
A thermometer is a device that measures temperature or temperature gradient. A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor in which some change occurs with a change in temperature; and (2) some means of converting this change into a numerical value. Thermometers are widely used in technology and industry to monitor processes, in meteorology, in medicine, and in scientific research.

Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots tele, 'remote', and metron, 'measure'. Systems that need external instructions and data to operate require the counterpart of telemetry: telecommand.

A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis to help find surface troughs, pressure systems and frontal boundaries.

A hygrometer is an instrument which measures the humidity of air or some other gas: that is, how much water vapor it contains. Humidity measurement instruments usually rely on measurements of some other quantities such as temperature, pressure, mass and mechanical or electrical changes in a substance as moisture is absorbed. By calibration and calculation, these measured quantities can lead to a measurement of humidity. Modern electronic devices use the temperature of condensation, or they sense changes in electrical capacitance or resistance to measure humidity differences. A crude hygrometer was invented by Leonardo da Vinci in 1480. Major leaps came forward during the 1600s; Francesco Folli invented a more practical version of the device, while Robert Hooke improved a number of meteorological devices including the hygrometer. A more modern version was created by Swiss polymath Johann Heinrich Lambert in 1755. Later, in the year 1783, Swiss physicist and Geologist Horace Bénédict de Saussure invented the first hygrometer using human hair to measure humidity.

Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermographic cameras usually detect radiation in the long-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms. Since infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero according to the black body radiation law, thermography makes it possible to see one's environment with or without visible illumination. The amount of radiation emitted by an object increases with temperature; therefore, thermography allows one to see variations in temperature. When viewed through a thermal imaging camera, warm objects stand out well against cooler backgrounds; humans and other warm-blooded animals become easily visible against the environment, day or night. As a result, thermography is particularly useful to the military and other users of surveillance cameras.

A cyclocomputer, cycle computer, cycling computer or cyclometer is a device mounted on a bicycle that calculates and displays trip information, similar to the instruments in the dashboard of a car. The computer with display, or head unit, usually is attached to the handlebar for easy viewing. Some GPS watches can also be used as display.

Temperature measurement describes the process of measuring a current temperature for immediate or later evaluation. Datasets consisting of repeated standardized measurements can be used to assess temperature trends.

An infrared thermometer is a thermometer which infers temperature from a portion of the thermal radiation sometimes called black-body radiation emitted by the object being measured. They are sometimes called laser thermometers as a laser is used to help aim the thermometer, or non-contact thermometers or temperature guns, to describe the device's ability to measure temperature from a distance. By knowing the amount of infrared energy emitted by the object and its emissivity, the object's temperature can often be determined within a certain range of its actual temperature. Infrared thermometers are a subset of devices known as "thermal radiation thermometers".
A medical thermometer or clinical thermometer is a device used for measuring the body temperature of a human or other animal. The tip of the thermometer is inserted into the mouth under the tongue, under the armpit, into the rectum via the anus, into the ear, or on the forehead.

Wearable technology is any technology that is designed to be used while worn. Common types of wearable technology include smartwatches and smartglasses. Wearable electronic devices are often close to or on the surface of the skin, where they detect, analyze, and transmit information such as vital signs, and/or ambient data and which allow in some cases immediate biofeedback to the wearer.
Withings is a French consumer electronics company headquartered in Issy-les-Moulineaux, France. It also has offices in Boston, Massachusetts, USA, and Hong Kong, and distributes its products worldwide. Withings is known for design and innovation in connected devices, such as the first Wi-Fi scale on the market, an FDA-cleared blood pressure monitor, a smart sleep system, and a line of automatic activity tracking watches. It also provides B2B services for healthcare providers and researchers.

Smart thermostats are Wi-Fi thermostats that can be used with home automation and are responsible for controlling a home's heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. They perform similar functions as a Programmable thermostat as they allow the user to control the temperature of their home throughout the day using a schedule, but also contain additional features, such as sensors and Wi-Fi connectivity, that improve upon the issues with programming.
Inder Singh is the founder and CEO of Kinsa. He formerly served as the Executive Vice President of the Clinton Foundation's Clinton Health Access Initiative, a global non-profit organization fighting malaria and other diseases. Singh is known for his work towards improving global health, most notably by brokering the deals announced by former President Clinton that reduced the price of life-saving treatments throughout the developing world, particularly aiding in malaria eradication. Singh is credited with saving over $1 billion in drug costs for developing nations. More than 2.6 million HIV/AIDS patients have received drugs subsidized through CHAI, and more than 30 million malaria patients have received drugs produced at lower cost thanks to CHAI licensing deals.

A body area network (BAN), also referred to as a wireless body area network (WBAN) or a body sensor network (BSN) or a medical body area network (MBAN), is a wireless network of wearable computing devices. BAN devices may be embedded inside the body as implants or pills, may be surface-mounted on the body in a fixed position, or may be accompanied devices which humans can carry in different positions, such as in clothes pockets, by hand, or in various bags. Devices are becoming smaller, especially in body area networks. These networks include multiple small body sensor units (BSUs) and a single central unit (BCU). Despite this trend, decimeter sized smart devices still play an important role. They act as data hubs or gateways and provide a user interface for viewing and managing BAN applications on the spot. The development of WBAN technology started around 1995 around the idea of using wireless personal area network (WPAN) technologies to implement communications on, near, and around the human body. About six years later, the term "BAN" came to refer to systems where communication is entirely within, on, and in the immediate proximity of a human body. A WBAN system can use WPAN wireless technologies as gateways to reach longer ranges. Through gateway devices, it is possible to connect the wearable devices on the human body to the internet. This way, medical professionals can access patient data online using the internet independent of the patient location.

A medical tricorder is a handheld portable scanning device to be used by consumers to self-diagnose medical conditions within seconds and take basic vital measurements. While the device is not yet on the mass market, there are numerous reports of other scientists and inventors also working to create such a device as well as improve it. A common view is that it will be a general-purpose tool similar in functionality to a Swiss Army Knife to take health measurements such as blood pressure and temperature, and blood flow in a noninvasive way. It would diagnose a person's state of health after analyzing the data, either as a standalone device or as a connection to medical databases via an Internet connection.

An activity tracker involves the practice of measuring and collecting data on an individual's physical and psychological activity to keep track and maintain documentation regarding their health and wellness. Used for many groups even animals as seen in collar-mounted activity trackers for dogs. A lot of the data is collected through wearable technology such as wristbands which sync with mobile apps through Apple and Samsung. As daily technologies such as phones and computers have been innovated, it paved the way for such wearable tracking technologies to be advanced. There are a variety of stakeholders involved in the usage of activity tracking through wearable technology and mobile health apps, knowing how much they track ranging from fitness, mood, sleep, water intake, medicine usage, sexual activity, menstruation, and potential diseases raises the concern on privacy given a lot of data is collected and analyzed. Through many studies that have been reviewed, data on the various demographics and goals these technologies are used provide more insight into their purposes.
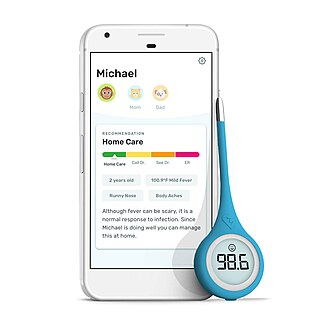
Kinsa Inc. is a health technology company with a powerful and robust AI platform that provides predictive insights for pharmaceutical companies, retailers, illness product companies, public health agencies, hospital systems, and communities. Kinsa aims to stop the spread of infectious illness through a network of smart thermometers that power their Insights platform.
Nearables is a term for a type of smart object, invented by Estimote Inc.. The term is used to describe everyday items that have small, wireless computing devices attached to them. These devices can be equipped with a variety of sensors and work as transmitters to broadcast digital data through a variety of methods, but they usually use the Bluetooth Smart protocol. Due to this, these objects are able to provide mobile devices in range with information about their location, state and immediate surroundings. The word 'nearables' is a reference to wearable technology – electronic devices worn as part of clothing or jewellery.

A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) is a device used for monitoring blood glucose on a continual basis instead of monitoring glucose levels periodically by drawing a drop of blood from a finger. This is known as continuous glucose monitoring. CGMs are used by people who treat their diabetes with insulin, for example people with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or other types of diabetes, such as gestational diabetes.
Bioinstrumentation or Biomedical Instrumentation is an application of biomedical engineering which focuses on development of devices and mechanics used to measure, evaluate, and treat biological systems. The goal of biomedical instrumentation focuses on the use of multiple sensors to monitor physiological characteristics of a human or animal for diagnostic and disease treatment purposes. Such instrumentation originated as a necessity to constantly monitor vital signs of Astronauts during NASA's Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo missions.















