Related Research Articles

Hindi cinema, often known as Bollywood and formerly as Bombay cinema, is the Indian Hindi-language film industry based in Mumbai. The term is a portmanteau of "Bombay" and "Hollywood". The industry is related to Cinema of South India and other Indian film industries, making up Indian cinema—the world's largest by number of feature films produced.

The Cleveland Indians are an American professional baseball team based in Cleveland. The Indians compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) Central division. Since 1994, they have played at Progressive Field. The team's spring training facility is at Goodyear Ballpark in Goodyear, Arizona. Since their establishment as a major league franchise in 1901, the team has won 10 Central Division titles, six American League pennants, and two World Series championships,. The team's World Series championship drought since 1948 is the longest active among all 30 current Major League teams.

India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the second-most populous country, the seventh-largest country by land area, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar and Indonesia.
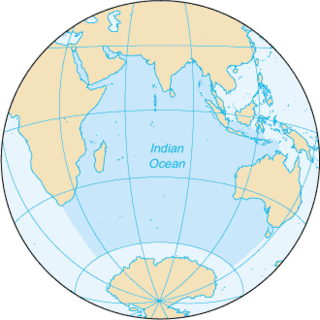
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering 70,560,000 km2 (27,240,000 sq mi) or 19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, the Laccadive Sea, the Somali Sea, Bay of Bengal, and the Andaman Sea.

India is the second most populated country in the world with nearly a fifth of the world's population. According to the 2019 revision of the World Population Prospects the population stood at 1,352,642,280.

Jawaharlal Nehru was an Indian independence activist and, subsequently, the first Prime Minister of India, as well as a central figure in Indian politics both before and after independence. He emerged as an eminent leader of the Indian independence movement, serving India as Prime Minister from its establishment in 1947 as an independent nation, until his death in 1964. He was also known as Pandit Nehru due to his roots with the Kashmiri Pandit community, while Indian children knew him better as Chacha Nehru.

Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist, and political ethicist, who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule, and in turn inspired movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific Mahātmā, first applied to him in 1914 in South Africa, is now used throughout the world.

Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans and other terms, are the indigenous peoples of the United States; sometimes including Hawaii and territories of the United States, and other times limited to the mainland. There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. "Native Americans" are indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives.

The Indian National Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British Empire in Asia and Africa. From the late 19th century, and especially after 1920, under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi, Congress became the principal leader of the Indian independence movement. Congress led India to independence from the United Kingdom, and powerfully influenced other anti-colonial nationalist movements in the British Empire, making it one of the world's oldest active political parties. The party has been overshadowed by the governments based on a haphazard mixture of Gandhism, socialism and capitalism. It stands for mixed economy and envisages a dominant role for the public sector. Its policies nationalized banks and insurance companies, to curb monopoly and concentration of wealth.

The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending the British rule in India. The movement spanned from 1857 to 1947. The first nationalistic revolutionary movement for Indian independence emerged from Bengal. It later took root in the newly formed Indian National Congress with prominent moderate leaders seeking only their fundamental right to appear for Indian Civil Service examinations in British India, as well as more rights for the people of the soil. The early part of the 20th century saw a more radical approach towards political self-rule proposed by leaders such as the Lal Bal Pal triumvirate, Aurobindo Ghosh and V. O. Chidambaram Pillai.

The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four-star general. Two officers have been conferred with the rank of field marshal, a five-star rank, which is a ceremonial position of great honour. The Indian Army originated from the armies of the East India Company, which eventually became the British Indian Army, and the armies of the princely states, which were merged into the national army after independence. The units and regiments of the Indian Army have diverse histories and have participated in a number of battles and campaigns around the world, earning many battle and theatre honours before and after Independence.

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks fourth amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial warfare during armed conflict. It was officially established on 8 October 1932 as an auxiliary air force of the British Empire which honoured India's aviation service during World War II with the prefix Royal. After India gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1947, the name Royal Indian Air Force was kept and served in the name of Dominion of India. With the government's transition to a Republic in 1950, the prefix Royal was removed.

The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major, but ultimately unsuccessful, uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the form of a mutiny of sepoys of the Company's army in the garrison town of Meerut, 40 mi (64 km) northeast of Delhi. It then erupted into other mutinies and civilian rebellions chiefly in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, though incidents of revolt also occurred farther north and east. The rebellion posed a considerable threat to British power in that region, and was contained only with the rebels' defeat in Gwalior on 20 June 1858. On 1 November 1858, the British granted amnesty to all rebels not involved in murder, though they did not declare the hostilities to have formally ended until 8 July 1859. Its name is contested, and it is variously described as the Sepoy Mutiny, the Indian Mutiny, the Great Rebellion, the Revolt of 1857, the Indian Insurrection, and the First War of Independence.

The Indian Navy is the naval branch of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Navy. The Chief of Naval Staff, a four-star admiral, commands the navy.

An Indian reservation is a legal designation for an area of land managed by a federally recognized Native American tribe under the U.S. Bureau of Indian Affairs rather than the state governments of the United States in which they are physically located. Each of the 326 Indian reservations in the United States is associated with a particular Native American nation. Some of the country's 574 federally recognized tribes have more than one reservation, while some share reservations, and others have no reservations at all. In addition, because of past land allotments, leading to some sales to non–Native Americans, some reservations are severely fragmented, with each piece of tribal, individual, and privately held land being a separate enclave. This jumble of private and public real estate creates significant administrative, political, and legal difficulties.

In Canada, the Indian residential school system was a network of boarding schools for Indigenous peoples. The network was funded by the Canadian government's Department of Indian Affairs and administered by churches. The school system was created for the purpose of removing Indigenous children from the influence of their own culture and assimilating them into the dominant, European-Canadian culture, "to kill the Indian in the child." Over the course of the system's more than hundred-year existence, around 150,000 were placed in residential schools nationally. By the 1930s about 30 percent of Indigenous children were believed to be attending residential schools. The number of school-related deaths remains unknown due to an incomplete historical record, though estimates range from 3,200 to upwards of 6,000.

Indian Idol is the Indian version of the Pop Idol format that has aired on Sony Entertainment Television since 2004. The show has spawned spin-off like Indian Idol Junior, which replaced the show for the seventh and eight seasons. The current winner of Season 11 is Sunny Hindustani.

The British Raj was the rule by the British Crown primarily on the Indian subcontinent from 1858 to 1947. The rule is also called Crown rule in India, or direct rule in India. The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage, and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British tutelage or paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially.

The Indian subcontinent, or simply the subcontinent or India, is a physiographical region in southern Asia, situated on the Indian Plate and projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, the Indian subcontinent generally includes all or part of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka, as well as the Maldives. Geologically, the Indian subcontinent is related to the landmass that rifted from the supercontinent Gondwana during the Cretaceous and merged with the Eurasian landmass nearly 55 million years ago. Geographically, it is the peninsular region in south-central Asia, delineated by the Himalayas in the north, the Hindu Kush in the west, and the Arakanese in the east. The terms Indian subcontinent and South Asia are sometimes used interchangeably to denote the region, although the term South Asia usually also includes Afghanistan.
The following notable deaths occurred in 2021. Names are reported under the date of death, in alphabetical order by surname or pseudonym. A typical entry reports information in the following sequence: