External links
| This electronics-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Silicon Integration Initiative (Si2) is a non-profit consortium of semiconductor, systems, EDA, and manufacturing companies, focused on improving the way integrated circuits are designed and manufactured. Si2 was founded in 1988 as CAD Framework Initiative, Inc., abbreviated as CFI. On the 34th Design Automation Conference (DAC) in 1997 the name changed to Si2.
| This electronics-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |

Molecular nanotechnology (MNT) is a technology based on the ability to build structures to complex, atomic specifications by means of mechanosynthesis. This is distinct from nanoscale materials. Based on Richard Feynman's vision of miniature factories using nanomachines to build complex products, this advanced form of nanotechnology would make use of positionally-controlled mechanosynthesis guided by molecular machine systems. MNT would involve combining physical principles demonstrated by biophysics, chemistry, other nanotechnologies, and the molecular machinery of life with the systems engineering principles found in modern macroscale factories.

Gallium arsenide (GaAs) It is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a zinc blende crystal structure.

Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum, is a semiconductor containing silicon and carbon. It occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite. Synthetic SiC powder has been mass-produced since 1893 for use as an abrasive. Grains of silicon carbide can be bonded together by sintering to form very hard ceramics that are widely used in applications requiring high endurance, such as car brakes, car clutches and ceramic plates in bulletproof vests. Electronic applications of silicon carbide such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and detectors in early radios were first demonstrated around 1907. SiC is used in semiconductor electronics devices that operate at high temperatures or high voltages, or both. Large single crystals of silicon carbide can be grown by the Lely method and they can be cut into gems known as synthetic moissanite.

The Honda Civic is a line of cars manufactured by Honda. Originally a subcompact, the Civic has gone through several generational changes, becoming both larger and more upscale, moving into the compact car segment. EPA guidelines for vehicle size class stipulate a car having combined passenger and cargo room of 110 to 119.9 cubic feet is considered a mid-size car, and as such the tenth generation Civic sedan is technically a small-end mid-size car, although it still competes in the compact class. The Civic coupé is still considered a compact car. The Civic currently falls between the Honda City and Honda Accord.
SiGe, or silicon-germanium, is an alloy with any molar ratio of silicon and germanium, i.e. with a molecular formula of the form Si1−xGex. It is commonly used as a semiconductor material in integrated circuits (ICs) for heterojunction bipolar transistors or as a strain-inducing layer for CMOS transistors. IBM introduced the technology into mainstream manufacturing in 1989. This relatively new technology offers opportunities in mixed-signal circuit and analog circuit IC design and manufacture. SiGe is also used as a thermoelectric material for high temperature applications.

Accellera Systems Initiative (Accellera) is a standards organization that supports a mix of user and vendor standards and open interfaces development in the area of electronic design automation (EDA) and integrated circuit (IC) design and manufacturing. It is less constrained than the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and is therefore the starting place for many standards. Once mature and adopted by the broader community, the standards are usually transferred to the IEEE.
OpenAccess is a proprietary API controlled by the OpenAccess Coalition that aims to facilitate Interoperability of electronic design automation software among the members of that coalition.

The Honda del Sol is a 2-seater targa top car manufactured by Honda in the 1990s. Based on the Honda Civic platform, the del Sol was the successor to the popular Honda CR-X. It debuted in 1992 in Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States.
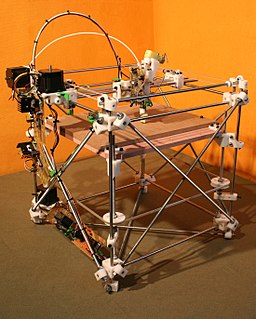
The open-design movement involves the development of physical products, machines and systems through use of publicly shared design information. This includes the making of both free and open-source software (FOSS) as well as open-source hardware. The process is generally facilitated by the Internet and often performed without monetary compensation. The goals and philosophy of the movement are identical to that of the open-source movement, but are implemented for the development of physical products rather than software. Open design is a form of co-creation, where the final product is designed by the users, rather than an external stakeholder such as a private company.

The Honda Civic Si is a sport compact trim of Honda's Civic. The Si trim was introduced for the third generation of Honda Civics in both Japan and North America. In Canada and elsewhere, the trim became known as the SiR for the sixth and seventh generations, and the Si trim was equivalent to the USDM EX model.
The Si2 Common Power Format, or CPF is a file format for specifying power-saving techniques early in the design process. In the design of integrated circuits, saving power is a primary goal, and designers are forced to use sophisticated techniques such as clock gating, multi-voltage logic, and turning off the power entirely to inactive blocks. These techniques require a consistent implementation in the design steps of logic design, implementation, and verification. For example, if multiple different power supplies are used, then logic synthesis must insert level shifters, place and route must deal with them correctly, and other tools such as static timing analysis and formal verification must understand these components. As power became an increasingly pressing concern, each tool independently added the features needed. Although this made it possible to build low power flows, it was difficult and error prone since the same information needed to be specified several times, in several formats, to many different tools. CPF was created as a common format that many tools can use to specify power-specific data, so that power intent only need be entered once and can be used consistently by all tools. The aim of CPF is to support an automated, power-aware design infrastructure.
Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) is an Indian state-owned aerospace and defence company with about nine factories, and several regional offices in India.

Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) are a subgroup of composite materials as well as a subgroup of ceramics. They consist of ceramic fibers embedded in a ceramic matrix. Both the matrix and the fibers can consist of any ceramic material, whereby carbon and carbon fibers can also be considered a ceramic material.

Bruce Foods Corporation, founded in New Iberia, Louisiana, in 1928, is one of "America's largest privately owned food manufacturers," manufacturing many food products under five major labels, and is credited with "pioneering the canning of Mexican food." With four stateside manufacturing plants, the company has more than 1,200 employees.

ODB++ is a proprietary CAD-to-CAM data exchange format used in the design and manufacture of electronic devices. Its purpose is to exchange printed circuit board design information between design and manufacturing and between design tools from different EDA/ECAD vendors. It was originally developed by Valor Computerized Systems, Ltd. as the job description format for their CAM system.
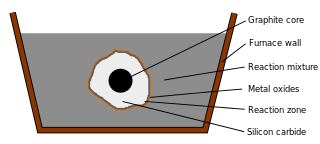
The Acheson process was invented by Edward Goodrich Acheson to synthesize silicon carbide (SiC) and graphite.

Make in India is an initiative by the Government of India to encourage companies to manufacture in India and incentivize dedicated investments into manufacturing. The policy approach was to create a conducive environment for investments, develop a modern and efficient infrastructure, and open up new sectors for foreign capital. The initiative targeted 25 economic sectors for job creation and skill enhancement, and aimed "to transform India into a global design and manufacturing hub."

KhalifaSat, also known as DubaiSat-3, is a remote sensing Earth observation satellite that was designed and built at the Space Technology Laboratories of the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Centre in Dubai. It is considered the first entirely Emirati-made satellite. It launched into orbit on 30 October 2018 from Japan's Tanegashima Space Center using the Korean Satrec SI-300 bus.

Amorphous silicon (a-Si) is the non-crystalline form of silicon used for solar cells and thin-film transistors in LCDs.
Satrec Initiative Co., Ltd. or SI or Satrec I is a South Korean satellite manufacturing company headquartered in Daejeon, South Korea The company was founded in 1999 by the engineers who developed the first Korean satellite (KITSAT-1) at KAIST Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTRec). The company designs and builds Earth observation satellites platform called SpaceEye-series, and SI provides various space components, including high resolution electro-optical payloads and star-trackers. SI's market entering began with a Malaysian Earth observation satellite, RazakSAT. SI has two subsidiaries, SI Imaging Service (SIIS), which is the main image data provider of KOMPSAT-series and SI Detection (SID), which provides radiation monitoring solutions.