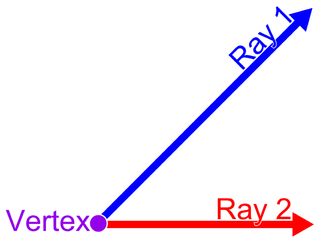
In Euclidean geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays, called the sides of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle. Angles formed by two rays lie in the plane that contains the rays. Angles are also formed by the intersection of two planes. These are called dihedral angles. Two intersecting curves may also define an angle, which is the angle of the rays lying tangent to the respective curves at their point of intersection.
Sensitivity may refer to:
Point or points may refer to:
Perfect commonly refers to:
Coherence, coherency, or coherent may refer to the following:
The statistical power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis when a specific alternative hypothesis is true. It is commonly denoted by , and represents the chances of a "true positive" detection conditional on the actual existence of an effect to detect. Statistical power ranges from 0 to 1, and as the power of a test increases, the probability of making a type II error by wrongly failing to reject the null hypothesis decreases.
Quantity or amount is a property that can exist as a multitude or magnitude, which illustrate discontinuity and continuity. Quantities can be compared in terms of "more", "less", or "equal", or by assigning a numerical value multiple of a unit of measurement. Mass, time, distance, heat, and angle are among the familiar examples of quantitative properties.
SMA or S.M.A. may refer to:
A ranking is a relationship between a set of items such that, for any two items, the first is either "ranked higher than", "ranked lower than" or "ranked equal to" the second. In mathematics, this is known as a weak order or total preorder of objects. It is not necessarily a total order of objects because two different objects can have the same ranking. The rankings themselves are totally ordered. For example, materials are totally preordered by hardness, while degrees of hardness are totally ordered. If two items are the same in rank it is considered a tie.
In mathematics, infinity plus one is a concept which has a well-defined formal meaning in some number systems, and may refer to:

In mathematics, the sign of a real number is its property of being either positive, negative, or zero. Depending on local conventions, zero may be considered as being neither positive nor negative, or it may be considered both positive and negative. Whenever not specifically mentioned, this article adheres to the first convention.

In mathematics, the irrational numbers are all the real numbers that are not rational numbers. That is, irrational numbers cannot be expressed as the ratio of two integers. When the ratio of lengths of two line segments is an irrational number, the line segments are also described as being incommensurable, meaning that they share no "measure" in common, that is, there is no length, no matter how short, that could be used to express the lengths of both of the two given segments as integer multiples of itself.
Validity or Valid may refer to:
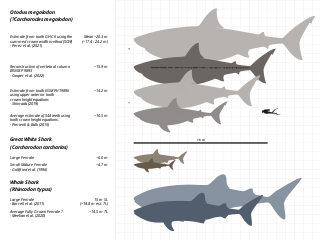
Size in general is the magnitude or dimensions of a thing. More specifically, geometrical size can refer to linear dimensions, area, or volume. Size can also be measured in terms of mass, especially when assuming a density range.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.



