Related Research Articles

A knife is a tool or weapon with a cutting edge or blade, usually attached to a handle or hilt. One of the earliest tools used by humanity, knives appeared at least 2.5 million years ago, as evidenced by the Oldowan tools. Originally made of wood, bone, and stone, over the centuries, in step with improvements in both metallurgy and manufacturing, knife blades have been made from copper, bronze, iron, steel, ceramic, and titanium. Most modern knives have either fixed or folding blades; blade patterns and styles vary by maker and country of origin.

A mace is a blunt weapon, a type of club or virge that uses a heavy head on the end of a handle to deliver powerful strikes. A mace typically consists of a strong, heavy, wooden or metal shaft, often reinforced with metal, featuring a head made of stone, bone, copper, bronze, iron, or steel.

The hilt is the handle of a knife, dagger, sword, or bayonet, consisting of a guard, grip, and pommel. The guard may contain a crossguard or quillons. A tassel or sword knot may be attached to the guard or pommel.

A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut. Blacksmiths produce objects such as gates, grilles, railings, light fixtures, furniture, sculpture, tools, agricultural implements, decorative and religious items, cooking utensils, and weapons. There was a historical distinction between the heavy work of the blacksmith and the more delicate operations of a whitesmith, who usually worked in gold, silver, pewter, or the finishing steps of fine steel. The place where a blacksmith works is variously called a smithy, a forge, or a blacksmith's shop.

The kukri or khukuri is a type of knife or short sword with a distinct recurve in its blade that originated in the Indian subcontinent. It serves multiple purposes as a melee weapon and also as a regular cutting tool throughout most of South Asia. The kukri, khukri, and kukkri spellings are of Indian English origin.

A pipe bomb is an improvised explosive device (IED) that uses a tightly sealed section of pipe filled with an explosive material. The containment provided by the pipe means that simple low explosives can be used to produce a relatively large explosion due to the containment causing increased pressure. The fragmentation of the pipe itself creates potentially lethal shrapnel.

A ferrule is any of a number of types of objects, generally used for fastening, joining, sealing, or reinforcement. They are often narrow circular rings made from metal, or less commonly, plastic. Ferrules are also often referred to as eyelets or grommets within the manufacturing industry.

Pliers are a hand tool used to hold objects firmly, possibly developed from tongs used to handle hot metal in Bronze Age Europe. They are also useful for bending and physically compressing a wide range of materials. Generally, pliers consist of a pair of metal first-class levers joined at a fulcrum positioned closer to one end of the levers, creating short jaws on one side of the fulcrum, and longer handles on the other side. This arrangement creates a mechanical advantage, allowing the force of the grip strength to be amplified and focused on an object with precision. The jaws can also be used to manipulate objects too small or unwieldy to be manipulated with the fingers.

A club is a short staff or stick, usually made of wood, wielded as a weapon or tool since prehistory. There are several examples of blunt-force trauma caused by clubs in the past, including at the site of Nataruk in Turkana, Kenya, described as the scene of a prehistoric conflict between bands of hunter-gatherers 10,000 years ago.

The sai is a pointed melee weapon from Okinawa. It was historically utilized in martial arts such as Okinawan kobudō and southern Chinese martial arts, and has been absorbed into the curriculum of many modern martial arts. Although similar weapons can be found in other parts of Asia, the sai is the Okinawan take on the basic concept and should not be confused with the other weapons. The sai is primarily used for stabbing, striking, parrying and disarming opponents. It consists of a pointed metal main prong, that projects from a one-handed handle, two shorter metal side prongs, which project from the opposite sides of the base of the main prong and point in the same direction as it, and a blunt metal pommel fixed to the bottom end of the handle. The sai came to international attention when Okinawan kobudō and karate reached international popularity in the mid-20th Century.

The Waco siege, also known as the Waco massacre, was the siege by U.S. federal government and Texas state law enforcement officials of a compound belonging to the religious cult known as the Branch Davidians, between February 28 and April 19, 1993. The Branch Davidians, led by David Koresh, were headquartered at Mount Carmel Center ranch in unincorporated McLennan County, Texas, 13 miles northeast of Waco. Suspecting the group of stockpiling illegal weapons, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms (ATF) obtained a search warrant for the compound and arrest warrants for Koresh and several of the group's members.

A baseball bat is a smooth wooden or metal club used in the sport of baseball to hit the ball after it is thrown by the pitcher. By regulation it may be no more than 2.61 inches (6.6 cm) in diameter at the thickest part and no more than 42 inches (1.067 m) in length. Although historically bats approaching 3 pounds (1.4 kg) were swung, today bats of 33 ounces (0.94 kg) are common, topping out at 34 to 36 ounces.

A mesh is a barrier made of interlaced strands of metal, fiber or other flexible or ductile materials. A mesh is similar to a web or a net in that it has many interwoven strands.

A trench knife is a combat knife designed to kill or incapacitate an enemy at close quarters, such as in a trench or other confined area. It was developed as a close combat weapon for soldiers attacking enemy trenches during the First World War. An example of a World War I trench knife is the German Army's Nahkampfmesser.

A jambiya, is a specific type of dagger with a short curved blade with a medial ridge that originated from the Hadhramaut region in Yemen. They have spread to other countries in the Middle East, to other countries in the Arab world, and to parts of South Asia and Southeast Asia. Men typically above the age of 14 wear it as an accessory to their clothing.

Okinawan kobudō (沖縄古武道), literally "old martial way of Okinawa", is the weapon systems of Okinawan martial arts.

A chain is a serial assembly of connected pieces, called links, typically made of metal, with an overall character similar to that of a rope in that it is flexible and curved in compression but linear, rigid, and load-bearing in tension. A chain may consist of two or more links. Chains can be classified by their design, which can be dictated by their use:

Trench raiding clubs, or trench maces were improvised melee weapons used by both the Allies and the Central Powers during World War I. Clubs were used during nighttime trench raiding expeditions as a quiet and effective way of killing or wounding enemy soldiers. The clubs were usually made out of wood. It was common practice to fix a metal object at the striking end in order to maximize the injury inflicted. Another common design comprised a simple stave with the end drilled out and a lead weight inserted, with rows of large hobnails hammered in around its circumference. Most designs had some form of cord or leather strap at the end to wrap around the user's wrist. Bosnian soldiers serving in the Austro-Hungarian army were fond of using maces. They were also used by officers to finish enemy soldiers wounded by poison gas attacks.

The Intelligence Branch (IB) division of the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) handles all intelligence functions, including information sharing policies and intelligence analysis for national security, homeland security, and law enforcement purposes. The IB operates through the use of embedded intelligence strategies.
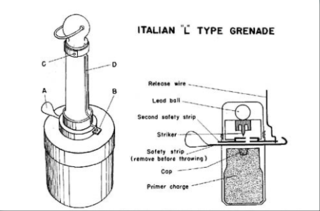
The Type L is an anti-tank hand grenade provided to the Royal Italian Army during World War II.