Related Research Articles

Vulcanization is a range of processes for hardening rubbers. The term originally referred exclusively to the treatment of natural rubber with sulfur, which remains the most common practice. It has also grown to include the hardening of other (synthetic) rubbers via various means. Examples include silicone rubber via room temperature vulcanizing and chloroprene rubber (neoprene) using metal oxides.

A tire or tyre is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide traction on the surface over which the wheel travels. Most tires, such as those for automobiles and bicycles, are pneumatically inflated structures, which also provide a flexible cushion that absorbs shock as the tire rolls over rough features on the surface. Tires provide a footprint, called a contact patch, that is designed to match the weight of the vehicle with the bearing strength of the surface that it rolls over by providing a bearing pressure that will not deform the surface excessively.

The Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company is an American multinational tire manufacturing company founded in 1898 by Frank Seiberling and based in Akron, Ohio. Goodyear manufactures tires for automobiles, commercial trucks, light trucks, motorcycles, SUVs, race cars, airplanes, farm equipment and heavy earth-moving machinery. It also makes bicycle tires, having returned from a break in production between 1976 and 2015. As of 2017, Goodyear is one of the top four tire manufacturers along with Bridgestone (Japan), Michelin (France) and Continental (Germany).

Carbon black is a material produced by the incomplete combustion of heavy petroleum products such as FCC tar, coal tar, ethylene cracking tar, or vegetable matter. Carbon black is a form of paracrystalline carbon that has a high surface-area-to-volume ratio, albeit lower than that of activated carbon. It is dissimilar to soot in its much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio and significantly lower polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) content. However, carbon black is widely used as a model compound for diesel soot for diesel oxidation experiments. Carbon black is mainly used as a reinforcing filler in tires and other rubber products. In plastics, paints, and inks, carbon black is used as a color pigment. It is used in some places, such as the EU, as a food colourant if produced from vegetable matter (E153).
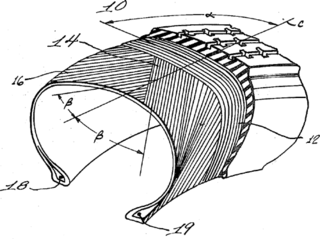
A radial tire is a particular design of vehicular tire. In this design, the cord plies are arranged at 90 degrees to the direction of travel, or radially. Radial tire construction climbed to 100% market share in North America following Consumer Reports finding the superiority of the radial design in 1968, and were standard by 1976.

Rolling resistance, sometimes called rolling friction or rolling drag, is the force resisting the motion when a body rolls on a surface. It is mainly caused by non-elastic effects; that is, not all the energy needed for deformation of the wheel, roadbed, etc., is recovered when the pressure is removed. Two forms of this are hysteresis losses, and permanent (plastic) deformation of the object or the surface. Note that the slippage between the wheel and the surface also results in energy dissipation. Although some researchers have included this term in rolling resistance, some suggest that this dissipation term should be treated separately from rolling resistance because it is due to the applied torque to the wheel and the resultant slip between the wheel and ground, which is called slip loss or slip resistance. In addition, only the so-called slip resistance involves friction, therefore the name "rolling friction" is to an extent a misnomer.
Accelerants are substances that can bond, mix or disturb another substance and cause an increase in the speed of a natural, or artificial chemical process. Accelerants play a major role in chemistry—most chemical reactions can be hastened with an accelerant. Accelerants alter a chemical bond, speed up a chemical process, or bring organisms back to homeostasis. Accelerants are not necessarily catalysts as they may be consumed by the process.

Polybutadiene [butadiene rubber BR] is a synthetic rubber. Polybutadiene rubber is a polymer formed from the polymerization of the monomer 1,3-butadiene. Polybutadiene has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tires, which consumes about 70% of the production. Another 25% is used as an additive to improve the toughness of plastics such as polystyrene and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). Polybutadiene rubber accounted for about a quarter of total global consumption of synthetic rubbers in 2012. It is also used to manufacture golf balls, various elastic objects and to coat or encapsulate electronic assemblies, offering high electrical resistivity.

Pneumatic tires are manufactured according to relatively standardized processes and machinery, in around 455 tire factories in the world. With over 1 billion tires manufactured worldwide annually, the tire industry is a major consumer of natural rubber. Tire factories start with bulk raw materials such as synthetic rubber, carbon black, and chemicals and produce numerous specialized components that are assembled and cured.

A flat tire is a deflated pneumatic tire, which can cause the rim of the wheel to ride on the tire tread or the ground potentially resulting in loss of control of the vehicle or irreparable damage to the tire. The most common cause of a flat tire is puncturing of the tire by a sharp object, such as a nail or pin, letting the air escape. Depending on the size of the puncture, the tire may deflate slowly or rapidly.
Si 363 is a bifunctional organosilane chemical used in the reinforcement of rubber articles, especially tires. SI363 is the trade name of a silane bonding agent in the trialkoxymercaptoalkyl-silane class and of formula SH(CH2)H3Si(OCHH2CHH3)(O(CHH2CHH2O)H5(CHH2)H12CHH3)H2.

Snow tires, also known as winter tires, are tires designed for use on snow and ice. Snow tires have a tread design with larger gaps than those on conventional tires, increasing traction on snow and ice. Such tires that have passed a specific winter traction performance test are entitled to display a "Three-Peak Mountain Snow Flake" symbol on their sidewalls. Tires designed for winter conditions are optimized to drive at temperatures below 7 °C (45 °F). Some snow tires have metal or ceramic studs that protrude from the tire to increase traction on hard-packed snow or ice. Studs abrade dry pavement, causing dust and creating wear in the wheel path. Regulations that require the use of snow tires or permit the use of studs vary by country in Asia and Europe, and by state or province in North America.

A bicycle tire is a tire that fits on the wheel of a bicycle or similar vehicle. These tires may also be used on tricycles, wheelchairs, and handcycles, frequently for racing. Bicycle tires provide an important source of suspension, generate the lateral forces necessary for balancing and turning, and generate the longitudinal forces necessary for propulsion and braking. Although the use of a pneumatic tire greatly reduces rolling resistance compared to the use of a rigid wheel or solid tire, the tires are still typically, the second largest source, after wind resistance, of power consumption on a level road. The modern detachable pneumatic bicycle tire contributed to the popularity and eventual dominance of the safety bicycle.
Polymer nanocomposites (PNC) consist of a polymer or copolymer having nanoparticles or nanofillers dispersed in the polymer matrix. These may be of different shape, but at least one dimension must be in the range of 1–50 nm. These PNC's belong to the category of multi-phase systems that consume nearly 95% of plastics production. These systems require controlled mixing/compounding, stabilization of the achieved dispersion, orientation of the dispersed phase, and the compounding strategies for all MPS, including PNC, are similar. Alternatively, polymer can be infiltrated into 1D, 2D, 3D preform creating high content polymer nanocomposites.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to tires:

The Charles Goodyear Medal is the highest honor conferred by the American Chemical Society, Rubber Division. Established in 1941, the award is named after Charles Goodyear, the discoverer of vulcanization, and consists of a gold medal, a framed certificate and prize money. The medal honors individuals for "outstanding invention, innovation, or development which has resulted in a significant change or contribution to the nature of the rubber industry". Awardees give a lecture at an ACS Rubber Division meeting, and publish a review of their work in the society's scientific journal Rubber Chemistry and Technology.

Bar grip tyres, or 'NDT' in US military parlance, are an early tyre tread pattern developed for off-road use.

Bis(triethoxysilylpropyl)tetrasulfide is an organosulfur compound with the formula S4[C3H6Si(OEt)3]2 (Et = C2H5). The molecule consists of two trialkoxysilyl propyl groups linked with a polysulfide. It is often sold as a mixture with the trisulfide. The compound is a colorless viscous liquid that is soluble in ordinary organic solvents such as toluene. Commercial samples often are yellowish. The compound is added to rubber compositions that contain silica filler.

Vinyltriethoxysilane is an organosilicon compound with the formula (C2H5O)3SiCH=CH2. It is a colorless liquid. The compound is bifunctional, featuring both a vinyl group and hydrolytically sensitive ethoxysilyl groups. As such it is a crosslinking agent.
Rubber pollution, similar to plastic pollution, occurs in various environments, and originates from a variety of sources, ranging from the food industry processing chain to tire wear. Synthetic and natural rubber dust and fragments now occur in food, airborne as particulates in air pollution, hidden in the earth as soil pollution, and in waterways, lakes and the sea.
References
- ↑ "3 TO RECEIVE RUBBER DIVISION HONORS IN SPRING". Rubber and Plastics News. November 6, 1995.
- ↑ "TIRE MAKERS TURN TO SILICA TO CUT ROLLING RESISTANCE: BUT INDUSTRY SLOW TO CHANGE; COSTS OF PRODUCTION AT LEAST 12% HIGHER". TireBusiness.com. October 31, 1994.
- ↑ Wolff, Siegfried (1996). "Wolff, S. (1996). Chemical aspects of rubber reinforcement by fillers". Rubber Chemistry and Technology. 69 (3): 325–346. doi:10.5254/1.3538376.