See also
- Supermajority, a voting requirement of a specified level of support which is greater than the "one half" threshold used for a simple majority.
Simple majority may refer to:
Plurality voting refers to electoral systems in the candidates in an electoral district who poll more than any other are elected. Used for elections of various offices or representative bodies, it is often contrasted with proportional representation. Plurality voting is also called simple majority or relative majority voting, however, is it also often explicitly distinguished from majority voting, in which a winning candidate must receive an absolute majority of votes: more than half of all votes.

Proportional representation (PR) refers to any type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions among voters. The essence of such systems is that all votes cast – or almost all votes cast – contribute to the result and are effectively used to help elect someone – not just a bare plurality or (exclusively) the majority – and that the system produces mixed, balanced representation reflecting how votes are cast.

The two-round system (TRS), also known as runoff voting, second ballot, or ballotage, is a voting method used to elect a single candidate. The first round is held using simple plurality to choose the top-two candidates, and then in the second round the winner is chosen by majority vote. The two-round system is widely used in the election of legislative bodies and directly elected presidents.

Voting is a method by which a group, such as a meeting or an electorate, convenes together for the purpose of making a collective decision or expressing an opinion usually following discussions, debates or election campaigns. Democracies elect holders of high office by voting. Residents of a jurisdiction represented by an elected official are called "constituents", and the constituents who choose to cast a ballot for their chosen candidate are called "voters." There are different systems for collecting votes, but while many of the systems used in decision-making can also be used as electoral systems, any which cater to proportional representation can only be used in elections.
Block voting, also known as bloc voting, refers to certain electoral systems where multiple candidates are elected simultaneously. They do not guarantee minority representation and allow a group of voters to ensure that only their preferred candidates are elected. In these systems, a voter can select as many candidates as there are open seats. That is, the voter has as many votes to cast as the number of seats to fill. The block voting systems are among various election systems available for use in multi-member districts where the voting system allows for the selection of multiple winners at once.
A majority is more than half of a total. It is a subset of a set consisting of more than half of the set's elements. For example, if a group consists of 31 individuals, a majority would be 16 or more individuals, while having 15 or fewer individuals would not constitute a majority.

A plurality vote or relative majority describes the circumstance when a party, candidate, or proposition polls more votes than any other but does not receive more than half of all votes cast.
A supermajority is a requirement for a proposal to gain a specified level of support which is greater than the threshold of more than one-half used for a simple majority. Supermajority rules in a democracy can help to prevent a majority from eroding fundamental rights of a minority, but they can also hamper efforts to respond to problems and encourage corrupt compromises at times when action is taken. Changes to constitutions, especially those with entrenched clauses, commonly require supermajority support in a legislature. Parliamentary procedure requires that any action of a deliberative assembly that may alter the rights of a minority have a supermajority requirement, such as a two-thirds vote. In consensus democracy the supermajority rule is applied in most cases.
Majority rule is the principle that a group which has more than half of all voters should be allowed to make the decisions for a group. Majority rule is the binary decision rule most often used in decision-making bodies, including many legislatures of democratic nations. Where no one party wins a majority of the seats in a legislature, the majority of legislators that wields power is partly composed of members of other parties in support.
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, electorate, or (election) precinct, is a subdivision of a larger state created to provide its population with representation in the larger state's constituency. That body, or the state's constitution or a body established for that purpose, determines each district's boundaries and whether each will be represented by a single member or multiple members. Generally, only voters (constituents) who reside within the district are permitted to vote in an election held there. District representatives may be elected by a first-past-the-post system, a proportional representative system, or another voting method. They may be selected by a direct election under universal suffrage, an indirect election, or another form of suffrage.
The majority criterion is a voting system criterion. The criterion states that "if only one candidate is ranked first by a majority of voters, then that candidate must win."
The mutual majority criterion is a criterion for evaluating electoral system. It requires that whenever a majority of voters prefer a group of candidates above all others, someone from that group must win.
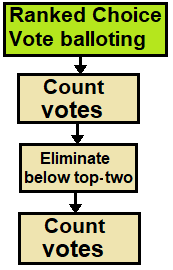
The contingent vote is an electoral system used to elect a single representative in which a candidate requires a majority of votes to win. It is a form of preferential voting. The voter ranks the candidates in order of preference, and when the votes are counted, the first preference votes only are counted. If no candidate has a majority of the votes cast, then all but the two leading candidates are eliminated and the votes received by the eliminated candidates are distributed among the two remaining candidates according to voters' preferences. This ensures that one candidate achieves a majority and is declared elected.
Deliberative assemblies – bodies that use parliamentary procedure to arrive at decisions – use several methods of voting on motions. The regular methods of voting in such bodies are a voice vote, a rising vote, and a show of hands. Additional forms of voting include a recorded vote and balloting.
The multiple non-transferable vote (MNTV) is a group of voting system, in which voters elect several representatives at once, with each voter having more than one vote. MNTV uses multi-member electoral districts or only one district, which contains all voters, which is used to provide at-large representation.
The term plurality refers to a part of a whole which is greater than any other part, but not necessarily a majority. It can also refer to the state of being plural, i.e. as a synonym for multiplicity.
Plurality block voting, also known as plurality-at-large voting, bloc vote or block voting (BV) is a non-proportional voting system for electing representatives in multi-winner elections. Each voter may cast as many votes as the number of seats to be filled. The usual result when the candidates divide into parties is that the most popular party in the district sees its full slate of candidates elected in a seemingly landslide victory.
Instant-runoff voting (IRV), also known as plurality with elimination or plurality loser, is a ranked-choice voting system that modifies plurality by repeatedly eliminating the last-place finisher until only one candidate is left. In the United Kingdom, it is generally called the alternative vote (AV). In the United States, IRV is often conflated with ranked-choice voting (RCV); however, this conflation is not completely standard, and social choice theorists tend to prefer more explicit terms.
An electoral system or voting system is a set of rules that determine how elections and referendums are conducted and how their results are determined. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, non-profit organisations and informal organisations. These rules govern all aspects of the voting process: when elections occur, who is allowed to vote, who can stand as a candidate, how ballots are marked and cast, how the ballots are counted, how votes translate into the election outcome, limits on campaign spending, and other factors that can affect the result. Political electoral systems are defined by constitutions and electoral laws, are typically conducted by election commissions, and can use multiple types of elections for different offices.
The 2020 French municipal elections were held from 15 March to 28 June to renew the municipal councils of the approximately 35,000 French communes. The first round took place on 15 March and the second round was postponed to 28 June due to the COVID-19 pandemic.