
Amiga is a family of personal computers introduced by Commodore in 1985. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16- or 16/32-bit processors, 256 KB or more of RAM, mouse-based GUIs, and significantly improved graphics and audio compared to previous 8-bit systems. These systems include the Atari ST—released earlier the same year—as well as the Macintosh and Acorn Archimedes. Based on the Motorola 68000 microprocessor, the Amiga differs from its contemporaries through the inclusion of custom hardware to accelerate graphics and sound, including sprites and a blitter, and a pre-emptive multitasking operating system called AmigaOS.

A central processing unit (CPU)—also called a central processor or main processor—is the most important processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs).

In computer architecture, a bus is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This expression covers all related hardware components and software, including communication protocols.

A motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as the central processor, the chipset's input/output and memory controllers, interface connectors, and other components integrated for general use.
In processor design, microcode is a technique that interposes an intermediate layer between the central processing unit (CPU) hardware and the programmer-visible instruction set architecture of a computer.

A video game console is an electronic device that outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can be played with a game controller. These may be home consoles, which are generally placed in a permanent location connected to a television or other display devices and controlled with a separate game controller, or handheld consoles, which include their own display unit and controller functions built into the unit and which can be played anywhere. Hybrid consoles combine elements of both home and handheld consoles.

A debugger or debugging tool is a computer program used to test and debug other programs. The main use of a debugger is to run the target program under controlled conditions that permit the programmer to track its execution and monitor changes in computer resources that may indicate malfunctioning code. Typical debugging facilities include the ability to run or halt the target program at specific points, display the contents of memory, CPU registers or storage devices, and modify memory or register contents in order to enter selected test data that might be a cause of faulty program execution.
Multiprocessing is the use of two or more central processing units (CPUs) within a single computer system. The term also refers to the ability of a system to support more than one processor or the ability to allocate tasks between them. There are many variations on this basic theme, and the definition of multiprocessing can vary with context, mostly as a function of how CPUs are defined.

A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. The term workstation has been used loosely to refer to everything from a mainframe computer terminal to a PC connected to a network, but the most common form refers to the class of hardware offered by several current and defunct companies such as Sun Microsystems, Silicon Graphics, Apollo Computer, DEC, HP, NeXT, and IBM which powered the 3D computer graphics revolution of the late 1990s.

In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the central processing unit (CPU) without soldering.
JTAG is an industry standard for verifying designs and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture.

Embedded software is computer software, written to control machines or devices that are not typically thought of as computers, commonly known as embedded systems. It is typically specialized for the particular hardware that it runs on and has time and memory constraints. This term is sometimes used interchangeably with firmware.

Hardware acceleration is the use of computer hardware designed to perform specific functions more efficiently when compared to software running on a general-purpose central processing unit (CPU). Any transformation of data that can be calculated in software running on a generic CPU can also be calculated in custom-made hardware, or in some mix of both.
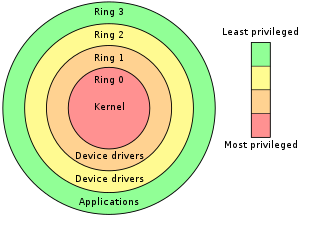
In computer science, hierarchical protection domains, often called protection rings, are mechanisms to protect data and functionality from faults and malicious behavior.
The Apple Network Server (ANS) was a line of PowerPC-based server computers designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Computer, Inc. from February 1996 to April 1997. It was codenamed "Shiner" and originally consisted of two models, the Network Server 500/132 and the Network Server 700/150, which got a companion model, the Network Server 700/200 with a faster CPU in November 1996.

Sun-1 was the first generation of UNIX computer workstations and servers produced by Sun Microsystems, launched in May 1982. These were based on a CPU board designed by Andy Bechtolsheim while he was a graduate student at Stanford University and funded by DARPA. The Sun-1 systems ran SunOS 0.9, a port of UniSoft's UniPlus V7 port of Seventh Edition UNIX to the Motorola 68000 microprocessor, with no window system. Early Sun-1 workstations and servers used the original Sun logo, a series of red "U"s laid out in a square, rather than the more familiar purple diamond shape used later.
In computing, an eFuse is a microscopic fuse put into a computer chip. This technology was invented by IBM in 2004 to allow for the dynamic real-time reprogramming of chips. In the abstract, computer logic is generally "etched" or "hard-wired" onto a chip and cannot be changed after the chip has finished being manufactured. By utilizing a set of eFuses, a chip manufacturer can allow for the circuits on a chip to change while it is in operation.

In computing, an emulator is hardware or software that enables one computer system to behave like another computer system. An emulator typically enables the host system to run software or use peripheral devices designed for the guest system. Emulation refers to the ability of a computer program in an electronic device to emulate another program or device.

Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the case, central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), monitor, mouse, keyboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, speakers and motherboard.













