In Greek mythology, Achilles or Achilleus was a hero of the Trojan War who was known as being the greatest of all the Greek warriors. A central character in Homer's Iliad, he was the son of the Nereid Thetis and Peleus, king of Phthia and famous Argonaut. Achilles was raised in Phthia along with his childhood companion Patroclus and received his education by the centaur Chiron. In the Iliad, he is presented as the commander of the mythical tribe of the Myrmidons.

Ares is the Greek god of war and courage. He is one of the Twelve Olympians, and the son of Zeus and Hera. The Greeks were ambivalent towards him. He embodies the physical valor necessary for success in war but can also personify sheer brutality and bloodlust, in contrast to his sister Athena, whose martial functions include military strategy and generalship. An association with Ares endows places, objects, and other deities with a savage, dangerous, or militarized quality.

In ancient Greek religion, Hera is the goddess of marriage, women, and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she is queen of the twelve Olympians and Mount Olympus, sister and wife of Zeus, and daughter of the Titans Cronus and Rhea. One of her defining characteristics in myth is her jealous and vengeful nature in dealing with any who offended her, especially Zeus's numerous adulterous lovers and illegitimate offspring.

Homer was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the Iliad and the Odyssey, two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the most revered and influential authors in history.

Hephaestus is the Greek god of artisans, blacksmiths, carpenters, craftsmen, fire, metallurgy, metalworking, sculpture and volcanoes. Hephaestus's Roman counterpart is Vulcan. In Greek mythology, Hephaestus was either the son of Zeus and Hera or he was Hera's parthenogenous child. He was cast off Mount Olympus by his mother Hera because of his lameness, the result of a congenital impairment; or in another account, by Zeus for protecting Hera from his advances.

In Greek mythology, Cedalion or Kedalion was a servant of Hephaestus in Lemnos. According to one tradition, he was Hephaestus's tutor, with whom Hera fostered her son on Naxos to teach him smithcraft. Kerenyi compares him to the Cabeiri, to Chiron, and to Prometheus.

The name Pelasgians was used by Classical Greek writers to refer either to the predecessors of the Greeks, or to all the inhabitants of Greece before the emergence of the Greeks. In general, "Pelasgian" has come to mean more broadly all the indigenous inhabitants of the Aegean Sea region and their cultures, and British historian Peter Green comments on it as "a hold-all term for any ancient, primitive and presumably indigenous people in the Greek world".

Lemnos or Limnos is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Myrina. At 477.583 square kilometres (184.396 sq mi), it is the 8th-largest island of Greece.

In ancient Greek religion and mythology, the twelve Olympians are the major deities of the Greek pantheon, commonly considered to be Zeus, Poseidon, Hera, Demeter, Aphrodite, Athena, Artemis, Apollo, Ares, Hephaestus, Hermes, and either Hestia or Dionysus. They were called Olympians because, according to tradition, they resided on Mount Olympus.

In Greek mythology, Nestor of Gerenia was a legendary king of Pylos. He is a prominent secondary character in Homer's Iliad and Odyssey, where he appears as an elderly warrior who frequently offers long-winded advice to the other characters.

The Epic Cycle was a collection of Ancient Greek epic poems, composed in dactylic hexameter and related to the story of the Trojan War, including the Cypria, the Aethiopis, the so-called Little Iliad, the Iliupersis, the Nostoi, and the Telegony. Scholars sometimes include the two Homeric epics, the Iliad and the Odyssey, among the poems of the Epic Cycle, but the term is more often used to specify the non-Homeric poems as distinct from the Homeric ones.
The Cypria is a lost epic poem of ancient Greek literature, which has been attributed to Stasinus and was quite well known in classical antiquity and fixed in a received text, but which subsequently was lost to view. It was part of the Epic Cycle, which told the entire history of the Trojan War in epic hexameter verse. The story of the Cypria comes chronologically at the beginning of the Epic Cycle, and is followed by that of the Iliad; the composition of the two was apparently in the reverse order. The poem comprised eleven books of verse in epic dactylic hexameters.
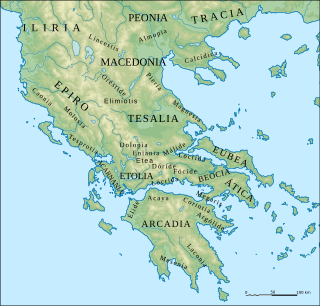
The Molossians were a group of ancient Greek tribes which inhabited the region of Epirus in classical antiquity. Together with the Chaonians and the Thesprotians, they formed the main tribal groupings of the northwestern Greek group. On their northern frontier, they neighbored the Chaonians and on their southern frontier neighbored the kingdom of the Thesprotians. They formed their own state around 370 BC and were part of the League of Epirus. The most famous Molossian ruler was Pyrrhus of Epirus, considered one of the greatest generals of antiquity. The Molossians sided against Rome in the Third Macedonian War and were defeated. Following the war, the region witnessed devastation while a considerable number of Molossians and other Epirotes were enslaved and transported to the Roman Republic, overwhelmingly in the Italian Peninsula itself.
Eurynome was a deity of ancient Greek religion worshipped at a sanctuary near the confluence of rivers called the Neda and the Lymax in classical Peloponnesus. She was represented by a statue of what we would call a mermaid. Tradition, as reported by the Greek traveller, Pausanias, identified her with the Oceanid, or "daughter of Ocean", of Greek poetry.

The Homeric Question concerns the doubts and consequent debate over the identity of Homer, the authorship of the Iliad and Odyssey, and their historicity. The subject has its roots in classical antiquity and the scholarship of the Hellenistic period, but has flourished among Homeric scholars of the 19th, 20th, and 21st centuries.

The shield of Achilles is the shield that Achilles uses in his fight with Hector, famously described in a passage in Book 18, lines 478–608 of Homer's Iliad. The intricately detailed imagery on the shield has inspired many different interpretations of its significance.

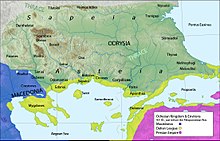
Heraclea Sintica, also known as Heraclea Strymonike, was an ancient Greek city located near what is now the village of Rupite in the modern region of Pirin Macedonia in modern south-western Bulgaria.

The Iliad is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the Odyssey, the poem is divided into 24 books and was written in dactylic hexameter. It contains 15,693 lines in its most widely accepted version. Set towards the end of the Trojan War, a ten-year siege of the city of Troy by a coalition of Mycenaean Greek states, the poem depicts significant events in the siege's final weeks. In particular, it depicts a fierce quarrel between King Agamemnon and a celebrated warrior, Achilles. It is a central part of the Epic Cycle. The Iliad is often regarded as the first substantial piece of European literature.

Sintice or Sintike was an ancient region and later district of the kingdom of Macedon. It was located north of Bisaltia and Odomantike up to Messapio mount and west of Crestonia and South Paeonia to Strymon river and Orvilos mount. Its name is derived from the Sintians, a tribe which once inhabited the region. Beyond it, was stretching Medike which was held by the powerful Thracian tribe of Medi with which the Macedonians were in constant wars.

Dolopia is a mountainous region of Greece, located north of Aetolia.