
Hartleton is a borough in Union County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 247 at the 2020 census. The borough, as well as the adjoining township of Hartley, are both named for Colonel Thomas Hartley, American politician and Revolutionary War leader, and local landowner. An alternative name was Hartleyton and later shortened to the present name. The original name was Kester's, and named for Peter Kester who was the first tenant of Hartley. Kester's was at the intersection of "great Reuben Haines road" from Northumberland through Dry Valley, New Berlin and the Penns Valley Narrows, and the first public road laid out in the area by Northumberland County court from Northumberland through Derrstown (Lewisburg) and Mifflinburg. Hartley never lived there, as his home was in York, PA. Hartley acquired the land in 1784 from original purchaser Colonel Philip Cole after Cole left the area because of the "Big Runaway" of 1778. Cole purchased the land in 1773, and was living there in 1775. Hartley laid out a town as early as 1798, and the first lot sold in 1799.

Uzturre is a modest mountain in Gipuzkoa, Basque Country of Spain. The mountain is an iconic landmark towering over Tolosa at 730 m (2,400 ft) high, very popular with the locals of the town and villages around.
Albion Correctional Facility is a medium security women's prison in Town of Albion, Orleans County, New York, United States, that is operated by the New York State Department of Correctional Services. The site was founded in 1894 as the Western House of Refuge for Women, then later the Albion State Training School. The prison is just outside the village of Albion.

Ramos Arizpe is a city and seat of the surrounding municipality of the same name in the Mexican state of Coahuila. Ramos Arizpe is located 11 km from the state capital of Saltillo. It is part of the Saltillo metropolitan area. The city reported a population of 48,228 in the 2005 census; the municipality had a population of 56,708. Its area is 5,306.6 km2.

Cananea is a municipality in the northern portion of the Mexican state of Sonora, on the U.S. border. Its municipal seat is the city of Cananea, located at 30°58′55″N110°18′02″W.

The Archdiocese of Hermosillo is a Roman Catholic Archdiocese located in Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico. Its area is 90,959 sq. miles, and its population (2004) 1,067,051. The bishop resides at Hermosillo.
Sylvania is a neighborhood of Louisville, Kentucky located near Terry Road along Sylvania Road.

Arizpe is a small town and the municipal seat of the Arizpe Municipality in the north of the Mexican state of Sonora. It is located at 30°20'"N 110°09'"W. The area of the municipality is 2,806.78 sq.km. The population in 2005 was 2,959 of which 1,743 lived in the municipal seat as of the 2000 census.

Bacoachi is a small town in Bacoachi Municipality in the north of the Mexican state of Sonora. The area of the municipality is 487 square miles (1,260.65 km2) and the population was 1,456 in 2005, with 924 inhabitants residing in the municipal seat. The elevation of the municipal seat is 4,429 feet above sea level.
Bácum is a small city and the county seat of Bácum Municipality, located in the south of the Mexican state of Sonora at 27°32′N110°05′W.
Banámichi is a small town in the north of the Mexican state of Sonora. It serves as the seat for the surrounding municipality of the same name. Geographical coordinates are 30°01′N110°13′W.

Baviácora is a small town and the municipal seat of the surrounding municipality of the Mexican state of Sonora. The geographical coordinates are 29°42′N110°09′W.

Art is an unincorporated community in Perry Township, Clay County, Indiana. It is part of the Terre Haute Metropolitan Statistical Area.
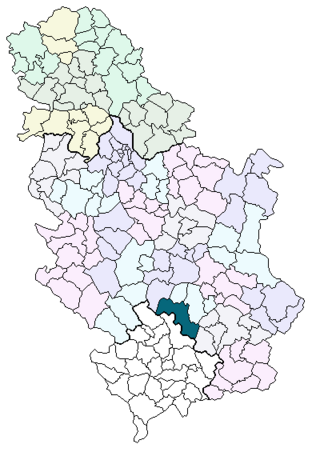
Gornja Mikuljana is a village in Serbia situated in the municipality of Kuršumlija, and the district of Toplica. In 2002, it had 117 inhabitants, of which 110 were Serbs (94,01%).

Cedar Crest is an unincorporated community in Fresno County, California. It is located on the north side of Huntington Lake 3.5 miles (5.6 km) northeast of Big Creek, at an elevation of 7077 feet. Cedar Crest was established as a resort community for boaters and hunters in the early 1920s.

Arizpe is a municipality in the state of Sonora in north-western Mexico. The municipality of Arizpe is one of the 72 municipalities of the state of Sonora, located in the north-central region of the state in the Sierra Madre Occidental area. It has 72 localities within the municipality, its municipal seat and the most populated locality is the homonymous town of Arizpe, while other important ones are: Sinoquipe, Bacanuchi and Chinapa. It was named for the first time as a municipality in 1813 and according to the 14th Population and Housing Census carried out in 2020 by the National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI) the municipality has a total population of 2,788 inhabitants. This municipality has an area of 1,186.56 square miles. Its Gross Domestic Product per capita is USD 11,012, and its Human Development Index (HDI) is 0.8292.

Cumpas is a municipality in the state of Sonora in north-western Mexico. The municipal seat is at Cumpas.

Gare de Carentan is a railway station serving the town Carentan, Manche department, Normandy, northwestern France.
Spanker is an unincorporated community in Montgomery County, in the U.S. state of Ohio.
Masters is an extinct town in Weld County, in the U.S. state of Colorado. The GNIS classifies it as a populated place.













