In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own, defense, and interactions with other organisms.

Microbial ecology is the ecology of microorganisms: their relationship with one another and with their environment. It concerns the three major domains of life—Eukaryota, Archaea, and Bacteria—as well as viruses. This relationship is often mediated by secondary metabolites produced by microorganisms. These secondary metabolites are known as specialized metabolites and are mostly volatile or non volatile compounds. These metabolites include terpenoids, sulfur compounds, indole compound and many more.
In organic chemistry, polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone and methylene groups: [−C(=O)−CH2−]n. First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or improved bioactivity.
Industrial fermentation is the intentional use of fermentation in manufacturing processes. In addition to the mass production of fermented foods and drinks, industrial fermentation has widespread applications in chemical industry. Commodity chemicals, such as acetic acid, citric acid, and ethanol are made by fermentation. Moreover, nearly all commercially produced industrial enzymes, such as lipase, invertase and rennet, are made by fermentation with genetically modified microbes. In some cases, production of biomass itself is the objective, as is the case for single-cell proteins, baker's yeast, and starter cultures for lactic acid bacteria used in cheesemaking.

The Joint Genome Institute (JGI) is a scientific user facility for integrative genomic science at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. The mission of the JGI is to advance genomics research in support of the United States Department of Energy's (DOE) missions of energy and the environment. It is one of three national scientific user facilities supported by the Office of Biological and Environmental Research (BER) within the Department of Energy's Office of Research. These BER facilities are part of a more extensive network of 28 national scientific user facilities that operate at the DOE national laboratories.

Jay D. Keasling is a professor of chemical engineering and bioengineering at the University of California, Berkeley. He is also associate laboratory director for biosciences at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and chief executive officer of the Joint BioEnergy Institute. He is considered one of the foremost authorities in synthetic biology, especially in the field of metabolic engineering.

Joan Wennstrom Bennett is a fungal geneticist who also is active in issues concerning women in science. Educated at Upsala College and the University of Chicago, she was on the faculty of Tulane University for 35 years. She is a past president of the American Society for Microbiology (1990-1991) and of the Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (2001-2002), and past Editor in Chief of Mycologia (2000-2004). She was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 2005.

The National Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, also known as NIMBB, is a research institute of the University of the Philippines (UP). It has four branches distributed across various UP campuses, namely: UP Diliman (NIMBB-Diliman), UP Los Baños (BIOTECH-UPLB), UP Manila and UP Visayas.
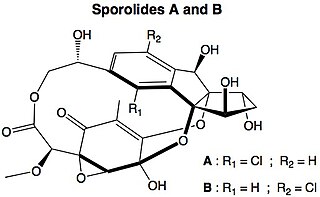
Sporolides A and B are polycyclic macrolides extracted from the obligate marine bacterium Salinispora tropica, which is found in ocean sediment. They are composed of a chlorinated cyclopenta[a]indene ring and a cyclohexenone moiety. They were the second group of compounds isolated from Salinispora, and were said to indicate the potential of marine actinomycetes as a source of novel secondary metabolites. The structures and absolute stereochemistries of both metabolites were elucidated using a combination of NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography.
Arnold L. Demain was an American microbiologist. During his 60-year career, he gained a reputation in the field of industrial microbiology. He was the Professor of Industrial Microbiology in the Biology Department at MIT and Founder and Head of Department of Fermentation Microbiology at Merck & Co. The August 2010 edition of The Journal of Antibiotics celebrated his scientific career. Demain was described as "one of the world's leading industrial microbiologists" and as "a scientist constantly in the forefront of industrial microbiology and biotechnology." He was "a pioneer in research on the elucidation and regulation of the biosynthetic pathways leading to the penicillins and cephalosporins" and "instrumental in the development of the beta-lactam industry". One feature of Demain's work, according to Microbiology Australia, was his "ability to undertake fundamental research on systems with clear industrial applications, recognising that biodiscovery is the start of the road that includes strain improvement to achieve levels of product synthesis that warrant further investment to take products into the marketplace."

Charles Thom was an American microbiologist and mycologist. Born and raised in Illinois, he received his PhD from the University of Missouri, the first such degree awarded by that institution. He studied the microbiology of dairy products and soil fungi, and in particular researched the genera Aspergillus and Penicillium. His work influenced the establishment of standards for food handling and processing in the USA. He pioneered the use of culture media to grow microorganisms, and, with food chemist James N. Currie, developed a process to mass-produce citric acid using Aspergillus. Thom played an important role in the development of penicillin in World War II.

James C. Liao is a Taiwanese-American chemist. He is the Parsons Foundation Professor and Chair of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the University of California, Los Angeles, and is the co-founder and lead scientific advisor of Easel Biotechnologies, LLC.

The Center for Biofilm Engineering (CBE) is an interdisciplinary research, education, and technology transfer institution located on the central campus of Montana State University in Bozeman, Montana. The center was founded in April 1990 as the Center for Interfacial Microbial Process Engineering with a grant from the Engineering Research Centers (ERC) program of the National Science Foundation (NSF). The CBE integrates faculty from multiple university departments to lead multidisciplinary research teams—including graduate and undergraduate students—to advance fundamental biofilm knowledge, develop beneficial uses for microbial biofilms, and find solutions to industrially relevant biofilm problems. The center tackles biofilm issues including chronic wounds, bioremediation, and microbial corrosion through cross-disciplinary research and education among engineers, microbiologists and industry.
Banwari Lal is an Indian environmental and industrial biotechnologist and the director of the Environmental and Industrial Biotechnology Division at The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI). Known for the development of oilzapper technology, Dr. Lal is the chief executive officer of ONGC-TERI Biotech Limited, a collaborative venture between TERI and the Oil and Natural Gas Corporation since 2008. The Department of Biotechnology of the Government of India awarded him the National Bioscience Award for Career Development, one of the highest Indian science awards, for his contributions to biosciences in 2004. He have many Indian and international joint patents with ONGC, DBT, IOCL, OIL INDIA and TERI.
Kristala Jones Prather is an American professor of chemical engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Her research is focused on using novel bioprocesses to design recombinant microorganisms to produce small molecules.
Jonathan Richard Lloyd is a professor of geomicrobiology and director of the Williamson Research Centre for Molecular Environmental Science, and is based in the Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences at the University of Manchester. His research is based at the interface between microbiology, geology and chemistry. His research focuses on the mechanisms of microbial metal-reduction, with emphasis on the environmental impact and biotechnological applications of metal-reducing bacteria. Some of the contaminants he studies include As, Tc, Sr, U, Np and Pu. Current activities are supported by funds from NERC, BBSRC, EPSRC, the EU and industry. Lloyd is also a senior visiting fellow at the National Nuclear Laboratory, which helps support the development of a nuclear geomicrobiology programme.
Lone Gram is Danish microbiologist known for her work in bacterial physiology, microbial communication, and biochemicals that originate from bacterial cultures. She is an elected member of the Royal Danish Academy of Sciences and Letters and has received the Order of the Dannebrog.
Willis Avery “Woody” Wood was an American microbiology professor, an inventor, and an entrepreneur. He was the president of the American Society for Microbiology in 1980. Wood was known for his research on bacterial enzymes and the molecular biology of sugars and amino acids.
Robert Lyman Starkey was an American microbiologist. He was the president of the American Society for Microbiology in 1963.
Carol Ann Darlene Litchfield was an American microbiologist whose research focused on halophile organisms. Litchfield joined George Mason University's biology department in 1993, serving as a research professor between 2005 and 2010 in the Department of Environmental Science and Policy.








