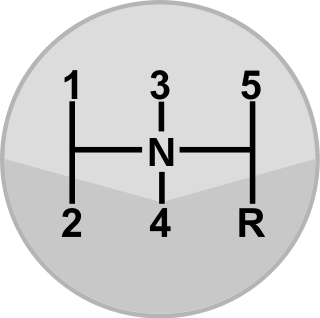
A gear stick, gear lever, gearshift or shifter is a metal lever attached to the shift assembly in an automobile transmission. The term gear stick mostly refers to the shift lever of a manual transmission, while in an automatic transmission, a similar lever is known as a gear selector. A gear stick will normally be used to change gear whilst depressing the clutch pedal with the left foot to disengage the engine from the drivetrain and wheels. Automatic transmission vehicles, including hydraulic automatic transmissions, automated manual and older Semi-automatic transmissions, like VW Autostick, and those with continuously variable transmissions, do not require a physical clutch pedal.
Shift time refers to the time interval between gear changes in a transmission. This interval is the time in which power delivery is interrupted and engine speed is reduced or increased to synchronize speed for the next selected gear. Shift time is usually in reference to motor vehicles but can apply to any gearbox. Reducing shift time is important in performance vehicles or race cars because the shifting process generally interrupts power delivery to the wheels. Shift time in a manual gearbox is dependent on the driver, but in automatic or automated manual cars the electronic or hydraulic control system must be calibrated and tuned to deliver a fast gear change.

A cross-drive steering transmission is a transmission which is used in tracked vehicles to allow precise and energy efficient steering.
Synchronized downshift rev-matching system is a technology invented by Nissan for use on the Nissan 370Z. In combination with the Engine Control Unit (ECU) and various sensors, the engine electronically blips the throttle for the driver during both downshifts and upshifts to allow for better and smoother shifting, and improved handling.

A motorcycle transmission is a transmission created specifically for motorcycle applications. They may also be found in use on other light vehicles such as motor tricycles and quadbikes, go-karts, offroad buggies, auto rickshaws, mowers, and other utility vehicles, microcars, and even some superlight racing cars.

Car controls are the components in automobiles and other powered road vehicles, such as trucks and buses, used for driving and parking.
References
- ↑ Sessions, Ron (1987). Turbo Hydra-Matic 350 Handbook. HP Trade. p. 226. ISBN 978-0-89586-051-4.
- ↑ "Powershifting Your Automatic". Popular Mechanics. 165 (May 1988): 126–127. 1988.
| This article about an automotive part or component is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |