
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in southern Central Europe.Spread over 20,271 km2, it is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and the Adriatic Sea to the southwest. Slovenia is mostly mountainous and forested, covers 20,271 square kilometres (7,827 sq mi), and has a population of 2.1 million. Slovenes constitute over 80% of the country's population. Slovene, a South Slavic language, is the official language. Slovenia has a predominantly temperate continental climate, with the exception of the Slovene Littoral and the Julian Alps. A sub-mediterranean climate reaches to the northern extensions of the Dinaric Alps that traverse the country in a northwest–southeast direction. The Julian Alps in the northwest have an alpine climate. Toward the northeastern Pannonian Basin, a continental climate is more pronounced. Ljubljana, the capital and largest city of Slovenia, is geographically situated near the centre of the country.

Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast and Central Europe for most of the 20th century. It came into existence in 1918 following World War I, under the name of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes from the merger of Kingdom of Serbia with the provisional State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, and constituted the first union of the South Slavic people as a sovereign state, following centuries in which the region had been part of the Ottoman Empire and Austria-Hungary. Peter I of Serbia was its first sovereign. The kingdom gained international recognition on 13 July 1922 at the Conference of Ambassadors in Paris. The official name of the state was changed to Kingdom of Yugoslavia on 3 October 1929.

Janez Drnovšek was a Slovenian liberal politician, President of the Presidency of Yugoslavia (1989–1990), Prime Minister of Slovenia and President of Slovenia (2002–2007).

The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY), commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yugoslavia occurring as a consequence of the Yugoslav Wars. Spanning an area of 255,804 square kilometres (98,766 sq mi) in the Balkans, Yugoslavia was bordered by the Adriatic Sea and Italy to the west, by Austria and Hungary to the north, by Bulgaria and Romania to the east, and by Albania and Greece to the south. It was a one-party socialist state and federation governed by the League of Communists of Yugoslavia, and had six constituent republics: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia. Within Serbia was the Yugoslav capital city of Belgrade as well as two autonomous Yugoslav provinces: Kosovo and Vojvodina.
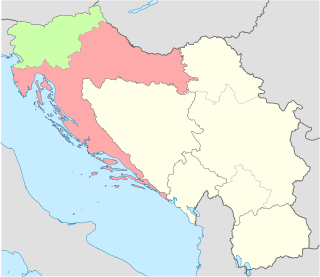
The Brioni Agreement, also known as the Brioni Declaration, is a document signed by representatives of Slovenia, Croatia, and Yugoslavia under the political sponsorship of the European Community (EC) on the Brijuni Islands on 7 July 1991. The agreement sought to create an environment in which further negotiations on the future of Yugoslavia could take place. However, ultimately it isolated the federal prime minister Ante Marković in his efforts to preserve Yugoslavia, and effectively stopped any form of federal influence over Slovenia. This meant the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) would focus on combat in Croatia, creating a precedent of redrawing international borders and staking the EC's interest in resolving the Yugoslav crisis.

The Slovene coat of arms consists of a red bordered blue shield on which there is a stylised white Mount Triglav, under which there are two wavy lines representing the sea and the rivers of the country. Above Mount Triglav, there are three golden six-pointed stars representing the Counts of Celje. It was designed in 1991 by Marko Pogačnik and adopted on 24 June 1991.
The economy of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY) was a unique system of socialist self-management that operated from the end of World War II until the country's dissolution in the 1990s. The Yugoslav economy was characterized by a combination of market mechanisms and state planning, with a focus on worker self-management and a decentralized approach to decision-making. Despite facing numerous challenges, including political instability and external pressures, the Yugoslav economy achieved significant growth and modernization during its existence, with a particularly strong emphasis on education, health care, and social welfare. However, the system ultimately proved unsustainable in the face of the global economic changes of the 1980s and the political tensions that led to the breakup of Yugoslavia in the 1990s. Despite common origins, the Yugoslav economy was significantly different from the economies of the Soviet Union and other Eastern European socialist states, especially after the Yugoslav-Soviet break-up in 1948. The occupation and liberation struggle in World War II left Yugoslavia's infrastructure devastated. Even the most developed parts of the country were largely rural, and the little industry of the country was largely damaged or destroyed.
The following is a list of television stations in Slovenia. The channels are being broadcast in Slovenia and are sorted by regions of coverage and type of content the channels broadcast. The list does not contain internet-only television stations.

The Ten-Day War, or the Slovenian War of Independence, was a brief armed conflict that followed Slovenia's declaration of independence from Yugoslavia on 25 June 1991. It was fought between the Slovenian Territorial Defence together with Slovene Police and the Yugoslav People's Army. It lasted from 27 June 1991 until 7 July 1991, when the Brioni Accords were signed.

The Socialist Republic of Slovenia, commonly referred to as Socialist Slovenia or simply Slovenia, was one of the six federal republics forming Yugoslavia and the nation state of the Slovenes. It existed under various names from its creation on 29 November 1945 until 25 June 1991.
Mladina is a Slovenian weekly left-wing political and current affairs magazine. Since the 1920s, when it was first published, it has become a voice of protest against those in power. Today, Mladina's weekly issues are distributed throughout the country. Mladina is considered one of the most influential political magazines in Slovenia.
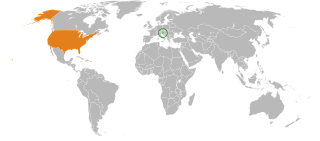
The United States has maintained an official presence in Slovenia since the early 1970s, when the United States Information Agency (USIS) opened a library and American press and cultural center in Ljubljana. From its opening through 1992, the American Center worked to develop closer grassroots relations between the United States and the people of the then-Socialist Republic of Slovenia, a constituent republic of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. On December 23, 1990, the Slovene people voted in a plebiscite to separate from greater Yugoslavia. On June 25, 1991, the new Republic of Slovenia officially declared its independence from the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. A 10-day war commenced, during which Slovenian territorial troops fought off incursions by the Yugoslav People's Army. The United States formally recognized the new republic on April 7, 1992. To develop U.S. diplomatic relations with the new state, the United States opened a new Embassy in Ljubljana in August 1992. From the departure of Yousif Ghafari in January 2009 till November 2010, the U.S. Ambassador position was vacant. From November 2010 to 2015 it was held by Joseph A. Mussomeli.

Radenska is a Slovenia-based worldwide known brand of mineral water, trademark of Radenska d.o.o. company. It is one of the oldest Slovenian brands.

Nogometni klub Svoboda Ljubljana, commonly referred to as NK Svoboda Ljubljana or simply Svoboda, is a Slovenian football club from Ljubljana which plays in the Slovenian Third League.
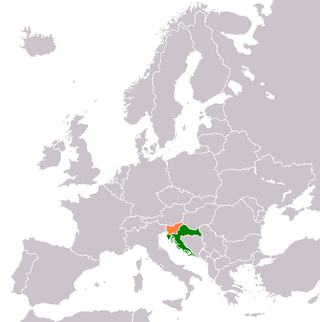
Croatia–Slovenia relations are foreign relations between Croatia and Slovenia. Croatia has an embassy in Ljubljana and two honorary consulates in Maribor and Koper. Slovenia has an embassy in Zagreb and an honorary consulate in Split. The countries share 670 km (420 mi) of common border. Relations between Slovenia and Croatia are generally considered to be friendly, but plagued with a series of unresolved border disputes and other vestiges from the time when both countries were the northernmost part of SFR Yugoslavia. Slovenia has given full support to Croatia's membership in the European Union and NATO.

Cerklje ob Krki Airport is the only military airport in Slovenia, and a civilian airport. The Cerklje ob Krki Air Base operates at it. The airport is in the midst of an enlargement and restructuring.

Iskra is a Slovenian and former Yugoslavian company for electromechanics, telecommunications, electronics and automation.
The deaf sign language of the nations of the former Yugoslavia, known variously as Croatian Sign Language, Kosovar Sign Language, Serbian Sign Language, Bosnian Sign Language, Macedonian Sign Language, Slovenian Sign Language, or Yugoslav Sign Language (YSL), got its start when children were sent to schools for the deaf in Austro-Hungary in the early 19th century. The first two local schools opened in 1840 in Slovenia and in 1885 in Croatia.
Revoz is a manufacturing subsidiary of Renault in Novo Mesto, Slovenia. It is the only automaker in the country and one of its largest exporters. The company was established in June 1988 as a joint venture between Renault and Industrija Motornih Vozil. In 2004, it became a wholly owned subsidiary of Renault.

The Agreement on Succession Issues of the Former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia is an international agreement on shared state succession of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia reached among its former constituents republics following the breakup of the country in early 1990s.















