Related Research Articles

A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on the organization, the organization's financial projections, and the strategies it intends to implement to achieve the stated targets. In its entirety, this document serves as a road-map that provides direction to the business.
A nonprofit organization (NPO), also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in contrast with an entity that operates as a business aiming to generate a profit for its owners. A nonprofit is subject to the non-distribution constraint: any revenues that exceed expenses must be committed to the organization's purpose, not taken by private parties. An array of organizations are nonprofit, including some political organizations, schools, business associations, churches, social clubs, and consumer cooperatives. Nonprofit entities may seek approval from governments to be tax-exempt, and some may also qualify to receive tax-deductible contributions, but an entity may incorporate as a nonprofit entity without securing tax-exempt status.
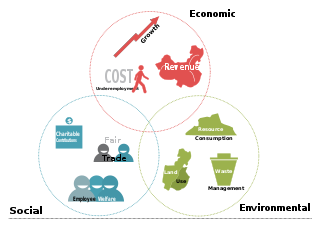
The triple bottom line is an accounting framework with three parts: social, environmental and economic. Some organizations have adopted the TBL framework to evaluate their performance in a broader perspective to create greater business value. Business writer John Elkington claims to have coined the phrase in 1994.
The Schwab Foundation for Social Entrepreneurship is a Swiss not-for-profit organization founded in 1998 that provides platforms at the country, regional and global levels to promote social entrepreneurship. The foundation is under the legal supervision of the Swiss Federal Government. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Each year, it selects 20–25 social entrepreneurs through a global "Social Entrepreneur of the Year" competition.
A social enterprise is an organisation that applies commercial strategies to maximize improvements in financial, social and environmental well-being. This may include maximizing social impact alongside profits for co-owners.
The social economy is formed by a rich diversity of enterprises and organisations, such as cooperatives, mutuals, associations, foundations, social enterprises and paritarian institutions, sharing common values and features:

Social entrepreneurship is an approach by individuals, groups, start-up companies or entrepreneurs, in which they develop, fund and implement solutions to social, cultural, or environmental issues. This concept may be applied to a wide range of organizations, which vary in size, aims, and beliefs. For-profit entrepreneurs typically measure performance using business metrics like profit, revenues and increases in stock prices. Social entrepreneurs, however, are either non-profits, or they blend for-profit goals with generating a positive "return to society". Therefore, they use different metrics. Social entrepreneurship typically attempts to further broad social, cultural and environmental goals often associated with the voluntary sector in areas such as poverty alleviation, health care and community development.
Marketisation or marketization is a restructuring process that enables state enterprises to operate as market-oriented firms by changing the legal environment in which they operate.

A philanthropreneur, also known as a philanthro-capitalist, is a portmanteau of entrepreneur and philanthropy. Internet entrepreneur Mark Desvauz claimed to coin this term in 2004. However, The Wall Street Journal used the term in a 1999 article, while a publication entitled The Philanthropreneur Newsletter existed as far back as 1997. Philanthropreneurship is often considered the start of a new era in philanthropy, characterized by the development of the philanthropist's role and the integration of business practices.
New Profit is a nonprofit social innovation organization and venture philanthropy fund based in Boston, Massachusetts.

John Elkington is an author, advisor and serial entrepreneur. He is an authority on corporate responsibility and sustainable development. He has written and co-authored 20 books, including the Green Consumer Guide, Cannibals with Forks: The Triple Bottom Line of 21st Century Business, The Power of Unreasonable People: How Social Entrepreneurs Create Markets That Change the World, and The Breakthrough Challenge: 10 Ways to Connect Tomorrow's Profits with Tomorrow's Bottom Line.
Impact investing refers to investments "made into companies, organizations, and funds with the intention to generate a measurable, beneficial social or environmental impact alongside a financial return". At its core, impact investing is about an alignment of an investor's beliefs and values with the allocation of capital to address social and/or environmental issues.
The Office of Social Innovation and Civic Participation was an office new to the Obama Administration, created within the White House, to catalyze new and innovative ways of encouraging government to do business differently. Its first director was the economist Sonal Shah. The final director was David Wilkinson.
Pamela Hartigan was the Director of the Skoll Centre for Social Entrepreneurship at Saïd Business School, University of Oxford. She was the founding partner of Volans Ventures and was also an advocate for the global non-profit social enterprise Cambia, at the World Economic Forum Davos meetings, and became a Director of Cambia in 2009 until her death.
A sustainability organization is (1) an organized group of people that aims to advance sustainability and/or (2) those actions of organizing something sustainably. Unlike many business organizations, sustainability organizations are not limited to implementing sustainability strategies which provide them with economic and cultural benefits attained through environmental responsibility. For sustainability organizations, sustainability can also be an end in itself without further justifications.
An inclusive business model is a type of business model that seeks to create value for low-income communities by integrating them into a company's value chain on the demand side as clients and consumers, and/or on the supply side as producers, entrepreneurs or employees in a sustainable way.
Collaborative partnerships are agreements and actions made by consenting organizations to share resources to accomplish a mutual goal. Collaborative partnerships rely on participation by at least two parties who agree to share resources, such as finances, knowledge, and people. Organizations in a collaborative partnership share common goals. The essence of collaborative partnership is for all parties to mutually benefit from working together.
The Power of Unreasonable People: How Social Entrepreneurs Create Markets that Change the World is a 2008 non-fiction book written by John Elkington and Pamela Hartigan and published by Harvard Business School Publishing. The title of the book is based on a quote from Irish playwright George Bernard Shaw: "The reasonable man adapts himself to the world; the unreasonable man persists in trying to adapt the world to himself. Therefore, all progress depends on the unreasonable man." The book focuses on two groups of "Unreasonable People": social entrepreneurs and environmental entrepreneurs.
Ecopreneurship is a term coined to represent the process of principles of entrepreneurship being applied to create businesses that solve environmental problems or operate sustainably. The term began to be widely used in the 1990s, and it is otherwise referred to as "environmental entrepreneurship." In the book Merging Economic and Environmental Concerns Through Ecopreneurship, written by Gwyn Schuyler in 1998, ecopreneurs are defined as follows:
"Ecopreneurs are entrepreneurs whose business efforts are not only driven by profit, but also by a concern for the environment. Ecopreneurship, also known as environmental entrepreneurship and eco-capitalism, is becoming more widespread as a new market-based approach to identifying opportunities for improving environmental quality and capitalizing upon them in the private sector for profit. "

The Nigerian Capital Development Fund (NCDF) is an independent social investment financial intermediary institution. This hybrid organization was set up mainly to address the challenges of poverty in low income rural communities in Nigeria. The institution mobilizes capital from the public and private sectors to invest in projects, businesses and social enterprises with the intention to generate good financial returns and measurable positive social-environmental impact, as well as act as a champion to help increase awareness and confidence on the advantages of impact investing.
References
- ↑ Elkington, John and Pamela Hartigan (2007). The Power of Unreasonable People: How Social Entrepreneurs Create Markets that Change the World. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press.
- ↑ Martin, Roger and Sally Osberg (2007). "Social Entrepreneurship: The Case for Definition." Stanford Social Innovation Review, Spring:28-39.