Related Research Articles

The Psychidae are a family of the Lepidoptera. The bagworm family is fairly small, with about 1,350 species described. Bagworm species are found globally, with some, such as the snailcase bagworm, in modern times settling continents where they are not native.

Grouse are a group of birds from the order Galliformes, in the family Phasianidae. Grouse are frequently assigned to the subfamily Tetraoninae, a classification supported by mitochondrial DNA sequence studies, and applied by the American Ornithologists' Union, ITIS, and others. Grouse inhabit temperate and subarctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere, from pine forests to moorland and mountainside, from 83°N to 28°N.

Peafowl is a common name for three species of birds in the genera Pavo and Afropavo of the Phasianidae family, the pheasants and their allies. Male peafowl are referred to as peacocks, and female peafowl as peahens, though peafowl of either sex are often referred to colloquially as "peacocks." The two Asiatic species are the blue or Indian peafowl originally of the Indian subcontinent, and the green peafowl of Southeast Asia; the one African species is the Congo peafowl, native only to the Congo Basin. Male peafowl are known for their piercing calls and their extravagant plumage. The latter is especially prominent in the Asiatic species, which have an eye-spotted "tail" or "train" of covert feathers, which they display as part of a courtship ritual.

The red-winged blackbird is a passerine bird of the family Icteridae found in most of North America and much of Central America. It breeds from Alaska and Newfoundland south to Florida, the Gulf of Mexico, Mexico, and Guatemala, with isolated populations in western El Salvador, northwestern Honduras, and northwestern Costa Rica. It may winter as far north as Pennsylvania and British Columbia, but northern populations are generally migratory, moving south to Mexico and the southern United States. Claims have been made that it is the most abundant living land bird in North America, as bird-counting censuses of wintering red-winged blackbirds sometimes show that loose flocks can number in excess of a million birds per flock and the full number of breeding pairs across North and Central America may exceed 250 million in peak years. It also ranks among the best-studied wild bird species in the world. The red-winged blackbird is sexually dimorphic; the male is all black with a red shoulder and yellow wing bar, while the female is a nondescript dark brown. Seeds and insects make up the bulk of the red-winged blackbird's diet.

The Canada goose is a large wild goose species with a black head and neck, white cheeks, white under its chin, and a brown body. Native to arctic and temperate regions of North America, its migration occasionally reaches northern Europe. It has been introduced to the United Kingdom, Ireland, New Zealand, Argentina, Chile, and the Falkland Islands. Like most geese, the Canada goose is primarily herbivorous and normally migratory; it tends to be found on or close to fresh water.

The killdeer is a large plover found in the Americas. It was described and given its current scientific name in 1758 by Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of his Systema Naturae. There are three subspecies. The killdeer's common name comes from its often-heard call. Its upperparts are mostly brown with rufous fringes, the head has patches of white and black, and there are two black breast bands. The belly and the rest of the breast are white. The nominate subspecies breeds from southeastern Alaska and southern Canada to Mexico. It is seen year-round in the southern half of its breeding range; the subspecies C. v. ternominatus is probably resident in the West Indies and C. v. peruvianus inhabits Peru and areas of the surrounding countries throughout the year. North American breeders winter from their resident range south to Central America, the West Indies, and the northernmost portions of South America.

The Mutillidae are a family of more than 7,000 species of wasps whose wingless females resemble large, hairy ants. Their common name velvet ant refers to their dense pile of hair, which most often is bright scarlet or orange, but may also be black, white, silver, or gold. Their bright colors serve as aposematic signals. They are known for their extremely painful stings,, hence the common name cow killer or cow ant. However, mutillids are not aggressive and sting only in defense. In addition, the actual toxicity of their venom is much lower than that of honey bees or harvester ants. Unlike true ants, they are solitary, and lack complex social systems.

Aglais io, the European peacock, more commonly known simply as the peacock butterfly, is a colourful butterfly, found in Europe and temperate Asia as far east as Japan. It was formerly classified as the only member of the genus Inachis. It should not be confused or classified with the "American peacocks" in the genus Anartia; these are not close relatives of the Eurasian species. The peacock butterfly is resident in much of its range, often wintering in buildings or trees. It therefore often appears quite early in spring. The peacock butterfly has figured in research in which the role of eyespots as an anti-predator mechanism has been investigated. The peacock is expanding its range and is not known to be threatened.

The ruby-throated hummingbird is a species of hummingbird that generally spends the winter in Central America, Mexico, and Florida, and migrates to Eastern North America for the summer to breed. It is by far the most common hummingbird seen east of the Mississippi River in North America.

The Eurasian skylark is a passerine bird in the lark family Alaudidae. It is a widespread species found across Europe and the Palearctic with introduced populations in New Zealand, Australia and on the Hawaiian Islands. It is a bird of open farmland and heath, known for the song of the male, which is delivered in hovering flight from heights of 50 to 100 metres. The sexes are alike. It is streaked greyish-brown above and on the breast and has a buff-white belly.

The handicap principle is a hypothesis originally proposed in 1975 by Israeli biologist Amotz Zahavi to explain how evolution may lead to "honest" or reliable signaling between animals which have an obvious motivation to bluff or deceive each other. The handicap principle suggests that reliable signals must be costly to the signaler, costing the signaler something that could not be afforded by an individual with less of a particular trait. For example, in the case of sexual selection, the theory suggests that animals of greater biological fitness signal this status through handicapping behaviour or morphology that effectively lowers this quality. The central idea is that sexually selected traits function like conspicuous consumption, signalling the ability to afford to squander a resource. Receivers know that the signal indicates quality because inferior quality signallers cannot afford to produce such wastefully extravagant signals.

Animal communication is the transfer of information from one or a group of animals to one or more other animals that affects the current or future behavior of the receivers. Information may be sent intentionally, as in a courtship display, or unintentionally, as in the transfer of scent from predator to prey. Information may be transferred to an "audience" of several receivers. Animal communication is a rapidly growing area of study in disciplines including animal behavior, sociology, neurology and animal cognition. Many aspects of animal behavior, such as symbolic name use, emotional expression, learning and sexual behavior, are being understood in new ways.
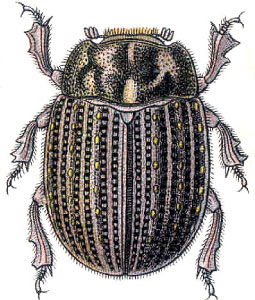
Trogidae, sometimes called hide beetles, is a family of beetles with a distinctive warty or bumpy appearance. Found worldwide, the family includes about 300 species contained in four or five genera.

The Guianan cock-of-the-rock is a species of cotinga, a passerine bird from South America. It is about 30 centimetres (12 in) in length and weighs about 200 to 220 grams. It is found in tropical rainforests, near its preferred habitat of rocky outcrops. The female's plumage is brownish / dark smokey grey in colour, and generally less noticeable coloured than the males because of their nesting work in rocky areas. The male's feathers are a bright orange. Both have a heavy body, broad based bill and wear a remarkable half-moon crest on the head. It is one of two species of the genus Rupicola, the other being the Andean cock-of-the-rock. The Guianan cock-of-the-rock lives across the forested region of northeastern South America. Its diet consists mostly of fruit, but sometimes includes small snakes and lizards.

The souimanga sunbird is a small passerine bird of the sunbird family, Nectariniidae. It is native to the islands of the western Indian Ocean where it occurs on Madagascar, the Aldabra Group and the Glorioso Islands.

Flight feathers are the long, stiff, asymmetrically shaped, but symmetrically paired pennaceous feathers on the wings or tail of a bird; those on the wings are called remiges, singular remex, while those on the tail are called rectrices, singular rectrix. The primary function of the flight feathers is to aid in the generation of both thrust and lift, thereby enabling flight. The flight feathers of some birds have evolved to perform additional functions, generally associated with territorial displays, courtship rituals or feeding methods. In some species, these feathers have developed into long showy plumes used in visual courtship displays, while in others they create a sound during display flights. Tiny serrations on the leading edge of their remiges help owls to fly silently, while the extra-stiff rectrices of woodpeckers help them to brace against tree trunks as they hammer on them. Even flightless birds still retain flight feathers, though sometimes in radically modified forms.

The variable oystercatcher is a species of wader in the family Haematopodidae. It is endemic to New Zealand. The Maori name is torea-pango. They are also known as 'red bills'.

The Raso lark is a small passerine bird with a highly restricted range, being found only on Raso islet in the Cape Verde Islands. This critically endangered member of the family Alaudidae lives in very arid terrain, and is considered one of the least known birds in the Western Palaearctic region, due to its remoteness and the lack of much ornithological study on the archipelago as a whole.

Distraction displays, also known as diversionary displays, or paratrepsis are anti-predator behaviors used to attract the attention of an enemy away from something, typically the nest or young, that is being protected by a parent. Distraction displays are sometimes classified more generically under "nest protection behaviors" along with aggressive displays such as mobbing. These displays have been studied most extensively in bird species, but also have been documented in populations of stickleback fish and in some mammal species.

Glamour photography is a genre of photography in which the subjects are portrayed in erotic poses ranging from fully clothed to nude. The term may be a euphemism for erotic photography. For glamour models, body shape and size are directly related to success.
References
- Peterson, Roger Tory (1990). Western Birds . Houghton Mifflin. p. 322. ISBN 0-395-51424-X.
| This article about ornithology is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This ethology article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |