Soap is a surfactant cleaning compound used for personal or other cleaning.

Snake oil is a term used to describe deceptive marketing, health care fraud, or a scam. Similarly, snake oil salesman is a common label used to describe someone who sells, promotes, or is a general proponent of some valueless or fraudulent cure, remedy, or solution. The term comes from the "snake oil" that used to be sold as a cure-all elixir for many kinds of physiological problems. Many 19th-century United States and 18th-century European entrepreneurs advertised and sold mineral oil as "snake oil liniment", making claims about its efficacy as a panacea. Patent medicines that claimed to be a panacea were extremely common from the 18th century until the 20th, particularly among vendors masking addictive drugs such as cocaine, amphetamine, alcohol, and opium-based concoctions or elixirs, to be sold at medicine shows as medication or products promoting health.
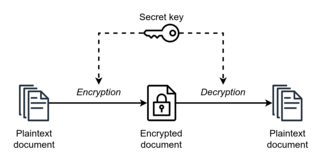
Symmetric-key algorithms are algorithms for cryptography that use the same cryptographic keys for both the encryption of plaintext and the decryption of ciphertext. The keys may be identical, or there may be a simple transformation to go between the two keys. The keys, in practice, represent a shared secret between two or more parties that can be used to maintain a private information link. The requirement that both parties have access to the secret key is one of the main drawbacks of symmetric-key encryption, in comparison to public-key encryption. However, symmetric-key encryption algorithms are usually better for bulk encryption. With exception of the one-time pad they have a smaller key size, which means less storage space and faster transmission. Due to this, asymmetric-key encryption is often used to exchange the secret key for symmetric-key encryption.
In cryptography and computer security, a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack or in-path attack is a cyberattack where the attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communications between two parties who believe that they are directly communicating with each other, as the attacker has inserted themselves between the two parties.
A birthday attack is a bruteforce collision attack that exploits the mathematics behind the birthday problem in probability theory. This attack can be used to abuse communication between two or more parties. The attack depends on the higher likelihood of collisions found between random attack attempts and a fixed degree of permutations (pigeonholes). With a birthday attack, it is possible to find a collision of a hash function with chance in , with being the classical preimage resistance security with the same probability. There is a general result that quantum computers can perform birthday attacks, thus breaking collision resistance, in .
Est, EST, est, -est, etc. may refer to:

A charlatan is a person practicing quackery or a similar confidence trick in order to obtain money, power, fame, or other advantages through pretense or deception. One example of a charlatan appears in The Pardoner's Tale, with the Pardoner who tricks sinners into buying fake religious relics. Synonyms for charlatan include shyster, quack, or faker. Quack is a reference to quackery or the practice of dubious medicine, including the sale of snake oil, or a person who does not have medical training who purports to provide medical services.
Hometown, HomeTown, or Home Town may refer to:

Alice and Bob are fictional characters commonly used as placeholders in discussions about cryptographic systems and protocols, and in other science and engineering literature where there are several participants in a thought experiment. The Alice and Bob characters were invented by Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman in their 1978 paper "A Method for Obtaining Digital Signatures and Public-key Cryptosystems". Subsequently, they have become common archetypes in many scientific and engineering fields, such as quantum cryptography, game theory and physics. As the use of Alice and Bob became more widespread, additional characters were added, sometimes each with a particular meaning. These characters do not have to refer to people; they refer to generic agents which might be different computers or even different programs running on a single computer.
In cryptography, snake oil is any cryptographic method or product considered to be bogus or fraudulent. The name derives from snake oil, one type of patent medicine widely available in 19th century United States.
In mathematics, permutation relates to the act of arranging all the members of a set into some sequence or order.
Dance with Me may refer to:
Phone cloning is the copying of identity from one cellular device to another.
Post-quantum cryptography (PQC), sometimes referred to as quantum-proof, quantum-safe, or quantum-resistant, is the development of cryptographic algorithms that are thought to be secure against a cryptanalytic attack by a quantum computer. The problem with popular algorithms currently used in the market is that their security relies on one of three hard mathematical problems: the integer factorization problem, the discrete logarithm problem or the elliptic-curve discrete logarithm problem. All of these problems could be easily solved on a sufficiently powerful quantum computer running Shor's algorithm or even faster and less demanding alternatives.

"Heartless" is a song by American producer Diplo featuring American country music singer Morgan Wallen. It was released through Mad Decent and Columbia Records on August 16, 2019. The music video was directed by Brandon Dermer and premiered on September 5, 2019.

Chapter 1: Snake Oil is the second studio album by American DJ and musician Diplo, released under his country moniker Thomas Wesley. It was released through Mad Decent and Columbia Records on May 29, 2020. The album features collaborations by Orville Peck, Cam, Morgan Wallen, the Jonas Brothers, Thomas Rhett, Young Thug, Blanco Brown, Noah Cyrus, Julia Michaels, Clever, Zac Brown, Danielle Bradbery, Ben Burgess, Lil Nas X, and Billy Ray Cyrus.





