| Look up slag in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Slag is a by-product of smelting ore.
Contents
Slag may also refer to:
| Look up slag in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Slag is a by-product of smelting ore.
Slag may also refer to:

Thermite is a pyrotechnic composition of metal powder and metal oxide. When ignited by heat or chemical reaction, thermite undergoes an exothermic reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction. Most varieties are not explosive, but can create brief bursts of heat and high temperature in a small area. Its form of action is similar to that of other fuel-oxidizer mixtures, such as black powder.

Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content in contrast to that of cast iron. It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag inclusions, which gives it a "grain" resembling wood that is visible when it is etched or bent to the point of failure. Wrought iron is tough, malleable, ductile, corrosion resistant, and easily welded.

A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut. Blacksmiths produce objects such as gates, grilles, railings, light fixtures, furniture, sculpture, tools, agricultural implements, decorative and religious items, cooking utensils, and weapons. There was an historical opposition between the heavy work of the blacksmith and the more delicate operation of a whitesmith, who usually worked in gold, silver, pewter, or the finishing steps of fine steel. The place where a blacksmith works is called variously a smithy, a forge or a blacksmith's shop.

Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), also known as manual metal arc welding, flux shielded arc welding or informally as stick welding, is a manual arc welding process that uses a consumable electrode covered with a flux to lay the weld.

Submerged arc welding (SAW) is a common arc welding process. The first SAW patent was taken out in 1935. The process requires a continuously fed consumable solid or tubular electrode. The molten weld and the arc zone are protected from atmospheric contamination by being "submerged" under a blanket of granular fusible flux consisting of lime, silica, manganese oxide, calcium fluoride, and other compounds. When molten, the flux becomes conductive, and provides a current path between the electrode and the work. This thick layer of flux completely covers the molten metal thus preventing spatter and sparks as well as suppressing the intense ultraviolet radiation and fumes that are a part of the shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) process.

Slag is the glass-like by-product left over after a desired metal has been separated from its raw ore. Slag is usually a mixture of metal oxides and silicon dioxide. However, slags can contain metal sulfides and elemental metals. While slags are generally used to remove waste in metal smelting, they can also serve other purposes, such as assisting in the temperature control of the smelting, and minimizing any re-oxidation of the final liquid metal product before the molten metal is removed from the furnace and used to make solid metal. In some smelting processes, such as ilmenite smelting to produce titanium dioxide, the slag is the valuable product instead of the metal.

Arc welding is a welding process that is used to join metal to metal by using electricity to create enough heat to melt metal, and the melted metals, when cool, result in a binding of the metals. It is a type of welding that uses a welding power supply to create an electric arc between a metal stick ("electrode") and the base material to melt the metals at the point of contact. Arc welders can use either direct (DC) or alternating (AC) current, and consumable or non-consumable electrodes.

In metallurgy, a flux is a chemical cleaning agent, flowing agent, or purifying agent. Fluxes may have more than one function at a time. They are used in both extractive metallurgy and metal joining.
Forge welding (FOW) is a solid-state welding process that joins two pieces of metal by heating them to a high temperature and then hammering them together. It may also consist of heating and forcing the metals together with presses or other means, creating enough pressure to cause plastic deformation at the weld surfaces. The process is one of the simplest methods of joining metals and has been used since ancient times. Forge welding is versatile, being able to join a host of similar and dissimilar metals. With the invention of electrical and gas welding methods during the Industrial Revolution, manual forge-welding has been largely replaced, although automated forge-welding is a common manufacturing process.
Stud may refer to:

An electric arc furnace (EAF) is a furnace that heats charged material by means of an electric arc.

Flux-cored arc welding is a semi-automatic or automatic arc welding process. FCAW requires a continuously-fed consumable tubular electrode containing a flux and a constant-voltage or, less commonly, a constant-current welding power supply. An externally supplied shielding gas is sometimes used, but often the flux itself is relied upon to generate the necessary protection from the atmosphere, producing both gaseous protection and liquid slag protecting the weld. The process is widely used in construction because of its high welding speed and portability.

A bloomery is a type of metallurgical furnace once used widely for smelting iron from its oxides. The bloomery was the earliest form of smelter capable of smelting iron. Bloomeries produce a porous mass of iron and slag called a bloom. The mix of slag and iron in the bloom, termed sponge iron, is usually consolidated and further forged into wrought iron. Blast furnaces, which produce pig iron, have largely superseded bloomeries.
Shuffling is a procedure used to randomize a deck of playing cards.
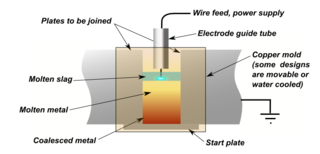
Electroslag welding(ESW) is a highly productive, single pass welding process for thick materials in a vertical or close to vertical position. (ESW) is similar to electrogas welding, but the main difference is the arc starts in a different location. An electric arc is initially struck by wire that is fed into the desired weld location and then flux is added. Additional flux is added until the molten slag, reaching the tip of the electrode, extinguishes the arc. The wire is then continuously fed through a consumable guide tube into the surfaces of the metal workpieces and the filler metal are then melted using the electrical resistance of the molten slag to cause coalescence. The wire and tube then move up along the workpiece while a copper retaining shoe that was put into place before starting is used to keep the weld between the plates that are being welded. Electroslag welding is used mainly to join low carbon steel plates and/or sections that are very thick. It can also be used on structural steel if certain precautions are observed, and for large cross-section aluminium busbars. This process uses a direct current (DC) voltage usually ranging from about 600 A and 40-50 V, higher currents are needed for thicker materials. Because the arc is extinguished, this is not an arc process.

Exothermic welding, also known as exothermic bonding, thermite welding (TW), and thermit welding, is a welding process that employs molten metal to permanently join the conductors. The process employs an exothermic reaction of a thermite composition to heat the metal, and requires no external source of heat or current. The chemical reaction that produces the heat is an aluminothermic reaction between aluminium powder and a metal oxide.

Oxy-fuel welding and oxy-fuel cutting are processes that use fuel gases and oxygen to weld or cut metals. French engineers Edmond Fouché and Charles Picard became the first to develop oxygen-acetylene welding in 1903. Pure oxygen, instead of air, is used to increase the flame temperature to allow localized melting of the workpiece material in a room environment. A common propane/air flame burns at about 2,250 K, a propane/oxygen flame burns at about 2,526 K, an oxyhydrogen flame burns at 3,073 K and an acetylene/oxygen flame burns at about 3,773 K.

Ratchet & Clank Future: Quest for Booty is a 2008 platform game developed by Insomniac Games and published by Sony Computer Entertainment for the PlayStation 3. The game is the second installment in the Ratchet & Clank Future series. It was released on PlayStation Network in North America and Europe on August 21, 2008 and on Blu-ray Disc in Europe on September 12, 2008 and in Asia on September 25, 2008. The game continues from where Tools of Destruction left off, where Clank was kidnapped by the Zoni, and follows Ratchet's quest to find him. Due to its length of approximately three to four hours of playtime, it was released at a lower price point than most standard retail games.
A welding defect is any flaw that compromises the usefulness of a weldment. There is a great variety of welding defects. Welding imperfections are classified according to ISO 6520 while their acceptable limits are specified in ISO 5817 and ISO 10042.

Welding slag is a form of slag, or vitreous material produced as a byproduct of some arc welding processes, most specifically shielded metal arc welding, submerged arc welding, and flux-cored arc welding. Slag is formed when flux, the solid shielding material used in the welding process, melts in or on top of the weld zone.(also known as Dross) Slag is the solidified remaining flux after the weld area cools.