
The Battle of Queenston Heights was the first major battle in the War of 1812. Resulting in a British victory, it took place on 13 October 1812 near Queenston, Upper Canada.

The Battle of Lundy's Lane, also known as the Battle of Niagara, was a battle fought on 25 July 1814, during the War of 1812, between an invading American army and a British and Canadian army near present-day Niagara Falls, Ontario. It was one of the bloodiest battles of the war, and one of the deadliest battles fought in Canada, with approximately 1,720 casualties including 258 killed.

General Sir Gordon Drummond, GCB was a Canadian-born British Army officer and the first official to command the military and the civil government of Canada. As Lieutenant Governor of Upper Canada, Drummond distinguished himself on the Niagara front in the War of 1812 and later became Governor-General and Administrator of Canada.

The Battle of Stoney Creek was a British victory over an American force fought on 6 June 1813, during the War of 1812 near present-day Stoney Creek, Ontario. British units made a night attack on the American encampment, and due in large part to the capture of the two senior officers of the American force, and an overestimation of British strength by the Americans, the battle resulted in a total victory for the British, and a turning point in the defence of Upper Canada.

The Battle of Chippawa, also known as the Battle of Chippewa, was a victory for the United States Army in the War of 1812, during its invasion on July 5, 1814, of the British Empire's colony of Upper Canada along the Niagara River. This battle and the subsequent Battle of Lundy's Lane demonstrated that trained American troops could hold their own against British regulars. The battlefield is preserved as a National Historic Site of Canada.
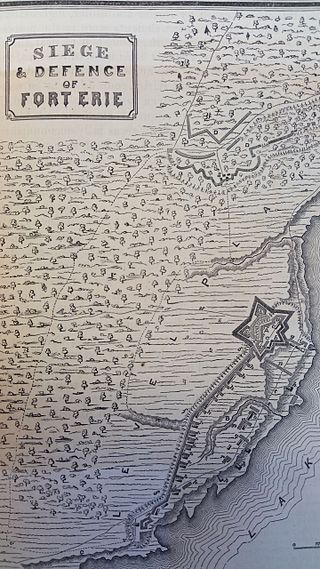
The Capture of Fort Erie by American forces in 1814 was a battle in the War of 1812 between the United Kingdom and the United States. The British garrison was outnumbered but surrendered prematurely, in the view of British commanders.

The siege of Fort Erie, also known as the Battle of Erie, from 4 August to 21 September 1814, was one of the last engagements of the War of 1812, between British and American forces. It took place during the Niagara campaign, and the Americans successfully defended Fort Erie against a British army. During the siege, the British suffered high casualties in a failed storming attempt; they also suffered casualties from sickness and exposure in their rough encampments. Unaware that the British were about to abandon the siege, the American garrison launched a sortie to destroy the British siege batteries, during which both sides again suffered high losses.

The Battle of Fort George was a battle fought during the War of 1812, in which the Americans defeated a British force and captured Fort George in Upper Canada. The troops of the United States Army and vessels of the United States Navy cooperated in a very successful amphibious assault, although most of the opposing British force escaped encirclement.
The Battle of Longwoods took place during the Anglo-American War of 1812. On 4 March 1814, a mounted American raiding party defeated an attempt by British regulars, volunteers from the Canadian militia and Native Americans to intercept them near Wardsville, in present-day Southwest Middlesex, Ontario.

The Capture of Fort Niagara took place late in 1813, during the War of 1812 between the United Kingdom and the United States. The American garrison was taken by surprise, and the fort was captured in a night assault by a select force of British regular infantry.

The Battle of Fort Ontario was a partially successful British raid on Fort Ontario and the village of Oswego, New York on May 6, 1814 during the War of 1812.

The Battle of Buffalo took place during the War of 1812 on December 30, 1813, in the State of New York, near the Niagara River. The British forces drove off the American defenders and destroyed many buildings and ships. The operation was retaliation for American troops burning the Canadian village of Newark.

The Battle of Frenchman's Creek took place during the War of 1812 between Great Britain and the United States in the early hours of November 28, 1812, in the Crown Colony of Upper Canada, near the Niagara River. The operation was conceived as a raid to prepare the ground for a larger American invasion. The Americans succeeded in crossing the Niagara and landing at both of their points of attack. They achieved one of their two objectives before withdrawing but the invasion was subsequently called off, rendering useless what had been accomplished. The engagement was named, "the Battle of Frenchman's Creek" by the Canadians, after the location of some of the severest fighting. To contemporary Americans, it was known as, "the Affair opposite Black Rock".
The Canadian Volunteers was a unit composed of pro-United States citizens or inhabitants of Upper Canada which fought for the United States of America during the Anglo-American War of 1812.
John Swift was an American military officer during the Revolutionary War and the War of 1812. He founded the town of Palmyra, New York.
The Battle of Ball's Farm took place on July 8th, 1813 during The War of 1812. A British and Native force successfully recovered medical supplies they buried on the Chourous farm a few kilometres from Fort George, Ontario. The medicine supplies were buried in the face of an advancing American army. During the recovery an American force of 500 sortied from the occupied Fort George. A small flanking force of 40 was cut off and almost entirely killed or captured.
The Battle of Lewiston saw Major General Phineas Riall lead a combined British and Native force against the American town of Lewiston. They defeated the Americans in the area and then looted and burnt the town.
On July 5, 1813, 34 Canadian militia and 7 British regulars from the 49th Regiment of Foot crossed the Niagara River and raided Fort Schlosser. They took the American garrison of 11 by surprise and captured them along with all the arms and stores.
The capture of HMS Caledonia and HMS Detroit was an action which took place in the Anglo-US portion of the War of 1812.
During the War of 1812, on October 11, 1813, an American expeditionary force entered the Missisquoi Bay of Lake Champlain in Quebec, Canada, intent on raiding the area. Their goal was to stop smuggling goods across the border. They succeeded in defeating a contingent of Canadian militia and raid the town of Philipsburg, Quebec.











