Related Research Articles
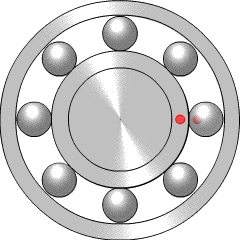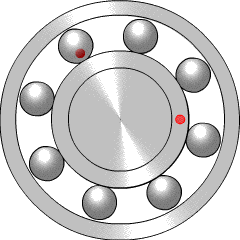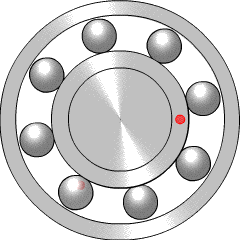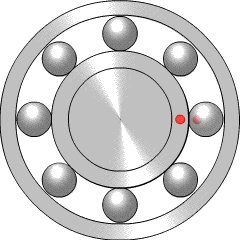
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
Fluid bearings are bearings in which the load is supported by a thin layer of rapidly moving pressurized liquid or gas between the bearing surfaces. Since there is no contact between the moving parts, there is no sliding friction, allowing fluid bearings to have lower friction, wear and vibration than many other types of bearings. Thus, it is possible for some fluid bearings to have near-zero wear if operated correctly.

A bearing is a machine element that constrains relative motion to only the desired motion, and reduces friction between moving parts. The design of the bearing may, for example, provide for free linear movement of the moving part or for free rotation around a fixed axis; or, it may prevent a motion by controlling the vectors of normal forces that bear on the moving parts. Most bearings facilitate the desired motion by minimizing friction. Bearings are classified broadly according to the type of operation, the motions allowed, or to the directions of the loads (forces) applied to the parts.

A plain bearing, or more commonly sliding contact bearing and slide bearing, is the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements. Therefore, the journal slides over the bearing surface. The simplest example of a plain bearing is a shaft rotating in a hole. A simple linear bearing can be a pair of flat surfaces designed to allow motion; e.g., a drawer and the slides it rests on or the ways on the bed of a lathe.

A rolling-element bearing, also known as a rolling bearing, is a bearing which carries a load by placing rolling elements between two bearing rings called races. The relative motion of the races causes the rolling elements to roll with very little rolling resistance and with little sliding.

Seismic retrofitting is the modification of existing structures to make them more resistant to seismic activity, ground motion, or soil failure due to earthquakes. With better understanding of seismic demand on structures and with our recent experiences with large earthquakes near urban centers, the need of seismic retrofitting is well acknowledged. Prior to the introduction of modern seismic codes in the late 1960s for developed countries and late 1970s for many other parts of the world, many structures were designed without adequate detailing and reinforcement for seismic protection. In view of the imminent problem, various research work has been carried out. State-of-the-art technical guidelines for seismic assessment, retrofit and rehabilitation have been published around the world – such as the ASCE-SEI 41 and the New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering (NZSEE)'s guidelines. These codes must be regularly updated; the 1994 Northridge earthquake brought to light the brittleness of welded steel frames, for example.
A linear-motion bearing or linear slide is a bearing designed to provide free motion in one direction. There are many different types of linear motion bearings.

Stone veneer is a thin layer of any stone used as decorative facing material that is not meant to be load bearing. Stone cladding is a stone veneer, or simulated stone, applied to a building or other structure made of a material other than stone. Stone cladding is sometimes applied to concrete and steel buildings as part of their original architectural design.

An expansion joint or movement joint is an assembly designed to hold parts together while safely absorbing temperature-induced expansion and contraction of building materials, and vibration, or to allow movement due to ground settlement or seismic activity. They are commonly found between sections of buildings, bridges, sidewalks, railway tracks, piping systems, ships, and other structures.

A spherical plain bearing is a bearing that permits angular rotation about a central point in two orthogonal directions. Typically these bearings support a rotating shaft in the bore of the inner ring that must move not only rotationally, but also at an angle.

Seismic base isolation, also known as base isolation, or base isolation system, is one of the most popular means of protecting a structure against earthquake forces. It is a collection of structural elements which should substantially decouple a superstructure from its substructure that is in turn resting on the shaking ground, thus protecting a building or non-building structure's integrity.
Dry lubricants or solid lubricants are materials that, despite being in the solid phase, are able to reduce friction between two surfaces sliding against each other without the need for a liquid oil medium.

The yaw bearing is the most crucial and cost intensive component of a yaw system found on modern horizontal axis wind turbines. The yaw bearing must cope with enormous static and dynamic loads and moments during the wind turbine operation, and provide smooth rotation characteristics for the orientation of the nacelle under all weather conditions. It has also to be corrosion and wear resistant and extremely long lasting. It should last for the service life of the wind turbine) while being cost effective.
A pipe support or pipe hanger is a designed element that transfer the load from a pipe to the supporting structures. The load includes the weight of the pipe proper, the content that the pipe carries, all the pipe fittings attached to pipe, and the pipe covering such as insulation. The four main functions of a pipe support are to anchor, guide, absorb shock, and support a specified load. Pipe supports used in high or low temperature applications may contain insulation materials. The overall design configuration of a pipe support assembly is dependent on the loading and operating conditions.
The MORGOIL Bearings division is a business unit of Primetals Technologies USA LLC, designers, manufacturers and service providers of high speed rod, bar, combination mills and handling equipment for the steel and non-ferrous industries. MORGOIL is headquartered in Worcester, Massachusetts, USA.

A bridge bearing is a component of a bridge which typically provides a resting surface between bridge piers and the bridge deck. The purpose of a bearing is to allow controlled movement and thereby reduce the stresses involved. Possible causes of movement are thermal expansion and contraction, creep, shrinkage, or fatigue due to the properties of the material used for the bearing. External sources of movement include the settlement of the ground below, thermal expansion, and seismic activity. There are several different types of bridge bearings which are used depending on a number of different factors including the bridge span, loading conditions, and performance specifications. The oldest form of bridge bearing is simply two plates resting on top of each other. A common form of modern bridge bearing is the elastomeric bridge bearing. Another type of bridge bearing is the mechanical bridge bearing. There are several types of mechanical bridge bearing, such as the pinned bearing, which in turn includes specific types such as the rocker bearing, and the roller bearing. Another type of mechanical bearing is the fixed bearing, which allows rotation, but not other forms of movement.
A composite bearing is used to maintain separation and control friction between two moving parts. The distinguishing characteristic of a composite bearing is that the bearing is made from a combination of materials such as a resin reinforced with fibre and this may also include friction reducing lubricants and ingredients. A composite bearing is not simply a PTFE bearing in a carrier of another material, this is a PTFE bearing in a carrier. The plain composite bearing can be lighter than a rolling element bearing but this is not always a feature as some composites are extremely dense which results in lower porosity. Another distinctive feature of the composite bearing is its lightweight design - it can be one-tenth the weight of the traditional rolling element bearing. No heavy metals are used in its manufacture.
This glossary of structural engineering terms pertains specifically to structural engineering and its sub-disciplines. Please see glossary of engineering for a broad overview of the major concepts of engineering.
A structural support is a part of a building or structure that provides the necessary stiffness and strength in order to resist the internal forces and guide them safely to the ground. External loads that act on buildings cause internal forces in building support structures. Supports can be either at the end or at any intermediate point along a structural member or a constituent part of a building and they are referred to as connections, joints or restraints.

A high performance positioning system (HPPS) is a type of positioning system consisting of a piece of electromechanics equipment that is capable of moving an object in a three-dimensional space within a work envelope. Positioning could be done point to point or along a desired path of motion. Position is typically defined in six degrees of freedom, including linear, in an x,y,z cartesian coordinate system, and angular orientation of yaw, pitch, roll. HPPS are used in many manufacturing processes to move an object smoothly and accurately in six degrees of freedom, along a desired path, at a desired orientation, with high acceleration, high deceleration, high velocity and low settling time. It is designed to quickly stop its motion and accurately place the moving object at its desired final position and orientation with minimal jittering.
References
- ↑ Piping Technology: Product Catalog, Piping Technology & Products, Inc.(retrieved 30 August 2010)
- ↑ "Singa Bearings Solutions | German Bearing Engineering and Consulting".
- ↑ Lubrite technologies
- ↑ "PTFE Slide Plate – Products | Piping Tech".
- ↑ "Singa Bearings Solutions | German Bearing Engineering and Consulting".
- ↑ Fluorogold Product Literature, Slide Bearings, LP (retrieved 20 January 2014)
- ↑ Slide Plate Applications Piping Technology & Products, (retrieved January 2012)
- ↑ http://www.pretread.com [ bare URL ]