
A psychologist is a professional who practices psychology and studies mental states, perceptual, cognitive, emotional, and social processes and behavior. Their work often involves the experimentation, observation, and interpretation of how individuals relate to each other and to their environments.
A dietitian, medical dietitian, or dietician is an expert in identifying and treating disease-related malnutrition and in conducting medical nutrition therapy, for example designing an enteral tube feeding regimen or mitigating the effects of cancer cachexia. Many dietitians work in hospitals and usually see specific patients where a nutritional assessment and intervention has been requested by a doctor or nurse, for example if a patient has lost their ability to swallow or requires artificial nutrition due to intestinal failure. Dietitians are regulated healthcare professionals licensed to assess, diagnose, and treat such problems. In the United Kingdom, dietitian is a 'protected title', meaning identifying yourself as a dietitian without appropriate education and registration is prohibited by law.

A laboratory information management system (LIMS), sometimes referred to as a laboratory information system (LIS) or laboratory management system (LMS), is a software-based solution with features that support a modern laboratory's operations. Key features include—but are not limited to—workflow and data tracking support, flexible architecture, and data exchange interfaces, which fully "support its use in regulated environments". The features and uses of a LIMS have evolved over the years from simple sample tracking to an enterprise resource planning tool that manages multiple aspects of laboratory informatics.

Current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) are those conforming to the guidelines recommended by relevant agencies. Those agencies control the authorization and licensing of the manufacture and sale of food and beverages, cosmetics, pharmaceutical products, dietary supplements, and medical devices. These guidelines provide minimum requirements that a manufacturer must meet to assure that their products are consistently high in quality, from batch to batch, for their intended use. The rules that govern each industry may differ significantly; however, the main purpose of GMP is always to prevent harm from occurring to the end user. Additional tenets include ensuring the end product is free from contamination, that it is consistent in its manufacture, that its manufacture has been well documented, that personnel are well trained, and that the product has been checked for quality more than just at the end phase. GMP is typically ensured through the effective use of a quality management system (QMS).
A nutritionist is a person who advises others on matters of food and nutrition and their impacts on health. Some people specialize in particular areas, such as sports nutrition, public health, or animal nutrition, among other disciplines. In many countries, a person can claim to be a nutritionist even without any training, education, or professional license, in contrast to a dietitian, who has a university degree, professional license, and certification for professional practice.
GxP is a general abbreviation for the "good practice" quality guidelines and regulations. The "x" stands for the various fields, including the pharmaceutical and food industries, for example good agricultural practice, or GAP.
Good clinical practice (GCP) is an international quality standard, which governments can then transpose into regulations for clinical trials involving human subjects. GCP follows the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), and enforces tight guidelines on ethical aspects of clinical research.
In the experimental (non-clinical) research arena, good laboratory practice or GLP is a quality system of management controls for research laboratories and organizations to ensure the uniformity, consistency, reliability, reproducibility, quality, and integrity of products in development for human or animal health through non-clinical safety tests; from physio-chemical properties through acute to chronic toxicity tests.

A medical laboratory scientist (MLS) or clinical laboratory scientist (CLS) or medical technologist (MT) performs diagnostic testing of blood and body fluids in clinical laboratories. The scope of a medical laboratory scientist's work begins with the receipt of patient or client specimens and terminates with the delivery of test results to physicians and other healthcare providers. The utility of clinical diagnostic testing relies squarely on the validity of test methodology. To this end, much of the work done by medical laboratory scientists involves ensuring specimen quality, interpreting test results, data-logging, testing control products, performing calibration, maintenance, validation, and troubleshooting of instrumentation as well as performing statistical analyses to verify the accuracy and repeatability of testing. Medical laboratory scientists may also assist healthcare providers with test selection and specimen collection and are responsible for prompt verbal delivery of critical lab results. Medical Laboratory Scientist in health settings also play an important role in the diagnosis of diseses conditions. An estimated 70% of medical decisions are based on laboratory test results and MLS contributions affect 95% of a health system's costs.

The Health Sciences Authority (HSA) is a statutory board under the Ministry of Health of the Government of Singapore. It is a multi-disciplinary agency, responsible for applying medical, pharmaceutical and scientific expertise to protect and advance public health and safety.
The European Forum for Good Clinical Practices (EFGCP) is a European think tank which works on the ethical, regulatory, and scientific framework of clinical research in Europe. The EFGCP is committed to the development of the standards for the protection of human subjects and data quality in clinical trials, both in Europe and abroad.
The International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine or IFCC is a global organization that promotes the fields of clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine. It was established in 1952 as the International Association of Clinical Biochemists to organize the various national societies of these fields. The organization aims to transcend the boundaries of the field of clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine, to build professionalism of members worldwide, to disseminate information on ”best practice” at various levels of technology and of economic development, to provide a forum of standardization and traceability, to enhance the scientific level and the quality of diagnosis and therapy for patients.
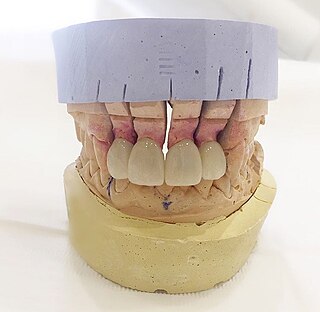
Dental laboratories manufacture or customize a variety of products to assist in the provision of oral health care by a licensed dentist. These products include crowns, bridges, dentures and other dental products. Dental lab technicians follow a prescription from a licensed dentist when manufacturing these items, which include prosthetic devices and therapeutic devices. The FDA regulates these products as medical devices and they are therefore subject to FDA's good manufacturing practice ("GMP") and quality system ("QS") requirements. In most cases, however, they are exempt from manufacturer registration requirements. Some of the most common restorations manufactured include crowns, bridges, dentures, and dental implants. Dental implants is one of the most advanced dental technologies in the field of dentistry.
The South African National Accreditation System (SANAS) is the official accreditation body for South Africa. Founded in 1996, SANAS is headquartered in Pretoria, South Africa. SANAS accreditation certificates are a formal recognition by the Government of South Africa that an organisation is competent to perform specific tasks.
The European Association of Urology (EAU) is a non-profit organisation committed to the representation of urology professionals worldwide. All active urology professionals, including urology nurses, are eligible for membership of the EAU.
Good clinical laboratory practice (GCLP) is a GxP guideline for laboratory samples from clinical studies.

NSF is a product testing, inspection, certification organization with headquarters in Ann Arbor, Michigan. NSF also offers consulting and training services worldwide.

The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PhMDA) is an Independent Administrative Institution responsible for ensuring the safety, efficacy and quality of pharmaceuticals and medical devices in Japan. It is similar in function to the Food and Drug Administration in the United States, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency in the United Kingdom or the Food and Drug Administration in the Philippines.
The Research Quality Association (RQA) is a not for profit membership association. Formerly known a Quality Assurance Group UK and the British Association of Research Quality Assurance (BARQA), the association changed its name to RQA in December 2012 in order to be able to act in a more global role.
Guidances for statistics in regulatory affairs are applicable to the pharmaceutical industry and medical devices industry. These Guidances represent the current thinking of regulatory agencies on a particular subject. It is to be noted that the term “Guidances” is used in the USA, whereas the term “Guidelines” is used in Europe.








