This article appears to be a dictionary definition .(May 2023) |
Skin tracks are a cutaneous condition that result secondary to intravenous drug abuse. [1]
This article appears to be a dictionary definition .(May 2023) |
Skin tracks are a cutaneous condition that result secondary to intravenous drug abuse. [1]

A skin tag, or acrochordon, is a small benign tumor that forms primarily in areas where the skin forms creases, such as the neck, armpit and groin. They may also occur on the face, usually on the eyelids. Though tags up to half an inch long have been seen, they are typically the size of a grain of rice. The surface of an acrochordon may be smooth or irregular in appearance and is often raised from the surface of the skin on a fleshy stalk called a peduncle. Microscopically, an acrochordon consists of a fibrovascular core, sometimes also with fat cells, covered by an unremarkable epidermis. However, tags may become irritated by shaving, clothing, jewellery or eczema.
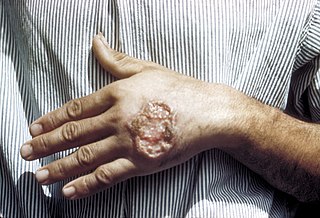
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by parasites of the Trypanosomatida genus Leishmania. It is generally spread through the bite of phlebotomine sandflies, Phlebotomus and Lutzomyia, and occurs most frequently in the tropics and sub-tropics of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and southern Europe. The disease can present in three main ways: cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral. The cutaneous form presents with skin ulcers, while the mucocutaneous form presents with ulcers of the skin, mouth, and nose. The visceral form starts with skin ulcers and later presents with fever, low red blood cell count, and enlarged spleen and liver.

Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma (cSCC), or squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin, also known as squamous-cell skin cancer, is one of the main types of skin cancer along with basal-cell carcinoma and melanoma. It usually presents as a hard lump with a scaly top but can also form an ulcer. Onset is often over months. Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma is more likely to spread to distant areas than basal cell cancer. When confined to the outermost layer of the skin, a precancerous or in situ form of cSCC is known as Bowen's disease.

A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, and is only named that because it looks like one. It is characterized by polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules and plaques with overlying, reticulated, fine white scale, commonly affecting dorsal hands, flexural wrists and forearms, trunk, anterior lower legs and oral mucosa. The hue may be gray-brown in people with darker skin. Although there is a broad clinical range of LP manifestations, the skin and oral cavity remain as the major sites of involvement. The cause is unknown, but it is thought to be the result of an autoimmune process with an unknown initial trigger. There is no cure, but many different medications and procedures have been used in efforts to control the symptoms.

Mycosis fungoides, also known as Alibert-Bazin syndrome or granuloma fungoides, is the most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It generally affects the skin, but may progress internally over time. Symptoms include rash, tumors, skin lesions, and itchy skin.
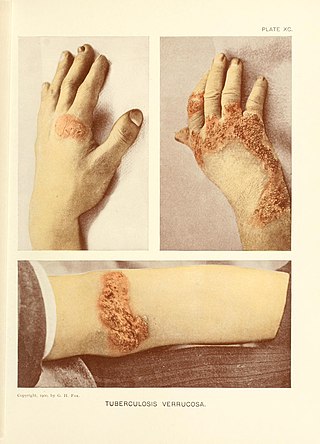
Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis is a rash of small, red papules and nodules in the skin that may appear two to four weeks after inoculation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a previously infected and immunocompetent individual.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a sensory nerve of the thigh. It is a branch of the sacral plexus. It supplies the skin of the posterior surface of the thigh, leg, buttock, and also the perineum.

The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a cutaneous nerve of the thigh. It originates from the dorsal divisions of the second and third lumbar nerves from the lumbar plexus. It passes under the inguinal ligament to reach the thigh. It supplies sensation to the skin on the lateral part of the thigh by an anterior branch and a posterior branch.

A blue nevus is a type of coloured mole, typically a single well-defined blue-black bump.

In medicine, a drug eruption is an adverse drug reaction of the skin. Most drug-induced cutaneous reactions are mild and disappear when the offending drug is withdrawn. These are called "simple" drug eruptions. However, more serious drug eruptions may be associated with organ injury such as liver or kidney damage and are categorized as "complex". Drugs can also cause hair and nail changes, affect the mucous membranes, or cause itching without outward skin changes.
Tuberculosis cutis orificialis is a form of cutaneous tuberculosis that occurs at the mucocutaneous borders of the nose, mouth, anus, urinary meatus, and vagina, and on the mucous membrane of the mouth or tongue.

Cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (CSVV), is inflammation of small blood vessels, usually accompanied by small lumps beneath the skin. The condition is also known as hypersensitivity vasculitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis, hypersensitivity angiitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic angiitis, cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis and cutaneous necrotizing venulitis,
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, or Bazex syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by psoriasiform changes of hands, feet, ears, and nose, with involvement of the nails and periungual tissues being characteristic and indistinguishable from psoriatic nails. The condition is associated with carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.
Cutaneous actinomycosis is a chronic disease that affects the deep subcutaneous tissue of the skin. Caused by an anaerobic, Gram-positive, filamentous type of bacteria in the genus Actinomyces, invasion of the soft tissue leads to the formation of abnormal channels leading to the skin surface that discharge pale yellow sulfur granules.

Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia refers to a groups of benign cutaneous disorders characterized by collections of lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells in the skin. Conditions included in this groups are:

Poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans (PVA), is a cutaneous condition characterized by hypo- or hyperpigmentation, telangiectasia and skin atrophy. Other names for the condition include prereticulotic poikiloderma and atrophic parapsoriasis. The condition was first described by pioneer American pediatrician Abraham Jacobi in 1906. PVA causes areas of affected skin to appear speckled red and inflamed, yellowish and/or brown, gray or grayish-black, with scaling and a thinness that may be described as "cigarette paper". On the surface of the skin, these areas may range in size from small patches, to plaques, to neoplasms.

Sarcoidosis, an inflammatory disease, involves the skin in about 25% of patients. The most common lesions are erythema nodosum, plaques, maculopapular eruptions, subcutaneous nodules, and lupus pernio. Treatment is not required, since the lesions usually resolve spontaneously in two to four weeks. Although it may be disfiguring, cutaneous sarcoidosis rarely causes major problems.