Related Research Articles
In the field of numerical analysis, the condition number of a function with respect to an argument measures how much the output value of the function can change for a small change in the input argument. This is used to measure how sensitive a function is to changes or errors in the input, and how much error in the output results from an error in the input. Very frequently, one is solving the inverse problem – given one is solving for x, and thus the condition number of the (local) inverse must be used. In linear regression the condition number of the moment matrix can be used as a diagnostic for multicollinearity.

Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the technology of indoor and vehicular environmental comfort. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation, as HVAC&R or HVACR or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR.

Operant conditioning is a learning process through which the strength of a behavior is modified by reinforcement or punishment. It is also a procedure that is used to bring about such learning.
In statistics, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a method of estimating the parameters of a statistical model, given observations. The method obtains the parameter estimates by finding the parameter values that maximize the likelihood function. The estimates are called maximum likelihood estimates, which is also abbreviated as MLE.
Calculus of variations is a field of mathematical analysis that uses variations, which are small changes in functions and functionals, to find maxima and minima of functionals: mappings from a set of functions to the real numbers. Functionals are often expressed as definite integrals involving functions and their derivatives. Functions that maximize or minimize functionals may be found using the Euler–Lagrange equation of the calculus of variations.
Classical conditioning refers to a learning procedure in which a biologically potent stimulus is paired with a previously neutral stimulus. It also refers to the learning process that results from this pairing, through which the neutral stimulus comes to elicit a response that is usually similar to the one elicited by the potent stimulus. These basic facts, which require many qualifications, were first studied in detail by Ivan Pavlov through experiments with dogs and published in 1897. Together with operant conditioning, classical conditioning became the foundation of behaviorism, a school of psychology which was dominant in the mid-20th century and is still an important influence on the practice of psychological therapy and the study of animal behavior. Classical conditioning is a basic learning process, and its neural substrates are now beginning to be understood.
Hypersexuality is a clinical diagnosis used by mental healthcare professionals for extremely frequent or suddenly increased libido. Nymphomania and satyriasis were terms previously used for the condition, in women and men respectively.

Dough is a thick, malleable, sometimes elastic, paste made out of any grains, leguminous or chestnut crops. Dough is typically made by mixing flour with a small amount of water and/or other liquid, and sometimes includes flour yeast or other leavening agents as well as other ingredients such as various fats or flavorings.

Savant syndrome is a condition in which someone with significant mental disabilities demonstrates certain abilities far in excess of average. The skills at which savants excel are generally related to memory. This may include rapid calculation, artistic ability, map making, or musical ability. Usually just one special skill is present.
In functional analysis, a bounded linear operator is a linear transformation L between normed vector spaces X and Y for which the ratio of the norm of L(v) to that of v is bounded above by the same number, over all non-zero vectors v in X. In other words, there exists some such that for all v in X
Blue balls is slang for the condition of temporary fluid congestion (vasocongestion) in the testicles accompanied by testicular pain, caused by prolonged sexual arousal in the human male without ejaculation. The term is thought to have originated in the United States, first appearing in 1916. Some urologists call this condition "epididymal hypertension". The condition is not experienced by all males.
In medicine, a differential diagnosis is the distinguishing of a particular disease or condition from others that present similar clinical features. Differential diagnostic procedures are used by physicians to diagnose the specific disease in a patient, or, at least, to eliminate any imminently life-threatening conditions. Often, each individual option of a possible disease is called a differential diagnosis.
The old quantum theory is a collection of results from the years 1900–1925 which predate modern quantum mechanics. The theory was never complete or self-consistent, but was rather a set of heuristic corrections to classical mechanics. The theory is now understood as the semi-classical approximation to modern quantum mechanics.
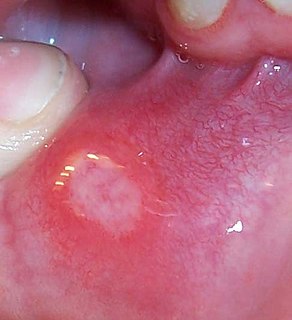
Aphthous stomatitis is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of benign and non-contagious mouth ulcers (aphthae) in otherwise healthy individuals. The informal term canker sores is also used, mainly in North America, although this may also refer to any mouth ulcers.

Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum, often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin, and also usually accompanied by an increase in the granular layer. As the corneum layer normally varies greatly in thickness in different sites, some experience is needed to assess minor degrees of hyperkeratosis.

Fissured tongue is a benign condition characterized by deep grooves (fissures) in the dorsum of the tongue. Although these grooves may look unsettling, the condition is usually painless. Some individuals may complain of an associated burning sensation.

Air conditioning is the process of removing heat and moisture from the interior of an occupied space, to improve the comfort of occupants. Air conditioning can be used in both domestic and commercial environments. This process is most commonly used to achieve a more comfortable interior environment, typically for humans and other animals; however, air conditioning is also used to cool/dehumidify rooms filled with heat-producing electronic devices, such as computer servers, power amplifiers, and even to display and store some delicate products, such as artwork.
Trachyonychia, sometimes called sandpapered nails, is a condition characterized by rough accentuated linear ridges on the nails of the fingers and toes. When the condition occurs on all the twenty nails of the fingers and toes, it is known as twenty-nail dystrophy, most evident in childhood, favoring males.
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, Bazex syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by psoriasiform changes of hands, feet, ears, and nose, with involvement of the nails and periungual tissues being characteristic and indistinguishable from psoriatic nails. The condition is associated with carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.
Sexual sadism disorder is the condition of experiencing sexual arousal in response to the extreme pain, suffering or humiliation of others. Several other terms have been used to describe the condition, and the condition may overlap with other conditions that involve inflicting pain. It is distinct from situations in which consenting individuals use mild or simulated pain or humiliation for sexual excitement. The words sadism and sadist are derived from Marquis de Sade.
References
- 1 2 Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. pp. 1587–8, 1778. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
| This dermatology article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |