
Type VII U-boats were the most common type of German World War II U-boat. 703 boats were built by the end of the war. The lone surviving example, U-995, is on display at the Laboe Naval Memorial located in Laboe, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.

U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic-warfare role and enforcing a naval blockade against enemy shipping. The primary targets of the U-boat campaigns in both wars were the merchant convoys bringing supplies from Canada and other parts of the British Empire, and from the United States, to the United Kingdom and to the Soviet Union and the Allied territories in the Mediterranean. German submarines also targeted Brazilian merchant ships during both World Wars and, twice over, precipitated Brazil's decision to give up its neutral stance and declare war on Germany.

Type XXI submarines were a class of German diesel–electric Elektroboot submarines designed during the Second World War. One hundred and eighteen were completed, with four being combat-ready. During the war only two were put into active service and went on patrols, but these were not used in combat.

An anti-submarine weapon (ASW) is any one of a number of devices that are intended to act against a submarine and its crew, to destroy (sink) the vessel or reduce its capability as a weapon of war. In its simplest sense, an anti-submarine weapon is usually a projectile, missile or bomb that is optimized to destroy submarines.

German submarine U-534 is a Type IXC/40 U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine built for service during World War II. She was built in 1942 in Hamburg-Finkenwerder by Deutsche Werft AG as yard number 352. She was launched on 23 September 1942 and commissioned on 23 December with Oberleutnant zur See Herbert Nollau in command.
Sieglindezeek-LIN-də is a Germanic feminine given name. It is derived from two German words or elements. Those being: "sigu" for victory and "lind" for soft, tender, flexible. The diminutive version is "Sigi" or "Siggie".

Anechoic tiles are rubber or synthetic polymer tiles containing thousands of tiny voids, applied to the outer hulls of military ships and submarines, as well as anechoic chambers. Their function is twofold:

An acoustic torpedo is a torpedo that aims itself by listening for characteristic sounds of its target or by searching for it using sonar. Acoustic torpedoes are usually designed for medium-range use, and often fired from a submarine.
The G7es (T5) "Zaunkönig" ("wren") was a passive acoustic torpedo employed by German U-boats during World War II. It was called the GNAT by the British.

Foxer was the code name for a British-built acoustic decoy used to confuse German acoustic homing torpedoes like the G7 torpedo during the Second World War. A US version codenamed FXR was deployed at the end of September 1943 on all transatlantic escort vessels. A Canadian version was also built called the CAAT device. It was replaced in US service by the Fanfare noisemaker.
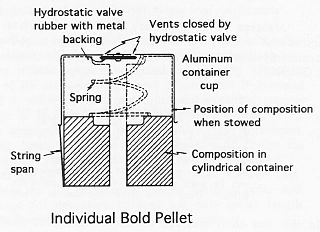
Bold was a German sonar decoy, used by U-boats during the Second World War from 1942 onwards. It consisted of a metal canister about 10 cm (3.9 in) in diameter filled with calcium hydride. It was launched by an ejector system colloquially referred to as Pillenwerfer.

Anti-submarine warfare is a branch of underwater warfare that uses surface warships, aircraft, submarines, or other platforms, to find, track, and deter, damage, or destroy enemy submarines. Such operations are typically carried out to protect friendly shipping and coastal facilities from submarine attacks and to overcome blockades.

German submarine U-1105, a Type VII-C/41 U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine, was built at the Nordseewerke Shipyard, Emden, Germany, and commissioned on 3 June 1944. Oberleutnant zur See Hans-Joachim Schwarz was given command. He would command U-1105 for the remainder of the war.

German submarine U-1308 was the last Type VIIC/41 submarine to be laid down, launched and commissioned by Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. The Oberkommando der Marine or OKM,, had decided near the end of World War II to put all of its resources into building newer types of Unterseeboot, such as the types XXI and XXIII. U-1308 was part of a batch of eight U-boats ordered on 1 August 1942 to be built at Flensburger Schiffbau-Gesellschaft, Flensburg. She was laid down on 16 February 1944 and launched on 22 November. The eight boats were commissioned over a 12-month period between February 1944 and 17 January 1945.
German submarine U-480 was an experimental Kriegsmarine Type VIIC U-boat of World War II.

A sonar decoy is a device for decoying sonar. Most are released from submarines to act as a false target.

German submarine U-1172 was a Type VIIC/41 U-boat built for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine for service during World War II. She was laid down on 7 June 1943 by Danziger Werft, Danzig as yard number 144, launched on 3 December 1943 and commissioned on 20 April 1944 under Oberleutnant zur See Jürgen Kuhlmann.
German submarine U-682 was a Type VIIC U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. The submarine was laid down on 21 December 1942 at the Howaldtswerke yard at Hamburg, launched on 7 March 1944, and commissioned on 17 April 1944 under the command of Leutnant zur See d.R. Sven Thienemann.

German submarine U-1306 was a Type VIIC/41 U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II.

German submarine U-1307 was a Type VIIC/41 U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II.











