Yahualica is a town and municipality in the northeastern part of Jalisco, Mexico. It is one of the 125 municipalities that make up the state of Jalisco.

Cocula is a city and municipality in the Mexican state of Jalisco. It is located 35 miles (56 km) southwest of Guadalajara, on Mexico Highway 80. It sits at an elevation of 4,460 feet (1,360 m). According to the 2020 census, the population of the municipality was 29,267 with 16,550 inhabitants living in the city. Other important towns in the municipality are Cofradía de la Luz, La Sauceda, and Santa Teresa.
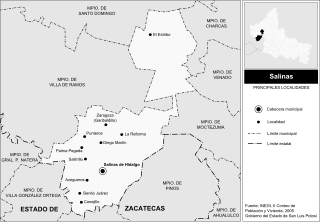
Salinas de Hidalgo, San Luis Potosí, Mexico also known as Salinas del Peñón Blanco, is a small town located in the northwestern part of the state. It is the seat of Salinas municipality in Mexico.
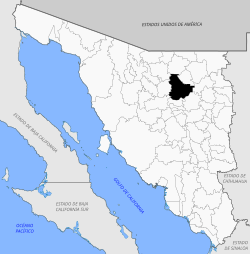
Ures is a small city and a municipality in the Mexican state of Sonora.

Zapotlanejo is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Jalisco.

Zapotiltic is a town and municipality in the south region of the state of Jalisco, Mexico. It is located approximately 115 km south of Guadalajara. According to the "Conteo de Poblacion y Vivienda of 2015" the municipality had a population of 29,190.

Acatlán de Juárez is a town and municipality, in Jalisco in central-western Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 154 km².

Amacueca is a town and municipality, in Jalisco in central-western Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 124.8 km2.
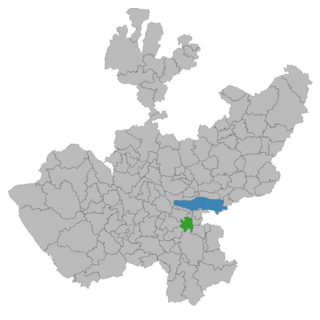
Concepción de Buenos Aires is a town and municipality, in Jalisco in central-western Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 265.6 km2.

El Arenal is a town and municipality in the state of Jalisco in central-western Mexico. El Arenal is known as the gateway to the so-called "blue agave" region in the Jaliscan Highlands. The municipality has an area of approximately 111.8 square kilometres (43.2 sq mi).

Jilotlán de los Dolores is a town and municipality, in Jalisco in central-western Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 1511.78 km2.

Villa Purificación is a town and municipality, in Jalisco in central-western Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 1,848 km².

Zapotitlán de Vadillo is a town and municipality, in Jalisco in central-western Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 305.8 km2.
Huatabampo is a municipality in the state of Sonora in northwestern Mexico, being the southernmost municipality in Sonora. As of 2015, the municipality had a total population of 80,524.

Ímuris is a municipality in the state of Sonora in north-western Mexico.

Magdalena is a municipality in the state of Sonora in northwestern Mexico. In the 2020 Census, the municipality reported a total population of 33,049, up by 11.2% from the 2010 result.

Puerto Peñasco is a municipality in the state of Sonora in north-western Mexico. As of 2015, the municipality had a total population of 62,177 inhabitants. The only locality with a significant population is the municipal seat, also named Puerto Peñasco, which contains almost 99% of the municipality's population.

San Luis Río Colorado is a municipality in the state of Sonora in northwestern Mexico, being the northwesternmost municipality in Sonora and covering an area of 8412.75 km2.
Charcas is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of San Luis Potosí. The municipality covers an area of 4.911 km2. As of 2020, the municipality had a total population of 14,117 people. Charcas is just south of the Tropic of Cancer. Due to its elevation of 2,219 metres (7,280 ft), the climate is mild.