Related Research Articles

Bacterial conjugation is the transfer of genetic material between bacterial cells by direct cell-to-cell contact or by a bridge-like connection between two cells. This takes place through a pilus. It is a parasexual mode of reproduction in bacteria.

Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus Escherichia that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes such as EPEC, and ETEC are pathogenic and can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut and are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of E. coli benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between E. coli and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship — where both the humans and the E. coli are benefitting each other. E. coli is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massively in fresh fecal matter under aerobic conditions for three days, but its numbers decline slowly afterwards.
A bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) is a DNA construct, based on a functional fertility plasmid, used for transforming and cloning in bacteria, usually E. coli. F-plasmids play a crucial role because they contain partition genes that promote the even distribution of plasmids after bacterial cell division. The bacterial artificial chromosome's usual insert size is 150–350 kbp. A similar cloning vector called a PAC has also been produced from the DNA of P1 bacteriophage.

A cloning vector is a small piece of DNA that can be stably maintained in an organism, and into which a foreign DNA fragment can be inserted for cloning purposes. The cloning vector may be DNA taken from a virus, the cell of a higher organism, or it may be the plasmid of a bacterium. The vector contains features that allow for the convenient insertion of a DNA fragment into the vector or its removal from the vector, for example through the presence of restriction sites. The vector and the foreign DNA may be treated with a restriction enzyme that cuts the DNA, and DNA fragments thus generated contain either blunt ends or overhangs known as sticky ends, and vector DNA and foreign DNA with compatible ends can then be joined by molecular ligation. After a DNA fragment has been cloned into a cloning vector, it may be further subcloned into another vector designed for more specific use.

Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are genetically engineered chromosomes derived from the DNA of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is then ligated into a bacterial plasmid. By inserting large fragments of DNA, from 100–1000 kb, the inserted sequences can be cloned and physically mapped using a process called chromosome walking. This is the process that was initially used for the Human Genome Project, however due to stability issues, YACs were abandoned for the use of Bacterial artificial chromosome
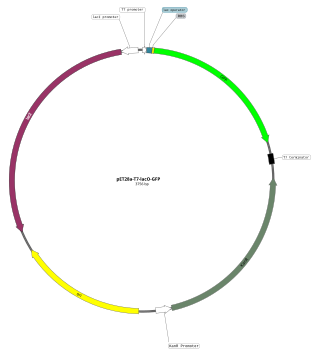
An expression vector, otherwise known as an expression construct, is usually a plasmid or virus designed for gene expression in cells. The vector is used to introduce a specific gene into a target cell, and can commandeer the cell's mechanism for protein synthesis to produce the protein encoded by the gene. Expression vectors are the basic tools in biotechnology for the production of proteins.

In molecular biology and genetics, transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material from its surroundings through the cell membrane(s). For transformation to take place, the recipient bacterium must be in a state of competence, which might occur in nature as a time-limited response to environmental conditions such as starvation and cell density, and may also be induced in a laboratory.

Stanley Norman Cohen is an American geneticist and the Kwoh-Ting Li Professor in the Stanford University School of Medicine. Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer were the first scientists to transplant genes from one living organism to another, a fundamental discovery for genetical engineering. Thousands of products have been developed on the basis of their work, including human growth hormone and hepatitis B vaccine. According to immunologist Hugh McDevitt, "Cohen's DNA cloning technology has helped biologists in virtually every field". Without it, "the face of biomedicine and biotechnology would look totally different." Boyer cofounded Genentech in 1976 based on their work together, but Cohen was a consultant for Cetus Corporation and declined to join. In 2022, Cohen was found guilty of having committed fraud in misleading investors into a biotechnology company he founded in 2016, and paid $29 million in damages.
Triparental mating is a form of bacterial conjugation where a conjugative plasmid present in one bacterial strain assists the transfer of a mobilizable plasmid present in a second bacterial strain into a third bacterial strain. Plasmids are introduced into bacteria for such purposes as transformation, cloning, or transposon mutagenesis. Triparental matings can help overcome some of the barriers to efficient plasmid mobilization. For instance, if the conjugative plasmid and the mobilizable plasmid are members of the same incompatibility group they do not need to stably coexist in the second bacterial strain for the mobilizable plasmid to be transferred.

Two-hybrid screening is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions (PPIs) and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.
Recombineering is a genetic and molecular biology technique based on homologous recombination systems, as opposed to the older/more common method of using restriction enzymes and ligases to combine DNA sequences in a specified order. Recombineering is widely used for bacterial genetics, in the generation of target vectors for making a conditional mouse knockout, and for modifying DNA of any source often contained on a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), among other applications.
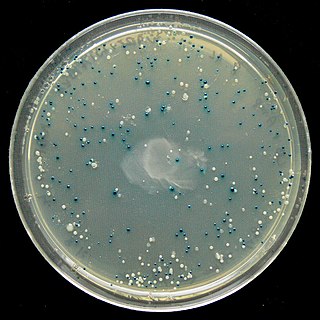
The blue–white screen is a screening technique that allows for the rapid and convenient detection of recombinant bacteria in vector-based molecular cloning experiments. This method of screening is usually performed using a suitable bacterial strain, but other organisms such as yeast may also be used. DNA of transformation is ligated into a vector. The vector is then inserted into a competent host cell viable for transformation, which are then grown in the presence of X-gal. Cells transformed with vectors containing recombinant DNA will produce white colonies; cells transformed with non-recombinant plasmids grow into blue colonies.

Biotechnology is the use of living organisms to develop useful products. Biotechnology is often used in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Notable examples include the use of bacteria to produce things such as insulin or human growth hormone. Other examples include the use of transgenic pigs for the creation of hemoglobin in use of humans.
The HIS3 gene, found in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast, encodes a protein called Imidazoleglycerol-phosphate dehydratase which catalyses the sixth step in histidine biosynthesis. It is analogous to hisB in Escherichia coli.
A shuttle vector is a vector constructed so that it can propagate in two different host species. Therefore, DNA inserted into a shuttle vector can be tested or manipulated in two different cell types. The main advantage of these vectors is they can be manipulated in E. coli, then used in a system which is more difficult or slower to use.
Transformation efficiency refers to the ability of a cell to take up and incorporate exogenous DNA, such as plasmids, during a process called transformation. The efficiency of transformation is typically measured as the number of transformants per microgram of DNA added to the cells. A higher transformation efficiency means that more cells are able to take up the DNA, and a lower efficiency means that fewer cells are able to do so.
A P1-derived artificial chromosome, or PAC, is a DNA construct derived from the DNA of P1 bacteriophages and Bacterial artificial chromosome. It can carry large amounts of other sequences for a variety of bioengineering purposes in bacteria. It is one type of the efficient cloning vector used to clone DNA fragments in Escherichia coli cells.
In molecular cloning, a vector is any particle used as a vehicle to artificially carry a foreign nucleic sequence – usually DNA – into another cell, where it can be replicated and/or expressed. A vector containing foreign DNA is termed recombinant DNA. The four major types of vectors are plasmids, viral vectors, cosmids, and artificial chromosomes. Of these, the most commonly used vectors are plasmids. Common to all engineered vectors are an origin of replication, a multicloning site, and a selectable marker.
Cell-free protein synthesis, also known as in vitro protein synthesis or CFPS, is the production of protein using biological machinery in a cell-free system, that is, without the use of living cells. The in vitro protein synthesis environment is not constrained by a cell wall or homeostasis conditions necessary to maintain cell viability. Thus, CFPS enables direct access and control of the translation environment which is advantageous for a number of applications including co-translational solubilisation of membrane proteins, optimisation of protein production, incorporation of non-natural amino acids, selective and site-specific labelling. Due to the open nature of the system, different expression conditions such as pH, redox potentials, temperatures, and chaperones can be screened. Since there is no need to maintain cell viability, toxic proteins can be produced.

A circular chromosome is a chromosome in bacteria, archaea, mitochondria, and chloroplasts, in the form of a molecule of circular DNA, unlike the linear chromosome of most eukaryotes.
References
- ↑ C.S. Hoffman; F. Winston (1987). "A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli". Gene. 57 (2–3): 267–72. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. PMID 3319781.