Related Research Articles

Film editing is both a creative and a technical part of the post-production process of filmmaking. The term is derived from the traditional process of working with film which increasingly involves the use of digital technology. When putting together some sort of video composition, typically, you would need a collection of shots and footages that vary from one another. The act of adjusting the shots you have already taken, and turning them into something new is known as film editing.

Video editing software or a video editor is software used for performing the post-production video editing of digital video sequences on a non-linear editing system (NLE). It has replaced traditional flatbed celluloid film editing tools and analog video tape editing machines.

In telecommunications and computer networking, multiplexing is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share a scarce resource – a physical transmission medium. For example, in telecommunications, several telephone calls may be carried using one wire. Multiplexing originated in telegraphy in the 1870s, and is now widely applied in communications. In telephony, George Owen Squier is credited with the development of telephone carrier multiplexing in 1910.

Aleatoricmusic is music in which some element of the composition is left to chance, and/or some primary element of a composed work's realization is left to the determination of its performer(s). The term is most often associated with procedures in which the chance element involves a relatively limited number of possibilities.
Sound design is the art and practice of creating soundtracks for a variety of needs. It involves specifying, acquiring or creating auditory elements using audio production techniques and tools. It is employed in a variety of disciplines including filmmaking, television production, video game development, theatre, sound recording and reproduction, live performance, sound art, post-production, radio, new media and musical instrument development. Sound design commonly involves performing and editing of previously composed or recorded audio, such as sound effects and dialogue for the purposes of the medium, but it can also involve creating sounds from scratch through synthesizers. A sound designer is one who practices sound design.
Cross-cutting is an editing technique most often used in films to establish action occurring at the same time, and often in the same place. In a cross-cut, the camera will cut away from one action to another action, which can suggest the simultaneity of these two actions but this is not always the case. Cross-cutting can also be used for characters in a film with the same goals but different ways of achieving them.

Compositing is the process or technique of combining visual elements from separate sources into single images, often to create the illusion that all those elements are parts of the same scene. Live-action shooting for compositing is variously called "chroma key", "blue screen", "green screen" and other names. Today, most, though not all, compositing is achieved through digital image manipulation. Pre-digital compositing techniques, however, go back as far as the trick films of Georges Méliès in the late 19th century, and some are still in use.
This article contains a list of cinematic techniques that are divided into categories and briefly described.
Montage is a film editing technique in which a series of short shots are sequenced to condense space, time, and information.

The single-camera setup, or single-camera mode of production, also known as portable single crew, portable single camera or single-cam, is a method of filmmaking and video production.
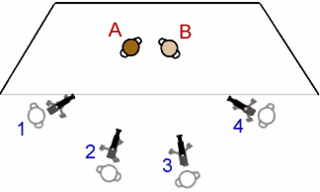
The multiple-camera setup, multiple-camera mode of production, multi-camera or simply multicam is a method of filmmaking and video production. Several cameras—either film or professional video cameras—are employed on the set and simultaneously record or broadcast a scene. It is often contrasted with a single-camera setup, which uses one camera.

Soviet montage theory is an approach to understanding and creating cinema that relies heavily upon editing. It is the principal contribution of Soviet film theorists to global cinema, and brought formalism to bear on filmmaking.

Stem-mixing is a method of mixing audio material based on creating groups of audio tracks and processing them separately prior to combining them into a final master mix. Stems are also sometimes referred to as submixes, subgroups, or buses.

L'Inhumaine is a 1924 French science fiction drama film directed by Marcel L'Herbier. It has the subtitle histoire féerique. L'Inhumaine is notable for its experimental techniques and for the collaboration of many leading practitioners in the decorative arts, architecture and music. The film caused controversy on its release.

A film – also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick – is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere through the use of moving images. These images are generally accompanied by sound and, more rarely, other sensory stimulations. The word "cinema", short for cinematography, is often used to refer to filmmaking and the film industry, and the art form that is the result of it.

The arts are a wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling, and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing, and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both dynamic and a characteristically constant feature of human life, they have developed into innovative, stylized, and sometimes intricate forms. This is often achieved through sustained and deliberate study, training, and/or theorizing within a particular tradition, across generations, and even between civilizations. The arts are a vehicle through which human beings cultivate distinct social, cultural, and individual identities while transmitting values, impressions, judgements, ideas, visions, spiritual meanings, patterns of life, and experiences across time and space.

Woman with a Horse is a large oil painting created toward the end of 1911, early 1912, by the French artist Jean Metzinger (1883–1956). The work was exhibited in Paris at the Salon des Indépendants in 1912 and the Salon de la Section d'Or, 1912. The following year La Femme au Cheval was reproduced in The Cubist Painters, Aesthetic Meditations by Guillaume Apollinaire (1913).

The Bathers {French: Les Baigneuses) is a large oil painting created at the outset of 1912 by the French artist Albert Gleizes. It was exhibited at the Salon des Indépendants in Paris during the spring of 1912; the Salon de la Société Normande de Peinture Moderne, Rouen, summer 1912; and the Salon de la Section d'Or, autumn 1912. The painting was reproduced in Du "Cubisme", written by Albert Gleizes and Jean Metzinger the same year: the first and only manifesto on Cubism. Les Baigneuses, while still 'readable' in the figurative or representational sense, exemplifies the mobile, dynamic fragmentation of form and multiple perspective characteristic of Cubism at the outset of 1912. Highly sophisticated, both in theory and in practice, this aspect of simultaneity would soon become identified with the practices of the Section d'Or group. Gleizes deploys these techniques in "a radical, personal and coherent manner". Purchased in 1937, the painting is exhibited in the permanent collection of the Musée d'Art Moderne de la Ville de Paris.
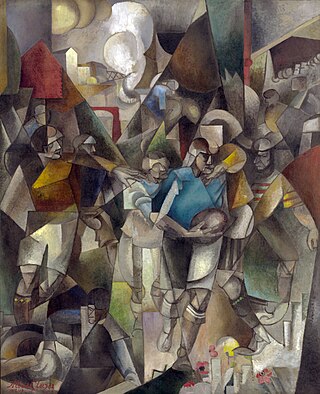
Football Players is a 1912–13 painting by the French artist Albert Gleizes. The work was exhibited at the Salon des Indépendants, Paris, March–May 1913. September through December 1913 the painting was exhibited at Erster Deutscher Herbstsalon, Berlin. The work was featured at Galeries Dalmau in Barcelona, 29 November – 12 December 1916, Gleizes' first one-person show. The work was again exhibited at Galeries Dalmau 16 October – 6 November 1926. Stylistically Gleizes' Football Players exemplifies the principle of mobile perspective laid out in Du "Cubisme", written by himself and French painter Jean Metzinger. Guillaume Apollinaire wrote about Les Joueurs de football in an article titled "Le Salon des indépendants", published in L'Intransigeant, 18 March 1913, and again in "A travers le Salon des indépendants", published in Montjoie!, Numéro Spécial, 18 March 1913.

Les Peintres Cubistes, Méditations Esthétiques, is a book written by Guillaume Apollinaire between 1905 and 1912, published in 1913. This was the third major text on Cubism; following Du "Cubisme" by Albert Gleizes and Jean Metzinger (1912); and André Salmon, Histoire anecdotique du cubisme (1912).
References
- 1 2 Read, Gray (2014). Modern Architecture in Theatre: The Experiments of Art et Action. Palgrave MacMillan. p. 3. ISBN 9781349474752 . Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- ↑ Kern, Stephen (2003). The Culture of Time and Space, 1880-1918: With a New Preface. Harvard University Press. p. 30. ISBN 9780674021693 . Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- ↑ Music In Video Games: Studying Play. Routledge. 2014-03-26. p. 118. ISBN 9781134692040 . Retrieved 31 July 2019.