Related Research Articles

Lingayatism or Veera Saivism is a Hindu denomination based on Shaivism. Initially known as Veerashaivas, since the 12th-century adherents of this faith are known as Lingayats. The terms Lingayatism and Veerashaivism have been used synonymously, but Veerashaivism may refer to the broader Veerashaiva philosophy which predates Lingayatism, to the historical community now called Lingayats, and to a contemporary (sub)tradition within Lingayatism with Vedic influences. Veerashaivas believe in the Varna system and patriachy while modern-day Lingayats do not, although these claims are not evidentially backed.

Basava, also called Basaveshwara and Basavanna, was a 12th-century CE Indian statesman, philosopher, poet, Lingayat social reformer in the Shiva-focussed bhakti movement, and a Hindu Shaivite social reformer during the reign of the Kalyani Chalukya/Kalachuri dynasty. Basava was active during the rule of both dynasties but reached the peak of his influence during the rule of King Bijjala II in Karnataka, India.

Akka Mahadevi ಅಕ್ಕ ಮಹಾದೇವಿ (c.1130–1160) was one of the early female poets of the Kannada literature and a prominent person in the Lingayat Shaiva sect in the 12th century. Her 430 extant Vachana poems, and the two short writings called Mantrogopya and the Yogangatrividh are considered her most notable contribution to Kannada literature. She composed fewer poems than other saints of the movement. The term Akka is an honorific given to her by great Lingayat saints such as Basavanna, Siddharama and Allamaprabhu and an indication of her high place in the spiritual discussions held at the "Anubhava Mantapa". She is seen as an inspirational woman in Kannada literature and in the history of Karnataka. She considered the god Shiva as her husband,.

Basavakalyana is a city and municipal council in the Bidar District of the Indian state of Karnataka. It was the two Dynasties capital like Kalyani Chalukya and Kalachuris of Kalyani.It is famous for the world's largest Basavanna statue tall. IT is one of the major city and industrial hub of Bidar district.

Allamaprabhu was a 12th-century mystic-saint and Vachana poet of the Kannada language, propagating the unitary consciousness of Self and Shiva. Allamaprabhu is one of the celebrated poets and the patron saint of the Lingayata movement that reshaped medieval Karnataka society and popular Kannada literature. He is included among the "Trinity of Lingayathism", along with Basavanna, the founder of the movement, and Akka Mahadevi, the most prominent woman poet.
Channabasavanna also known as " Guru Channabasaveshwara " was Basava's nephew and one of the foremost Sharanas of the 12th century. He, along with Basava, Allama Prabhu and Akka Mahadevi, played a pivotal role in the propagation of the Lingayat faith. He was the youngest among the sharana leaders and grew up in the household of Basavanna as he was the son of Nagalambike, Basava's own sister. He also wrote the Karana Hasuge which is one of the most sacred texts of the Lingayats, among many vachanas. He propounded the "shatasthala" philosophy associated with the six holy places of Veerashaiva Lingayat creed. He succeeded to the Shunya Simhasana at Anubhava Mantapa, Kalyana after the departure of Allama Prabhu, circa 1162ad. His young shoulders carried on the legacy of Basava after the latter's departure to Kudalasangama in 1162ad. He is credited to have systematised the entire manual of simple rituals for the followers. He was a strong advocate of the Ishtalinga wearing and expounded the material as well as the esoteric meaning of that divine symbol. He held together the nascent group of Shivasharanas and Jangmas in tumultuous times of clashes with the orthodox Brahmins and heretic Jains. Following the assassination of Kalachuri King Bijjala II in 1167 A.D, Channabasava along with his followers migrated to Ulavi safeguarding the Vachana literature. He attained Samadhi state there at the age of 25 passing on the leadership of the movement to Siddarama.

Kudalasangama in India is an important centre of pilgrimage for Lingayats. It is located about 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) from the Almatti Dam in Bagalkote district of Karnataka state. The Krishna and Malaprabha River rivers merge here and flow east towards Srisailam Andhra Pradesh. The Aikya Mantapa or the holy Samādhi of Basavanna, the founder of the Lingayatism along with Linga, which is believed to be self-born (Swayambhu), is here. The Kudala Sangama Development Board takes care of the maintenance and development.

Anubhava Mantapa, established by Basavanna in the 12th century C.E. is located in Basavakalyan in Bidar district of Karnataka. It is the first religious parliament in the world, whose literal meaning is "experience pavilion", and was an academy of mystics, saints and philosophers of the lingayat faith in the 12th century. It was the fountainhead of all religious and philosophical thought pertaining to the lingayat. It was presided over by the mystic Allama Prabhu and numerous Sharanas from all over Karnataka and other parts of India were participants. This institution was also the fountainhead of the Vachana literature which was used as the vector to propagate Veerashaiva religious and philosophical thought. Other giants of veerashaiva theosophy like Akka Mahadevi, Channabasavanna and Basavanna himself were participants in the Anubhava Mantapa. The Anubhava Mantapa is also called the Mahaamane.
A large body of Western Chalukya literature in the Kannada language was produced during the reign of the Western Chalukya Empire in what is now southern India. This dynasty, which ruled most of the western Deccan in South India, is sometimes called the Kalyani Chalukya Dynasty after its royal capital at Kalyani, and sometimes called the Later Chalukya Dynasty for its theoretical relationship to the 6th-century Chalukya dynasty of Badami. For a brief period (1162–1183), the Kalachuris of Kalyani, a dynasty of kings who had earlier migrated to the Karnataka region from central India and served as vassals for several generations, exploited the growing weakness of their overlords and annexed the Kalyani. Around 1183, the last Chalukya scion, Someshvara IV, overthrew the Kalachuris to regain control of the royal city. But his efforts were in vain, as other prominent Chalukya vassals in the Deccan, the Hoysalas, the Kakatiyas and the Seunas destroyed the remnants of the Chalukya power.
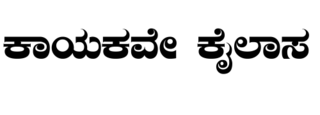
Vachana sahitya is a form of rhythmic writing in Kannada that evolved in the 11th century and flourished in the 12th century, as a part of the Sharana movement. Madara Chennaiah, an 11th-century cobbler-saint who lived during the reign of the Western Chalukyas is regarded by some scholars as the "father of Vachana poetry." The word "vachanas" literally means "(that which is) said". These are readily intelligible prose texts.

Vijayanagara literature in Kannada is the body of literature composed in the Kannada language of South India during the ascendancy of the Vijayanagara Empire which lasted from the 14th through the 16th century. The Vijayanagara empire was established in 1336 by Harihara I and his brother Bukka Raya I. Although it lasted until 1664, its power declined after a major military defeat by the Shahi Sultanates in the battle of Talikota in 1565. The empire is named after its capital city Vijayanagara, whose ruins surround modern Hampi, now a World Heritage Site in Karnataka.
Harihara was a noted Kannada poet and writer in the 12th century. A native of Halebidu in modern Hassan district, he came from a family of accountants (Karnikas) and initially served in that capacity in the court of Hoysala King Narasimha I. Later, he moved to Hampi and authored many landmark classics. Among his important writings, the Girijakalyana written in champu metre is considered one of the enduring classics of Kannada language.

Yediyuru Siddhalingeshwara Temple is a very famous pilgrimage centre situated in Yedeyuru Village, Kunigal Town of Karnataka State in India.

Siddheshwar also known as Siddharameshwar and Siddharama was one among the five acharya ("saint") of the Lingayat faith. Siddheshwar was a great contributor to Lingayat sampradaya of Hinduism. He was a great mystic and a Kannada poet who was a part of Basavanna's Lingayat revolution during the 12th century. His philosophy was one of service to mankind, the path of karmayoga. Siddarama was instrumental in saving the vachana literature from destruction. Shri Siddharameshwar was born in Solapur City of Maharashtra.
Devara Daasimayya, was an Indian mid-11th century poet and vachanakaara in Kannada. He was born in Mudanuru, a village in Shorapur Taluk, Yadagiri district in Karnataka. Being a weaver by profession, His village had a Ramanatha temple among its many temples, dedicated to Shiva as worshiped by Rama, the epic hero and incarnation of Vishnu. That is why Dasimayya's signature name (ankitanama) is Ramanatha, meaning Rama's Lord, i.e. Shiva.
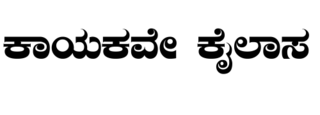
The Basava Purana is a 13th-century Telugu epic poem. It was written by Palkuriki Somanatha. It is a sacred text of Lingayat. The epic poem narrates the life story of philosopher and social reformer Basava, the founder of Lingayat. He is also known by several other names such as Basavanna, Basaweshwara, Basavesha, and Basavaraja. It is also an anthology of several Lingayat saints and their philosophies. In contrast to campu style, Somanatha adopted the desi (native) style and composed the purana in dwipada (couplets), a meter popular in oral tradition and closely related to folk songs.
Sharana (Kannada:ಶರಣ) meaning "to surrender" denotes egoless surrender and refuge in Shiva, the Deity of Hinduism. In practice, the word sharana refers specifically to a person who is a follower of the Lingayat tradition. Sharanas through centuries were responsible for the spread of Lingayatism in India.
Dr. Phakirappa Gurubasappa Halakatti was an Indian scholar and Kannada writer and also known for the resurrection of Vachana sahitya. Dr. Phakeerappa Halakatti was born on July 2, 1880, to Gurubasappa and Danamma in Dharwad. He was the founding father of BLDEA an educational trust in Bijapur.

Annadanaiah (Annadanayya) Puranik, Indian writer, cultural activist, freedom fighter, modern vachanakara and an advocate. After Indian independence, he has served as an Advocate in state high court of Karnataka for five decades. He was also conferred the title Sahityaratna, for his contribution to Kannada literature and enormous contribution during a secretarial term with Kannada Sahitya Parishat.